Summary of Contents for GE Voluson S6
- Page 1 GE Healthcare Voluson® S6/S8 Basic User Manual English (English) Revision 4 HCAT# H46812LA 5433669-100 SW 12.0.0 GE imagination at work © by General Electric...
- Page 2 Revision History Revision Date Revision 1 November 2011 Revision 2 April 2012 Revision 3 June 2012 Revision 4 January 2013 Voluson® S6/S8 Basic User Manual i-ii 5433669-100 Revision 4...
-
Page 3: Table Of Contents
Contacting GE Healthcare Ultrasound - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -... - Page 4 Table of Contents Contrast Imaging - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 6-34 Chapter 7 –...
- Page 5 Table of Contents Image History - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 12-30 Exam Review - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 12-31 Selecting Exams - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 12-39 Settings - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 12-41...
- Page 6 This page was intentionally left blank. Voluson® S6/S8 Basic User Manual i-vi 5433669-100 Revision 4...
-
Page 7: Chapter 1 - General
Chapter 1 General This chapter consists of information concerning indications for use and contact information. Voluson® S6/S8 Basic User Manual 5433669-100 Revision 4... -
Page 8: Contacting Ge Healthcare Ultrasound
The Voluson® S6/S8 is an Active Diagnostic Medical Product belonging to Class IIa according to the MDD 93/42/EWG regulation for use on human patients. The Voluson® S6/S8 is developed and produced by GE Healthcare. For more Information, please contact: GE Healthcare... - Page 9 General Information Request To request the latest GE Accessories catalog or equipment brochures in the United States, call the Response Center Phone: (1) 800-643-6439 In other locations, contact your local Applications, Sales or Service Representative. Placing an Order To order accessories, supplies or service parts in the United States,...
- Page 10 P.O.Box 330, 00031 GE Finland Phone: (+358) 10 39 48 220 Fax: (+358) 10 39 48 221 FRANCE GE Medical Systems Ultrasound and Primary Care Diagnostics F-78457 Velizy Fax: (+33) 13 44 95 202 General Imaging: Phone: (+33) 13 449 52 43...
- Page 11 KOREA Seoul, Korea Phone: (+82) 2 6201 3114 LUXEMBOURG Phone: 0800 2603 toll free MEXICO GE Sistemas Medicos de Mexico S.A. de C.V. Rio Lerma #302, 1º y 2º Pisos Colonia Cuauhtemoc 06500-Mexico, D.F. Phone: (5) 228-9600 Fax: (5) 211-4631...
- Page 12 General POLAND GE Medical Systems Polska Sp. z o.o., ul. Wołoska 9 02-583 Warszawa, Poland Phone: (+48) 22 330 83 00 Fax: (+48) 22 330 83 83 PORTUGAL General Electric Portuguesa SA. Avenida do Forte, n° 4 Fraccao F, 2795-502 Carnaxide...
-
Page 13: Manufacturer
P.O. Box #11549, Dubai U.A.E. Phone: +971 4 4296161 Phone: +971 4 4296101 Fax: +971 4 4296201 UNITED KINGDOM GE Medical Systems Ultrasound 71 Great North Road Hatfield, Hertfordshire, AL9 5EN Phone: (+44) 1707 263570 Fax: (+44) 1707 260065 GE Healthcare... - Page 14 General The screen graphics and illustrations in this manual are for illustrational purposes only and may be different from what you see on the screen or device All references to standards / regulations and their revisions are valid for the time of publication of the user manual.
-
Page 15: Chapter 2 - Safety
Chapter 2 Safety Describes the safety and regulatory information pertinent for operating this ultrasound system. Voluson® S6/S8 Basic User Manual 5433669-100 Revision 4... - Page 16 Safety The Voluson® S6/S8 scanner system has been designed for utmost safety for patient and user. Read the following chapters thoroughly before you start working with the machine! The manufacturer guarantees safety and reliability of the system only when all the following cautions and warnings are observed.
-
Page 17: Warning Labels Used In The Basic User Manual
Safety Describes precautions necessary to prevent the risk of injury through moving or tipping hazard! Describes precautions necessary to prevent the risk of injury through mechanical hazard! 2.1 Warning labels used in the Basic User Manual 2.2 Symbols and Labels used on the system Some symbols and labels used with electrical medical equipment have been accepted as standard by IEC. - Page 18 Safety CE Conformity mark according to This product consists of devices that Medical Device Directive 93/42/EEC may contain mercury, which must be recycled or disposed of in accordance with local, state, or country laws. (Within this system, the backlight lamps in the monitor display, contain mercury.) This symbol signifies that the user Tipping danger.
- Page 19 Safety Push this button to eject a CD/DVD These symbols indicate that the DVD from the drive. drive can read and write DVDs. Use this button to change brightness Use these buttons to navigate in the and contrast of the monitor. monitor menu.
-
Page 20: Classification
Safety 2.3 Classification Classifications Type of protection against electric shock • Class I Equipment (*1) Degree of protection against electric shock • Type BF Applied part (*2) (for all Probes) • Type CF Applied part (*3) (for ECG marked with CF symbol) Continuous Operation System is Ordinary Equipment (IPX0) Footswitch is IPX8... -
Page 21: System Safety And Maintenance
Only ultrasound probes conforming to type BF requirements may be used with the Voluson® S6/S8. • Do not install software on the system, that has not been released by GE Healthcare, as this may lead to erroneous data transfer and thereby decrease system performance. •... - Page 22 Thermal Safety. Maintaining a safe thermal environment for the patient has been a design priority at GE Healthcare. Software settings limit the power dissipated for the ultrasound transducer as well as the motor-drive to values low enough to ensure that operating temperatures stay below 43˚C.
- Page 23 Safety Do not operate the system in the vicinity of a heat source, of strong electric or magnetic fields (close to a transformer), or near instruments generating high-frequency signals, such as HF surgery. These can affect the ultrasound images adversely. In the event the equipment has been brought from a cold environment (stock room, airfreight) into a warm room, allow several hours for temperature balance and passing of condensation humidity before switching on for the first time.
- Page 24 Safety The Voluson® S6/S8 weighs 90 kg or more, depending on installed peripherals, (200 lbs., or more) when ready for use. Care must be used when moving it or replacing its parts. Failure to follow the precautions listed could result in injury, uncontrolled motion and costly damage. ALWAYS: •...
- Page 25 • Monitor: Not for use as a cardiac monitor. • Only the patient cable supplied by GE Healthcare, and only recommended electrodes must be used. • Take care that neither bare parts of one of the three electrodes nor the patient comes into contact with conductive parts (e.g., metal parts of the examination bed, trolley, or...
- Page 26 No covers or panels must be removed from the system (high-voltage risk). Only service personnel from GE Healthcare must perform service and repairs. Attempting do-it-yourself repairs invalidate warranty, and are an infringement to regulations and are inadmissible acc. to IEC 60601-1.
- Page 27 Safety 2.5.4.1 Safety Test Scan time limits: According to respective national regulations, and according to the manufacturer recommendations for the medical-technical system. Range: Visual Housing, connection, operating elements, display facilities, inspection: labels, accessories, user manual. Functional test: Checking of functions (according to user manual), check also modular combinations and common operability of system and accessories.
-
Page 28: Probe Safety And Maintenance
Safety The subfolders have the names fbX where X is a number (e.g., Z:\fullbackup\fb1). The data resides within a directory structure within these subfolders. It is possible to move the subfolders, even leaving gaps in the numeration sequence. However, NO change MUST be fbX folders itself, otherwise the backup data cannot be restored! made to the contents of the 2.6 Probe Safety and Maintenance... - Page 29 DO NOT kink, tightly coil, or apply excessive force on the probe cable. Insulation failure may result. • Electrical leakage checks should be performed on a routine basis by GE Service or qualified hospital personnel. Refer to the service manual for leakage check procedures. 2.6.4 Mechanical Hazards A defective probe or excessive force can cause patient injury or probe damage: •...
- Page 30 If any damage is found, the probe must not be placed into any liquid (e.g. for disinfection) and must not be used until it has been inspected and repaired/ replaced by a GE Healthcare Service Representative. Note Keep a log of all probe maintenance, along with a picture of any probe malfunction.
- Page 31 If any damage is found, the probe must not be placed into any liquid (e.g. for disinfection) and must not be used until it has been inspected and repaired/replaced by a GE Healthcare Service Representative. Prepare a solution of a suitable cleaning-disinfectant with the right concentration according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
- Page 32 Also, inspect the probe functionality by live scan. If any damage is found, do not use the probe until it has been inspected and repaired/replaced by a GE service representative. 2.6.7.6 Environmental requirements for Probes Probes must be operated, stored, or transported within the parameters outlined below.
-
Page 33: Biopsy Safety And Maintenance
Safety Probe Environmental Requirements Operational Storage Transport +18º to +30º C +64º to -10º to +50º C +14º to -10º to +50º +14º to Temperature +86º F +122º F +122º F Max. 80% non- Max. 90% non- Max. 90% non- Humidity condensing condensing... - Page 34 Safety There may be restrictions on performing IVF, CVS or PUBS. Please consider the local laws and regulations! 2.7.1.1 Preparing the Patient • Prepare the patient according to the usual procedures for the purpose. • An ultrasound examination with this system must be performed either under supervision, or by adequately trained and qualified medical staff.
-
Page 35: Manufacturer Responsibility
2.9.1 Service Software – Remote Access By using the remote access feature, a GE field engineer can access the ultrasound system via a modem connection. The field engineers are required to contact/call the affected site in advance prior to establish a connection to the system. -
Page 36: Bioeffects And Safety Of Ultrasound Scans
Safety Network Security: The remote access features enables, after checkout has been performed, network services like ftp or telnet on the ultrasound system. Therefore, it is advisable to restrict network access to system for unauthorized personnel. It is strongly recommended to use a firewall to restrict network access from and to an ultrasound system with the remote access feature installed. - Page 37 Safety in the risk of potential thermal bioeffects and it provides a relative magnitude that can be used to implement ALARA. In addition to tissue heating due to the generated ultrasound field, the temperature of the probe head itself can also increase during the examination. The operator shall be aware, that in the tissue region near the ultrasonic transducer, there will be a superposition with the heating due to the ultrasound field, which is not considered by the TI values.
-
Page 38: Disposal
Safety body contrast agents. Often an MI value of 0.4 or less is suggested for examinations of tissue containing stabilized gas bodies. This value arises from operating experience and is not confirmed. Some examples where the MI and TI, respectively, are more or less important are shown in Particular requirements for the basic safety and essential the following table according to performance of ultrasonic medical diagnostic and monitoring equipment, IEC 60601-2-37 2nd... - Page 39 Safety accessories and US console. It is user responsibility to comply with regional environmental protection policy. For more detailed information about recycling of this product, please contact your local city office, your household waste disposal service or the shop where you purchased the product.
- Page 40 Safety This page was intentionally left blank. Voluson® S6/S8 Basic User Manual 2-26 5433669-100 Revision 4...
-
Page 41: Chapter 3 - Description Of The System
Chapter 3 Description of the System Describes the console overview and operator controls. Voluson® S6/S8 Basic User Manual 5433669-100 Revision 4... -
Page 42: Product Description
Description of the System 3.1 Product Description The Voluson® S6/S8 is a professional, innovative, most versatile real-time scanning system. It opens new sonographic possibilities with the 3D/4D VOLUME scanning technique. The vast array of probes makes it suitable for many applications. The system offers the following Indications for use: diagnostic possibilities:... -
Page 43: System Assembly
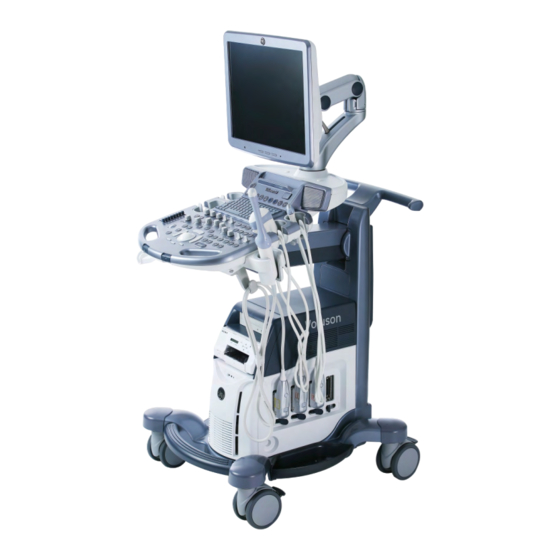
Description of the System 3.2 System Assembly 1. Monitor rotate and height adjust- and inclinable 2. Loudspeaker 3. Control Console rotate and height adjustable 4. Probeholder 5. DVD drive 6. Place for BW printer 7. Place for Color printer or Drawer 8. -
Page 44: Mechanical Adjustment
Description of the System 3.3 Mechanical Adjustment Be careful when adjusting mechanical parts of the system: Danger of injury! 3.3.1 Mechanical Monitor Adjustment The monitor can be rotated, moved forward and backward and adjusted in height: Incline the monitor Move back and forth Move up and down 3.3.1.1 Lock monitor parts Lock heigth adjustment:... - Page 45 Description of the System 3.3.1.2 Preparing for transport To ensure that no part of the monitor can be damaged when transporting or moving the system, the monitor has to be in a secure position. For more information see 'Lock monitor parts' on page 3-4. Lock all monitor parts.
- Page 46 Description of the System 3.3.2.1 Console-Transportlock There is a lever for locking and unlocking the control console, mounted at the front below the control console. When preparing the system for transport, the lock shall be engaged in order to secure the console against uncontrolled rotation. The bolt set to the locking position, the lock catches in when the console is rotated to its center 0˚...
-
Page 47: Concept Of Operation
Description of the System 1 steering blockable and brake caster: Lower Position : caster brake on Top Position : caster freely Lower Position : steering blocked* movable * The steering will only be blocked when the wheel is in center position. 3.4 Concept of Operation The control center of the Voluson®... - Page 48 Description of the System Main group 1: Main menu keys for: • Presets • Sub window probe dependent functions • Image up/down • Image left/right • Virtual Convex mode • FFC (Focus and Frequency Composite) • XBeam CRI (CrossBeam Compound Resolution Imaging) CE (Coded Excitation) •...
- Page 49 Description of the System 3.5.3 Position of Display Annotation Logo 15.) Measurement results Patient Name (Last-, First-, 16.) Status bar area Middle Name) Patient ID-number; GA 17.) P Buttons (Gestational Age) Probe / Application 18.) Run/Freeze/Cine Depth / Frame rate 19.) Trackball Mechanical Index...
- Page 50 Description of the System 3.5.3.1 Detailed Image information Image Info: B (2D) Mode User program Name of user program 7.5-5.0 Receiver frequency [MHz] Acoustic power [%] or fixed to maximum power 100% Gn -12 Gain [dB] C5 / M7* Dynamic curve [number] and Gray map [number]* P6 / E4 Persistence [number] and Edge enhancement [number] Image Info:...
-
Page 51: Button Description
Description of the System Remarks: • When the Automatic Optimization function is active, an asterisk (* next to the Gray map number) is displayed in the B mode Image Info area. • The Image Info in 3D/4D Mode depends on the selected Acquisition and Visualization Mode. - Page 52 Description of the System Flip (Left/Right) Flip (Top/Down) Press this key to flip the image left and Press this key to flip the image top and right alternatively. down alternatively. XTD-View (Extended View) No function Pressing activates/deactivates the XTD- View function. Functions depend on current probe.
- Page 53 Description of the System For more information see 'P-keys' on For more information Programmable key, page 14-4. see 'P-keys' on page 14-4. Programmable key, For more information Programmable key, For more information see 'P-keys' on page 14-4. see 'P-keys' on page 14-4. Freeze/Scan (Read/Write) Dual-Screen Format (vertical distribution) When bright: image is frozen (freeze...
- Page 54 Description of the System Power Doppler Color Mode (on/off) Pressing activates/deactivates the Power Pressing activates/deactivates the Color Doppler mode. Functions depend on mode. Functions depend on current current probe. Rotating allows to set the probe. Rotating allows setting of the CF Power Doppler gain and HD-Flow gain mode gain within the probe-defined within the probe-defined range.
-
Page 55: Remove Usb Devices
Description of the System DICOM Spooler Eject Opens the DICOM job spooler window on Opens a dialog window with all medias For more information see screen, that can be ejected. on page 13-30. 'Connectivity' Set Home/Home Delete Abc An image annotation function, For more Deletes all image annotations in the information see 'Annotation' on page 4-... -
Page 56: Electronic User Manual (Eum)
Description of the System Press [Stop Device]. Then a progressbar appears. The following dialog appears: Confirm with [OK]. You can now remove the USB stick safely. Press [Close] to close the “USB and Network Drives” dialog and return to the previous operating state. - Page 57 Description of the System 3.8.1 Navigation Tools [Hide] the Help book navigation tools on the left portion of the screen. To view the left side of the screen again, click the [Show] icon. To go back to the previous selected topic. To view the topic which was displayed before clicking the [Back] button.
- Page 58 Description of the System • To Save a Favorite Topic: 'To Save a Favorite Topic' on page 3-20 3.8.2.1 To View the Contents Click on the [+] sign next to the chapter you want to view to open up that section. Open up the page to view that page’s information.
- Page 59 Description of the System 3.8.2.3 To Search for a Topic To search for a specific topic, click on the “Search” tab. Type in the keyword to find: field. Topics with the word or Type in the topic name in the Select Topic to display: area.
- Page 60 Description of the System 3.8.2.4 To Save a Favorite Topic You may find that there are topics you need to refer to often. In this case, it is a good idea to save these topics as Favorites. To save a topic as a favorite, click on the “Favorites” tab. Topics: field and click the [Add] button.
-
Page 61: Chapter 4 - Operating The System
Chapter 4 Operating the System Describes powering on the system, transducer connection, programm selection and patient datas. Voluson® S6/S8 Basic User Manual 5433669-100 Revision 4... -
Page 62: General Remarks
Operating the System 4.1 General Remarks Installation, switching on for the first time and check-up of the system must only be performed by authorized persons. The Voluson® S6/S8 is delivered with recommended basic settings. These offer suitable conditions for a large number of applications. Depending on the user’s experience these default settings can be changed and stored as new User Programs. -
Page 63: Power Off / Shutdown
Operating the System Once system is switched on, it is completely reset. The boot-up time is about 2 minutes, and then the 2D mode main menu for the previously selected transducer is displayed. In case you disconnect the previously selected transducer, the menu "PROBE/PROGRAM" will appear, even if it has been disconnected during shutdown. - Page 64 Operating the System • If a service technician is currently remote servicing your system, the following dialog appears. • If the current Exam is not finished, the following warning message will be displayed. 2. If desired, switch OFF the main switch at the rear of the system. During Full Backup or Image Backup a shutdown is not possible.
-
Page 65: Transducer Connection
Operating the System 4.5 Transducer Connection Prior to connecting or disconnecting a probe freeze the image. It is not necessary to switch off the system. If a probe is disconnected while running (scan mode) a software error may occur. In this case switch OFF the system and, after an intervall of 10 seconds, switch it ON again. (perform a reset). - Page 66 Operating the System For example: VOLUSON ® TRANSVAGINAL TRANSDUCER RIC5-9W-RS 1. Medical probe-sheath 4.6.1 Probe Usage For details about connecting, activating, deactivating, disconnecting, transporting and storing the probes, refer to: 'Transducer Connection' on page 4-5 and Probe/Program Selection 'Probe/Program Selection' on page 4-7 .
-
Page 67: Probe/Program Selection
Operating the System When scanning in air (Ultrasound probe is not in contact with a human body or a phantom) most of the ultrasound energy is reflected at the lens - air surface and bounces back and forward between that interface and the transducer ceramics. Already the smallest deviation from the ideal geometrical shape of the reflecting interfaces can cause irregularities in the reverberation pattern across the transducer surface. - Page 68 Operating the System fields of application. To store a user setting under an application, review: 'General' on page 13- [Probe] key (hard key): This key activates and deactivates the “probe select” menu. Behavior of probe select function, when connecting/disconnecting a probe, review: 'Transducer on page 4-5 Connection' Probe selection menu on the menu area:...
- Page 69 Operating the System 4.7.1 Starting the System Selecting the desired settings group will load the preset. Click on the desired setting and the probe will be started. The probe is initialized, the main menu (2D mode) and the ultrasound image appears on the monitor in write mode (real time display.
-
Page 70: Entering Patient Data
Operating the System 4.8 Entering Patient Data Patient Data is to be entered by using a patient data form. This information will be used in calculations, patient worksheets, DICOM settings and is displayed on the screen to identify images. All entries into the data fields are stored on the internal database. Press the [Patient] key (hard key) on the control panel. - Page 71 Operating the System If the “End Exam Dialog” field in the System Setup is marked by a check mark, the ”End Exam” dialog will be displayed on the monitor before ending the current exam. on page 13-15 'General' 1. Incomplete measurement exists: Select No: Dialog window disappears (exit to previous operating state) Select Yes: “End Exam”...
- Page 72 Operating the System Current Patient menu (screen) For more information see Chapter 1. Archive:Switches to Archive. Voluson® S6/S8 Basic User Manual 4-12 5433669-100 Revision 4...
- Page 73 Operating the System Clear Current:All temporary patient data is cleared '“Patient Information” screen' on page 4- 13 If MPPS is used, and a step is in progress, send MPPS discontinue message to cancel the step. Hide Patient Info:Hides the patient info on screen during an exam Continue Exam:Starts an exam with the current patient.
- Page 74 Operating the System patient age ---- , female, male (selection in pull down menu) Note Upon entering the day of birth: The age is calculated and displayed automatically. 2. Select Application. ( 'Patient Information – Abdomen (ABD)' on page 4-15 ) Obstetrics (OB) ( Abdomen (ABD) on page 4-16 ) Gynecology (GYN) ( 'Patient 'Patient Information –...
- Page 75 Operating the System 4.8.3.1 Patient Information – Abdomen (ABD) Application Data: Height: Enter the patient’s height in one of the dimensions (cm, ft, inch). Weight: Enter the patient’s weight in one of the dimensions (kg, lb, oz). Dimension selection: Position the cursor into the Dimension selection field using the trackball and press the left or right trackball key.
- Page 76 Operating the System 4.8.3.2 Patient Information – Obstetrics (OB) Application Data: Enter the date of the last menstrual period using the selected format (e.g., mm-dd-yyyy). Note: The first day of the last period must be entered. Enter the date of conception. Enter the estimated date of delivery, GA is calculated automatically.
- Page 77 Operating the System LMP/GA d/EDD calculation Duration of gestation: 280 days LMP + 280d Can be changed to 41 weeks actual date – LMP (actual date = date of Voluson® S6/S8) EDD – 280d For more information see '“Patient Information” screen' on page 4-13. Note Select this button to invoke the Past exam dialog.
- Page 78 Operating the System Create a new entry by entering an exam date (values between actual date and LMP are possible). Enter measurement data from previous exams performed on different systems. Use the “Up/Down” arrows to scroll through the list, if the list is longer than the available amount of lines.
- Page 79 Operating the System 4.8.3.3 Patient Information – Gynecology (GYN) Application Data: The first day of the last menstrual period must be entered using the selected format (e.g., mm-dd-yyyy). Note: The first day of the last period must be entered. Exp. Ovul. Date of expected ovulation Day of Cycles Day of cycles...
- Page 80 Operating the System 4.8.3.4 Patient Information – Cardiology (CARD) Application Data: Height Enter the patient’s height in one of the dimensions (cm, ft, inch) Weight Enter the patient’s weight in one of the dimensions (kg, lp, oz) Body Surface Area (calculation value, no input) Heart Rate Dimension selection: Position the cursor into the dimension field using the trackball and press the left or right trackball key.
- Page 81 Operating the System 4.8.3.5 Patient Information – Urology (URO) Application Data: Enter the value of the Prostate-specific antigen PPSA Coefficient 1 Enter the 1st value of the predicted PSA Coefficient. PPSA Coefficient 2 Enter the 2nd value of the predicted PSA Coefficient. The PPSA is a number in dimensions of ng/ml/grams which gives the normal level of PSA that Note would be expected for a prostate of a given volume.
- Page 82 Operating the System Press the [Enter] or [Tab] (input fields are selected in successive order). 2. ENTER PATIENT INFORMATION Use the keyboard to type the patient information. Upon pressing the [Enter] key on the keyboard the data is entered and the next input field is selected.
- Page 83 Operating the System To quit the dialog: [Yes]: The current measurements are dedicated to the Exam. [No]: The current measurements and the screen are cleared and 2D starts. The Patient procedure is closed and the previous operating state is activated. If no old patient exists, no save/send in progress and no auto-start acquisition, the system will display an info dialog “Start Exam with old ultrasound image?”...
- Page 84 Operating the System To sort the list of exams click the appropriate caption, e.g. Date/Time as image above. Whatever criterion you choose for ordering your list will be indicated by a blue triangle and stored. Select the desired “Search” field with the trackball. Click this button to search for the corresponding input (Use the “%”...
- Page 85 Operating the System Select one of these buttons to navigate through the detailed DICOM information of the relevant procedure steps. Select the [Close] button to return to worklist. 2. Highlight an entry from this list using the trackball and press the [Select] button. The “Procedure Step”...
- Page 86 Operating the System Highlight an entry from this list using the trackball and press the central trackball button. Detailed DICOM information is displayed. The status of a step can be none (not started), in progress, completed or discontinued. Select this button to complete the step by sending a MPPS complete message (only possible if status of step is “in progress”).
-
Page 87: Image Annotation
Operating the System The “Search Results” dialog menu appears on screen. Search procedure: • Enter ID or Name into the corresponding input field using the keyboard keys. • Select the result using the trackball cursor and the left or right trackball key. The result is highlighted. - Page 88 Operating the System 4.9.1 Annotation This function enables text writing onto the ultrasound image using the keyboard, in freeze mode or in scan mode, respectively. The inscription will be erased upon selection of a probe or a program. Inscription is not possible outside the annotation area. Operation: Activate the Annotation Mode via [ABC] key or [Space Bar].
- Page 89 Operating the System Select the same word from the screen using the trackball. The selected word appears at the cursor position. Select a new word, (a "blank" is inserted between the prior and new word) or enter a character using the keyboard (a "blank" is inserted between the prior word and the new character).
- Page 90 Operating the System • The Trackball, the [Home] key, or the arrow keys on the keyboard can set the left margin of the image annotation. 4.9.3 Indicator Indicator key [F2] on the keyboard Pressing the [F2] key causes the menu area to change to the Indicator menu..
- Page 91 Operating the System Operation: The last selected pictogram appears in the last selected place of the annotation area. To change the displayed pictogram, press the cursor key and select the appropriate pictogram. Use the upper trackballkey to switch between moving or rotating the scan plane identification line direction with the trackball.
-
Page 92: Scan Assistant
Operating the System After selecting another application the menu changes back to the Bodymark menu with the bodymark symbols of the selected application. Return to the Bodymark menu, if no new application is selected. Please note: The main application (chosen in the “Probe Selection” menu) does not change! After selecting the [Appl.] key the screen menu changes to the “Application Select”... - Page 93 Operating the System 4.10.1 Scan Assistant Details See the Scan Assistant by clicking on the arrows of the Scan Assistant. Dropdown menu to switch between the activated Scan Assistant lists. All Scan Assistant items. Confirmed items will have a checkmark in the box. 4.10.1.1 Pause the Scan Assistant Press the “Pause”...
- Page 94 Operating the System This page was intentionally left blank. Voluson® S6/S8 Basic User Manual 4-34 5433669-100 Revision 4...
-
Page 95: Chapter 5 - Probes And Biopsies
Chapter 5 Probes and Biopsies Describes probe precautions and -handling, pobe applications and features, care and maintenance of probes and biopsies. Voluson® S6/S8 Basic User Manual 5433669-100 Revision 4... -
Page 96: Probes
5.1.1 Labeling Each probe is labeled with the following information: • Manufacturer • GE part number • Probe serial number • Probe designation provided on the probe grip and the top of the connector housing, so it is easily read when mounted on the system and is also automatically displayed on the screen when the probe is selected. - Page 97 Probes and Biopsies Displayed Probe Information (1 = Probe Information Location) 5.1.2 Applications The manual refers to probes that can be connected to the device. It might be possible that some probes are NOT available in some countries! Some features and options are not available in some countries! The Multi Angle Biopsy is only possible with C1-5-RS*, 12L-RS, 4C-RS, 9L-RS, 3Sc-RS, Note ML6-15-RS* probes.
- Page 98 Probes and Biopsies 5.1.3 Features (Coded Virtual 2D Probe XBeam Wide Contrast Harmoni Convex Applications Sector Imaging Mode Imaging) E8C-RS C1-5-RS* AB2-7-RS 12L-RS 4C-RS 9L-RS 3Sc-RS ML6-15-RS* 8C-RS MCFM Extend Tissue 2D Probe (MColo Elastog Dopple Dopple HPRF Biopsy Applications r Flow Flow raphy...
- Page 99 Probes and Biopsies Exten Tissue Elasto 3D4D Probe (MCol STIC Biops Doppl Flow STIC HPRF graph Applications CFPD View Color Flow Mode) RAB4-8-RS RIC5-9W-RS RAB2-5-RS 5.1.4 Settings Depth[cm 2D Angle [Degree] (/ Doppler Frequency[MHz] Center Frequency wide Probe Designation [MHz] phased) High max.
- Page 100 Probes and Biopsies Slight noise emissions may occur in 3D/4D probes, when operating in volume mode! 5.1.5.1 3D/4D Probes on page 5-4 For Probefeatures: 'Features' (1) Applied Section ; (2) User Section VOLUSON ® ABDOMINAL Intended Uses Capabilities TRANSDUCER RAB4-8-RS •...
- Page 101 Probes and Biopsies VOLUSON ® ENDOCAVITY Intended Uses Capabilities TRANSDUCER RIC5-9W-RS • • Obstetrics 3D/4D Real Time imaging • • Gynecology Wide field of view • • Urology Small probe tip and shaft • Biopsy guide available • CF, MCF, HD-Flow, Power and PW Doppler •...
- Page 102 Probes and Biopsies VOLUSON ® CURVED ARRAY Intended Uses Capabilities TRANSDUCER E8C-RS • • Obstetrics Wide field of view • • Gynecology Small probe tip and shaft • • Urology Power and PW Doppler • Broad bandwidth, Multi- frequency • Biopsy guide available •...
-
Page 103: Biopsies
Probes and Biopsies VOLUSON ® LINEAR ARRAY Intended Uses Capabilities TRANSDUCER ML6-15-RS* • • Small Parts 3D/4D Real Time Imaging • • Peripheral Vascular Wild field of view • • Pediatrics Small probe tip and shaft • • CFM, MCFM, HDFlow, Power and PW Doppler •... - Page 104 Probes and Biopsies Refer to the biopsy guide’s user manual for detailed information on how to mount and use the biopsy guide. • The cold-sterilized transducer can be kept sterile by placing a sterile sheath over the shaft (sterile coupling gel between transducer and sheath). Technical data: The materials of all reusable biopsy needle guides are stainless steel type 304 and 303 (AISI No).
- Page 105 Probes and Biopsies E8385MZ for Voluson® Phased Array Transducer 3Sc-RS Press the needle guide onto the transducer shaft and push it forward until the small swelling of the needle guide catches in the notch at the transducer tip. PEC 74 for Voluson® Abdominal Transducer RAB4-8-RS Place the needle guide onto the transducer;...
- Page 106 Probes and Biopsies PEC 78 for Voluson® Abdominal Transducer RAB2-5-RS Press the needle guide onto the transducer shaft and push it forward until the small swelling of the needle guide catches in the notch at the transducer tip. PEC 83 for Curved Array Transducer AB2-7-RS Place the needle guide onto the transducer;...
- Page 107 Probes and Biopsies H40432LC for Linear Array Transducer 12L-RS Press the needle guide onto the transducer shaft and push it forward until the small swelling of the needle guide catches in the notch at the transducer tip. H4906BK for Linear Array Transducer 9L-RS Press the needle guide onto the transducer shaft and push it forward until the small swelling of...
- Page 108 Probes and Biopsies Control for rotation of the Biopsy line. To invoke the Biopsy Setup: Condition: To invoke the Biopsy Setup, 2D mode must be active. Press the [Utilites] key on the control panel. Following menu appears, if Single Angle Biopsy is possible for an activated probe: Biopsy kit name and the “Biopsy Line”...
- Page 109 Probes and Biopsies TThese ‘Biopsy Lines’ appear if Multi Angle Biopsy is possible for the activated Probe. See ‘To program a Multi Angle Biopsy Line’ on page 5‐17 for more information. Biopsy Kit informations are grayed, if needle path was not calibrated once (Biopsy Setup). Note 5.2.3 To program a Single Angle Biopsy Line Condition: Place the probe with the biopsy guide secured and with the needle attached into a...
- Page 110 Probes and Biopsies 1. Place the line over the needle echoes by positioning with the trackball. 2. Rotate the line with the first encorder on the control panel. 3. Select [Save&Exit]. The needle line is stored, and exit to the 2D main menu. 4.
- Page 111 Probes and Biopsies Needle This yellow marker indicates the access point of the needle in the Biopsy Guide! The distance between dots is 10mm. 1. Place the line over the needle echoes by positioning with the trackball. 2. Rotate the line with the left control. 3.
- Page 112 Probes and Biopsies 6. Select the [Store MBX-3] key to store the second line. 7. Exit to the 2D main menu without saving. 8. Select the [Exit + Save] key to store biopsy setup. The MBX-2 line will be automatically calculated. It is absolutely necessary to ensure that before performing a biopsy, the selected and displayed biopsy line corresponds to the biopsy needle guide mounted to the transducer (left/ right).
- Page 113 Probes and Biopsies Biopsy Probe Capabilities and Features Illustration PEC78 RAB4-8-RS Needle diameters: Gauge 21: 0,813 mm Gauge 18: 1,270 mm Gauge 14: 2,108 RAB2-5-RS Material: Plastic PEC 83 AB2-7-RS Needle diameters: < 1 mm < 1.4 mm < 2.2 mm Material: Stainless Steel Sterilization with autoclave possible! E8385NA(m...
- Page 114 Probes and Biopsies Biopsy Probe Capabilities and Features Illustration H40432LC( 12L-RS Needle diameters: multiangle) >0,6mm <2,1mm Material: Plastic The biopsy bracket is reusable. Please refer to the manufacturer’s instructions included in the biopsy kit! H4906BK 9L-RS Needle diameters: (multiangle) >0,6mm <2,9mm Material: Plastic The biopsy bracket is reusable.
- Page 115 Chapter 6 2D Mode Describes the general functions of the 2D- Mode. Image quality is the essential performance of the system. Please read this chapter carefully. Voluson® S6/S8 Basic User Manual 5433669-100 Revision 4...
-
Page 116: Main Menu
2D Mode The 2D display consists of the ultrasound image, an orientation marker, patient data, image information, a Gray scale bar, a depth scale with focal zone markers, and an actual TGC curve. The ultrasound image is derived from the tissue echoes that return to the scan head. They are amplified, converted, and then mapped to an image processing curve that relates each echo’s intensity to a shade of gray. -
Page 117: Operation
2D Mode Example: 2D Main/Sub menu area Example: 2D rotaries Remarks: • In freeze-Mode changing the Angle, β-View, Focal Zones, OTI, Frequency, Virtual Convex mode, CE, FFC and XBeam CRI, (and combinations of these modes) is impossible. • The keys for the functions Focal Zones, OTI, β-View, Angle, Frequency, FFC, XBeam CRI, CE, SRI and Virtual Convex mode only appear on the menu area if they are available for the selected probe. - Page 118 2D Mode • '2D Mode Depth' on page 6-4 • '2D Image Angle' on page 6-5 • 'TGC Slider Controls' on page 6-5 • on page 6-6 '2D Automatic Optimization' • on page 6-6 'Transmit Power' • on page 6-7 'Receiver Frequency Range' •...
-
Page 119: Image Angle
2D Mode Remarks: • The maximum and minimum depth depend on the selected probe. The actual depth in [cm] is displayed in the Information Header. • freeze mode: The displayed 2D image is positioned on the monitor again without change in the depth range. -
Page 120: Automatic Optimization
2D Mode 6.2.5 2D Automatic Optimization This function will optimize the contrast resolution according to the histogram of the scan area. The shape of the ROI will depend on the probe, scan depth and scan angle. The primary result is a value for the lower and upper endpoint of the histogram. Pressing the [auto] key causes automatic optimization of the gray scale to enhance the contrast. -
Page 121: Receiver Frequency Range
2D Mode Use the [Foc.Zones] control key to select the number of focal zones. The possible number of focal zones depends on the probe in use. Arrows at the left side of the 2D image mark the active focal zones by their position. Use the [Focus Depth] digipot to select the depth position of the current focus one(s). -
Page 122: Β-View (Beta View)
2D Mode Switch on / off the “Coded” [Harmonic Imaging] function in 2D mode. brightly illuminated: Harmonic Imaging is active (receiving frequency is the double of the transmitted frequency). Weakly illuminated: Harmonic Imaging can be used, with the selected probe, but is not active (the last adjusted transmitting frequency is active). -
Page 123: Virtual Convex Mode
2D Mode 6.2.12 Virtual Convex Mode Advantage of the Virtual Convex mode: The scan area is increased in relation to the linear display by steering the ultrasound lines on the edge of the probe. Selection of Linear- or Virtual Convex mode display. Remarks: •... -
Page 124: Speckle Reduction Imaging (Sri)
2D Mode • If the [XBeam CRI] function is enabled in 2D Mode, it is also used in 3D preparation mode and during a Static 3D acquisition. • The CRI can also be used in Virtual Convex mode. 6.2.16 Speckle Reduction Imaging (SRI) on page 9-46 'Speckle Reduction Imaging (SRI)' 6.2.17 Image Orientation... - Page 125 2D Mode There are three 2D mode display modes each one having a different screen layout. • Single-Screen Format • on page 6-11 'Dual-Screen Format' • on page 6-12 'Quad-Screen Format' 6.2.18.1 Dual-Screen Format [Dual] Screen Format keys (hard key): Press these keys to change the display mode from Single or Quad display Mode to the “Dual”- display mode.
- Page 126 2D Mode 3. Select the next display position by using the format key. 4. Freeze the next image. If the image is frozen and you use [Update 2D] (the right trackball key) the next image is selected and active. If the image is active (in real time mode) by pressing the [Update 2D] (the right trackball key) the next image is selected and active.
- Page 127 2D Mode 1. Select Quad display mode. 2. Freeze the image. 3. Select the next display position by using the format key. 4. Freeze the next image. If the image is frozen and you use [Update 2D] (the right trackball key) the same image is selected and active.
- Page 128 2D Mode 1. Press the [Zoom] digipot to switch to Zoom Pre Mode. 2. Place the zoom box over the region of interest. The trackball has two functions: adjusting position and size of the zoom box. The activated function is displayed in the status bar area on the monitor. Press the upper trackball key to change the function of the trackball from position to size or vice versa.
-
Page 129: Cine Mode
2D Mode 6. To change the Zoom factor, turn the [Zoom] digipot. Remarks: • In the overview image the zoom box is depicted with a yellow border and is identical with the zoomed sector on screen. Using read zoom has not effect whatsoever on the zoom box in the overview image. - Page 130 2D Mode Move the trackball horizontally to display the 2D images of the stored sequence, one by one. The last stored sequence consists of images from the last scan procedure and will be stored until the next scan procedure by [Freeze].
- Page 131 2D Mode • The number of stored images depends on the number of scan lines, scan depth and magnification. In freeze mode the length of the sequence is indicated on the status bar. Display: Cine xxx • Starting the Cine mode erases measuring marks and measuring displays. •...
- Page 132 2D Mode 6.3.4 Cine-Split Function After Freeze of a sequence in Multi-format 2D mode, two or four different images of the sequence can be displayed simultaneously in Dual or Quad display mode. Move the trackball horizontally to display the 2D images of the stored sequence. You can also use the flipswitch below the control panel.
- Page 133 2D Mode 3. Select the starting image of the sequence. The selected ultrasound image is simultaneously displayed on the screen. 4. Select the final image of the sequence. The image is displayed on the screen. Voluson® S6/S8 Basic User Manual 5433669-100 Revision 4 6-19...
-
Page 134: Sub Menu
2D Mode 5. Select the review speed. 100% corresponds to the recorded speed (real time). 6. Select the read zoom (factor 0.8 to 3.4) by turning the [Zoom] rotary control. 7. Select the Cine Mode review direction. Images are only displayed from Start to End. Images are displayed from Start to End and back. - Page 135 2D Mode • 'Dynamic Control' on page 6-22 • 'Optimized Tissue Imaging (OTI)' on page 6-22 • 'Enhance' on page 6-22 • on page 6-22 'Reject' • on page 6-22 'Line Density' • on page 6-22 'Gray Map' • on page 13-2 'Utilities' 6.4.1 Persistence Filter “Persistence”...
-
Page 136: Gray Map
2D Mode 6.4.4 Dynamic Control on page 7-8 'Dynamic Control' 6.4.5 Optimized Tissue Imaging (OTI) The function OTI allows the examiner to “fine tune” the system for scanning different kinds of tissue. Use the [OTI] control to adjust the respective parameter. Four positions are possible: adipose, solid, cystic or normal tissue. -
Page 137: B-Flow
2D Mode 6.5.1 2D Gray Map This defines the relation between echo amplitude (input) and brightness (output) in a look-up table. In total 18 Gray Maps are available.You can select a certain map independently for each one of the imaging modes (e.g., Map 5 for 2D- and Map 2 for M-imaging etc.). For 3D Gray Map selection: '3D Gray Chroma Map' on page 9-47 1. - Page 138 2D Mode • better resolution than Color-Doppler mode. It is therefore a more realistic (intuitive) representation of flow information, allowing to view both high and low velocity flow at the same time. on page 6-24 To adjust the B-Flow settings: 'B-Flow To use the B-Flow: 'B-Flow Main Menu' on page 6-25 Sub Menu'...
- Page 139 2D Mode 6.6.2.2 Back- ground This function adjusts the display level of the background anatomy (e.g., switch off the background when imaging the kidney, liver and spleen) and adds merging the B-Image information to the B-Flow Image. Switch the Background with the flip switch control below the menu area. Three steps are possible: 0, 1 and 2 6.6.2.3 Accu- mulation Accumulation detects the maximum signal and holds it for the level specified.
-
Page 140: Xtd-View (Extended View)
2D Mode By using [S./PRI], the sensitivity can be changed for each anatomy of interest. Sixteen steps are possible. 6.7 XTD-View (Extended View) XTD-View provides the ability to construct and view a static 2D image which is wider than the field of view of a given transducer. - Page 141 2D Mode Example: Linear Array Remarks: • XTD-View is an option. If the option is not installed, the [XTD] key is not active. • XTD-View is intended for scanning areas too large to fit in a regular frame. Always scan slowly and in uniform motion lengthwise, in either direction relative to the probe marker.
- Page 142 2D Mode 6.7.2 XTD-View Operation The image-optimizing functions, like gain, power, depth, image angle, focus, OTI, etc. are the on page 6-3 ) To perform an exam using XTD-View: same as in 2D mode. '2D Operation' on page 6-28 ) 'Using XTD-View' The quality and usefulness of XTD-View images is affected by the transducer’s motion.
- Page 143 2D Mode 4. To start acquiring the image, press the right trackball key [Start]. During the acquisition the following message will be displayed on the menu area. If you press the [Exit / Stop acquisition] key the recorded information will be cleared. 5.
- Page 144 2D Mode Guidance and precautions for interpretation of XTD-images: • Always adopt a critical attitude to images created in XTD-mode. • Be aware that any diagnostic conclusion must not be drawn from XTD-images alone, but have to be checked with other diagnostic procedures. •...
- Page 145 2D Mode A good XTD image has a smooth edge, with no sharp curves. It has a clear direction, with almost no curves. When reviewed with the corresponding 2D-images, the cursor moves linearly over the XTD-image, e.g. equal trackball distances lead to an equal movement of the blue rectangle.
- Page 146 2D Mode 6.7.4.2 XTD Rotation Use the [XTD rot.] control to rotate the XTD-image. 6.7.4.3 Frame Review Two “Split-screen” display formats are available for reviewing the acquired frames. Vertical image distribution Horizontal image distribution Remarks: • The blue border of the 2D image is displayed for orientation. It indicates the position of the 2D image in the XTD-image.
- Page 147 2D Mode The trackball has two functions: Frame and Position (pos) (Frame move the blue box in the XTD-image and Position will move the B-image itself. The activated function is displayed in the status bar area on the monitor. To change the current function, press the upper trackball key. 6.7.4.4 XTD Image Size Two different XTD Image Sizes are possible: fit: The XTD-image fits to the border of the screen, which is the default setting.
-
Page 148: Contrast Imaging
2D Mode 6.8 Contrast Imaging Injected contrast agents re-emit incident acoustic energy at a harmonic frequency much more efficiently than the surrounding tissue. Blood containing the contrast agent stands out brightly against a dark background of normal tissue. Possible clinical uses are to detect and characterize tumors of the liver, kidney and pancreas and to enhance flow signals in the determination of stenosis or thrombus. - Page 149 2D Mode Remarks: • Contrast Imaging is an option. If the option is not installed (or the selected probe is not applicable for this feature), the [Contrast] key is not active. • Contrast Imaging is also available in 3D volume mode. (4D acquisition is impossible). •...
- Page 150 2D Mode Precautions when using a contrast medium: • GE Medical Systems is not liable for any damage or injury resulting from improper use of contrast media. Handle the contrast medium as described in the operation manual supplied with the contrast medium.
- Page 151 2D Mode 6.8.3.2 Speckle Reduction Imaging (SRI) Select the [SRI] key to activate the SRI function and change the level of smoothing using the [+] and [-] keys. on page 6-10 'Speckle Reduction Imaging (SRI)' 6.8.3.3 Contrast Clock The Contrast Clock measures the time since injection. Select the [Contrast Clock] button to activate it at the time of injection (On).
- Page 152 2D Mode 6.8.3.7 Back-ground For more information see 'B-Flow Operation' on page 6-24. 6.8.4 Contrast Sub Menu The “Contrast Main” menu must be active. Changes are only possible in scan mode (controls have no function in freeze mode). Only Note changes in the Gray Chroma Map are also possible in freeze mode.
-
Page 153: Chapter 7 - M Mode
Chapter 7 M Mode Describes the general functions of the M Mode. Image quality is the essential performance of the system. Please read this chapter carefully. Voluson® S6/S8 Basic User Manual 5433669-100 Revision 4... -
Page 154: M Main Menu
M Mode M mode imaging provides Time and Motion echo information derived from a stationary ultrasound beam. M mode is used along with a 2D image. A straight line running through the 2D image, called the M-cursor, identifies the position of the stationary ultrasound beam from which the echo information is being gathered. -
Page 155: M Operation
M Mode Remarks: • In freeze mode (frozen image) changing the Gain and Frequency is not possible. 7.1.1 Principle The M mode display is derived from a 2D image display. When switching on the M mode, the M-cursor line is inserted into the 2D image. It symbolizes the ultrasound beam and defines the position of the M mode trace. - Page 156 M Mode • 'Activation of M Mode' on page 7-4 • 'M Gain Control' on page 7-4 • 'Sweep Speed' on page 7-5 • on page 7-5 'Invert' • on page 7-5 'Frequency' • on page 7-5 'TGC Slider Controls' •...
- Page 157 M Mode [M Mode] key:rotate it to adjust the gain (brightness) of the entire image. When the GAIN control is turned clockwise the entire image gets brighter. When the GAIN control is turned counterclockwise the entire image gets less bright. Remark: The current gain value is displayed on the screen [GN ...].
-
Page 158: M Sub Menu
M Mode 7.2.9 M Mode Depth on page 6-4 The function is the same as 2D mode depth '2D Mode Depth' 7.2.10 M Cineloop Several 2D image frames and M mode trace information can be recalled. When freezing, a certain time frame (M information of the last examination sequence) is stored in the loop memory. - Page 159 M Mode Changes are only possible in scan mode (Controls have no function in freeze mode). Changes Note in the Gray Chroma Map, Tint Map and Display Size are possible in rfreeze mode. Available functions For more information, see: • on page 7-7 'Reject' •...
-
Page 160: Mcf Mode (M Color Flow Mode)
M Mode The Reject state is displayed in the Image Info area on the screen. Reject range max.: 255 Reject range min.: 0 step size: 5 7.3.2 Enhance With the “Enhance” function the echo information is digitally processed such that certain existing information becomes easily visible (e.g., adjacent media layers). - Page 161 M Mode • To use special utilities: 'Utilities' on page 13-2 and 'Gray Map' on page 6-22 Note The MCF mode is available if the selected probe is capable of the MCF mode. 7.4.1 MCF Main Menu [M Mode] key + [CF Mode] key (hard keys) By pressing the [M] control and the [CF] control, the MCF mode is switched on in the preparation mode.
- Page 162 M Mode Remarks: • In freeze mode changing the Wall Motion Filter, PRF and Gain is not possible. • In MCF mode only one focus zone is available. • When the MCF-box is moved, the focus position is set to the center of the Color box. 7.4.2 MCF Operation The MCF operations For more information, see:...
- Page 163 M Mode • 'Display Format' on page 7-8 • 'Display Size' on page 7-8 The [Freeze] key stops the 2D image and MCF mode trace. By pressing the [Freeze] key again, the MCF-cursor appears on the active 2D image. Note 7.4.2.3 MCF Gain Control The adjustment of the Gain control determines the amount of amplification applied to the received echoes.
-
Page 164: Mtd Mode (M Tissue Doppler Mode)
M Mode Note Changes are only possible in scan mode! Changes in the Displ. Mode, MCF Map, Scale, Baseline and Threshold are also possible in freeze mode. The submenu settings are the same as those of the CF mode. See ‘CF Sub Menu’ on page 8‐ 17 for more information. - Page 165 M Mode or M mode image. Tissue Doppler overlays color on the M mode trace using velocity and variance color maps. The Tissue Doppler wedge overlays the 2D mode image and M mode timeline. The description of MTD mode is subdivided in two groups: •...
- Page 166 M Mode Remarks: • In freeze mode changing the PRF and Gain is not possible. • In MTD mode only one focus zone is available. • When the MTD-box is moved, the focus position is set to the center of the Color box. 7.5.2 MTD Operation The MTD operations: •...
- Page 167 M Mode • 'Display Size' on page 7-8 The [Freeze] key stops the 2D image and MTD mode trace. By pressing the [Freeze] key again, the MTD-cursor appears on the active 2D image. Note 7.5.2.3 MTD Gain Control The adjustment of the Gain control determines the amount of amplification applied to the received echoes.
-
Page 168: Mhdf Mode (Mhd-Flow Mode)
M Mode Changes are only possible in scan mode! Changes in the MTD Map, Scale, Baseline are Note Threshold are also possible in freeze mode. on page 8-30 The submenu settings are the same as those of the TD mode. 'TD Sub Menu' 7.6 MHDF Mode (MHD-Flow Mode) HDF Mode and HD-Flow M Mode are Doppler modes intended to add color-coded qualitative information concerning the relative velocity and direction of blood flow within the 2D mode or... - Page 169 M Mode M mode image. HDF Mode overlays color on the M mode trace using velocity and variance color maps. The HDF Mode wedge overlays the 2D mode image and M mode timeline. The description of MHDF mode is subdivided in two groups: •...
- Page 170 M Mode Remarks: • In freeze mode changing the Wall Motion Filter, PRF and Gain is not possible. • In MHDF mode only one focus zone is available. • When the MHDF-box is moved, the focus position is set to the center of the Color box. 7.6.2 MHDF Operation The MHDF operation consists of: •...
- Page 171 M Mode • 'Display Format' on page 7-8 • 'Display Size' on page 7-8 The [Freeze] key stops the 2D image and MHDF mode trace. By pressing the [Freeze] key again, the MHDF-cursor appears on the active 2D image. Note 7.6.2.3 MHDF Gain Control The adjustment of the Gain control determines the amount of amplification applied to the received echoes.
-
Page 172: Stic With M-Mode
M Mode Changes are only possible in scan mode! Changes in the MHDF Map, Scale and Threshold Note are also possible in freeze mode. For more information see 'HD-Flow Sub Menu' on page 8-26. 7.7 STIC with M-Mode See `Upon [Freeze] a certain number of volumes will be stored in the cine memory. The sequence can be reviewed volume by volume. -
Page 173: Anatomical M-Mode (Amm)
M Mode 7.8 Anatomical M-Mode (AMM) General: Anatomical M-Mode is an option. If this option is not installed, the [AMM] key is hidden. To activate Anatomical M-Mode, press [AMM] key on your menu area: Press the right or left trackball key to activate the AMM. After pressing the [M] control adjust the AMM-cursor using the trackball in the 2D single image. - Page 174 M Mode 7.8.1.1 View Modes (1) 2D Image ; (2) AMM ; (3) Motion Voluson® S6/S8 Basic User Manual 7-22 5433669-100 Revision 4...
- Page 175 M Mode 7.8.1.2 Rotate Rotate the menu-control button to set the direction of the AMM line. 7.8.2 AMM Sub menu The AMM Submenu consists of: • 'Gray Map' on page 6-22 Voluson® S6/S8 Basic User Manual 5433669-100 Revision 4 7-23...
- Page 176 M Mode • 'Display Size' on page 7-8 • 'Frequency' on page 7-5 Voluson® S6/S8 Basic User Manual 7-24 5433669-100 Revision 4...
-
Page 177: Chapter 8 - Doppler Modes
Chapter 8 Doppler Modes Describes the general functions of the Spectral Doppler Mode (PW), Continuos Wave Doppler (CW), Color Flow Mode (CFM), Power Doppler (PD), High Definition Flow (HD-Flow) and Tissue Doppler. Image quality is the essential performance of the system. Please read this chapter carefully. -
Page 178: Pulsed Wave Doppler Mode (Pw Mode)
Doppler Modes Doppler Modes: • on page 8-2 'Pulsed Wave Doppler Mode (PW Mode)' • ‘Continuous Wave Doppler Mode (CW Mode)’ on page 8‐8 • on page 8-17 'Power Doppler Mode (PD Mode)' • on page 8-23 'HD-Flow Mode (Bi-directional Angio Mode)' •... - Page 179 Doppler Modes 8.1.1 PW Main Menu [PW Mode] key (hard key) Press the [PW] control to activate the PW mode in the preparation mode. First only the PW-cursor appears on the active 2D image. on page 8-4 To To start and use the PW mode: 'PW Operation' on page 8-6 adjust the PW settings: 'PW Sub Menu' This hard key is also the Gain control for the PW mode in scan mode...
- Page 180 Doppler Modes • The Steering function is only available with linear probes. 8.1.2 PW Operation The PW operations: • on page 8-4 'Gate Position and Gate Width' • on page 8-5 'Activation of PW Mode' • on page 8-5 'PW Gain Control' •...
- Page 181 Doppler Modes 8.1.2.2 Activation of PW Mode By pressing the left or right trackball key the screen is divided asymmetrically. The 2D image appears on top, below the PW spectrum starts running. Two display formats and three display sizes are possible. •...
- Page 182 Doppler Modes 8.1.2.5 Freeze The [Freeze] control starts and stops the 2D image and PW Doppler spectrum. 'To Freeze on page 4-9 an Image' 8.1.2.6 PW Cineloop The baseline can be shifted up in 8 steps or down in 8 steps. Several 2D image frames and the Doppler spectrum information can be recalled.
- Page 183 Doppler Modes Select the key [PW Sub]. The PW Submenu appears. Changes are only possible in scan mode! However, changes of the Gray Map, Tint Map, Scale Note Unit, Display Sizes, Angle and Baseline are also possible in freeze mode. The following functions are available: •...
-
Page 184: Continuous Wave Doppler Mode (Cw Mode)
Doppler Modes In scan and freeze mode it is possible to switch between PW menu, CF menu and the appendant Submenus to readjust the settings. 2. PW + 2D Mode + Power Mode (PD) In scan and freeze mode it is possible to switch between PW menu, PD menu and the appendant Submenus to readjust the settings. - Page 185 Doppler Modes Remarks: • Changing the Gain, Speed, CW-cursor position, CW-Focus, Wall Motion Filter and the PRF is not possible in freeze mode. 8.2.2 CW Operation The CW operations: • ‘Cursor Position and Focus’ on page 8‐10 • ‘Activation of CW Mode’ on page 8‐10 •...
- Page 186 Doppler Modes • ‘CW Cineloop’ on page 8‐11 8.2.2.1 Cursor Position and Focus In Continuous Wave Doppler, a specific area along the ultrasound beam is sampled. The location of the CW cursor can be changed with the trackball. The angle correction line on the CW cursor is also the depth marker for the focus.When changing the focal depth, you see the current value displayed in centimeters on the left side of the display in the image info.
- Page 187 Doppler Modes Press the control [S Sub]. The CW Submenu appears. Changes are only possible in scan mode! However, changes of the Gray Chroma Map, the Note angle and the baseline are also possible in freeze mode. The following functions are available: •...
-
Page 188: Color Flow Mode (Cfm)
Doppler Modes In scan mode it is possible to switch between CW menu, CFM menu and the Submenus to readjust the settings. 2. CW + 2D Mode + Power Mode (PD) In scan mode it is possible to switch between CW menu, PD menu and the Submenus to readjust the settings. - Page 189 Doppler Modes 8.3.1 CF Main Menu CF Mode key (hard key) Pressing the [CF] control activates the CF mode. The CF box appears in the active 2D image. To use the CF mode: See ‘CF Operation’ on page 8‐15 for more information.To adjust the CF settings: See ‘CF Sub Menu’...
- Page 190 Doppler Modes Probe Angle 1 Angle 2 Angle 3 linear probes Remarks: • Changing the Gain, Quality, Wall Motion Filter, PRF and 2D+2D/C is only possible in scan mode. • Beam steering is only possible with linear probes and in scan mode. 8.3.2 CF Operation The CF operations: •...
- Page 191 Doppler Modes 8.3.2.2 CF Gain Control CF Gain must be adjusted properly to ensure that continuous flow is displayed. CF Gain should be set as high as possible without displaying random Color speckle. If you set the CF Gain control too low, the lack of sensitivity will make it difficult to detect small abnormalities in flow and will possibly result in an underestimation of the large flow disturbances.
- Page 192 Doppler Modes Select the [Sub CF] key. The CF Submenu appears. The following functions are available: • ‘CF Map and Display Mode’ on page 8‐18 • 'Frequency' on page 8-36 • 'Flow Resolution' on page 8-34 • 'Scale' on page 8-39 •...
-
Page 193: Power Doppler Mode (Pd Mode)
Doppler Modes • 'Line Filter' on page 8-38 • 'Utilities' on page 13-2 and 'Gray Map' on page 6-22 8.3.3.1 CF Map and Display Mode This function allows selection of the color-coding for the blood flow display (similar to the post- processing curves with gray scale 2D). - Page 194 Doppler Modes with slow flows can be seen (e.g. kidney, liver, prostate, etc.). This new technique is not intended to replace established sonographic techniques, but to complete them especially in the above-mentioned fields. Advantages when compared to Color-Doppler: • less dependent on the incident angle •...
- Page 195 Doppler Modes The “PD Main” menu appears on the Main Window (scan mode). Example: PD Main/Sub menu window Example: PD Main/Sub Rotraries Once HD-Flow has been activated, it is automatically activated each time the PD hardkey is Note pressed, until the user switches to PD again by using the PD hardkey. Remarks: •...
- Page 196 Doppler Modes 8.4.2.1 PD Box Position and PD Box Size In 2D imaging, the relations between 2D frame rate, line density, and sector width were detailed to show how these three factors can be used to obtain optimal 2D images. A similar relationship exists in Power-Doppler imaging.
- Page 197 Doppler Modes 8.4.3 PD Sub Menu The “PD Main” menu has to be active. Select the [PD Sub] key. The PD Submenu appears.Changes are only possible n scan mode. Only changes in the Gray Chroma Map and PD Map are possible in freeze mode. Following functions are available: •...
- Page 198 Doppler Modes • 'Gray Map' on page 6-22 • 'Utilities' on page 13-2 8.4.3.1 PD Map This function allows selection of the color coding for an optimized view of blood flow (similar to the post-processing curves with gray scale 2D-scans). It is useful especially with low flow rates.
-
Page 199: Hd-Flow Mode (Bi-Directional Angio Mode)
Doppler Modes In scan mode it is possible to switch between PD menu, CW menu and the Submenus to readjust the settings. 8.5 HD-Flow Mode (Bi-directional Angio Mode) Directional Power Doppler (HD-Flow) is a Power Doppler mode incorporating the flow direction (much like Color Doppler) into the displayed image. - Page 200 Doppler Modes Example: HDF Main/Sub menu window Example: HDF Rotaries Remarks: • Changing the Gain, Quality, WMF, PRF, Steering and 2D+2D/HDF is only possible in scan mode! • Beam steering is only possible with linear probe and in scan mode. 8.5.2 HD-Flow Operation The HD-Flow operations: •...
- Page 201 Doppler Modes • 'Wall Motion Filter (WMF)' on page 8-41 • 'Velocity Range (PRF)' on page 8-40 • '2D + 2D/HDF' on page 8-25 8.5.2.1 HD-Flow Box Position and HD-Flow Box Size In 2D imaging, the relations between 2D frame rate, line density, and sector width were detailed to show how these three factors can be used to obtain optimal 2D images.
- Page 202 Doppler Modes 8.5.3 HD-Flow Sub Menu The “HD-Flow Main” menu has to be active. Select the [HD-Flow Sub] key. The HD-Flow Submenu appears. Note Changes are only possible in scan mode. Changes in the HDF Map, Balance, Scale and Threshold are also possible in freeze mode. 8.5.3.1 HDF Map This function allows selection of the color coding for an optimization of the display of blood flow (similar to the post-processing curves with gray scale 2D-scans).
-
Page 203: Tissue Doppler Mode (Td Mode )
Doppler Modes HDF Map 5 HDF Map 6 HDF Map 7 HDF Map 8 cyan pink white yellow dark blue dark red dark grey dark red dark blue dark red dark grey dark red cyan Pink white yellow Strong echo: lighter hue (high brightness) Weak echo : darker hue (low brightness) Selection of a HD-Flow Map curve: Select the [HDF Map] key and select the HDF Map curve by selecting key 1 to 8. - Page 204 Doppler Modes The Tissue-Doppler captures low flow but high amplitude signals associated with wall motion and creates a color-coded tissue image. The TD mode is subdivided in two groups: on page 8-28 To adjust TD settings: 'TD Sub Menu' on To use the TD mode: 'TD Main Menu' page 8-30 To use special utilities: 'Utilities'...
- Page 205 Doppler Modes • Changing the Gain, Quality, PRF and 2D +2D/TD is only possible in scan mode. • The [TD] control is only visible if the selected probe is capable of the Tissue mode. 8.6.2 TD Operation The TD operations: •...
- Page 206 Doppler Modes [CF Mode] keyadjusts the TD Gain. When the GAIN control is turned clockwise the Color gets more intense. When the GAIN control is turned counterclockwise the Color gets less intense. 8.6.2.3 2D + 2D/TD The “2D+2D/TD” function changes the single image display to two simultaneous half frames. The left frame shows only the 2D mode image.
-
Page 207: Doppler Mode Functions And Filters
Doppler Modes • 'Flow Resolution' on page 8-34 • 'Scale' on page 8-39 • 'Balance' on page 8-32 • on page 8-39 'Smoothing' • on page 8-33 'Ensemble' • on page 8-37 'Line Density' • on page 8-33 'Baseline' • on page 8-38 'Line Filter' •... - Page 208 Doppler Modes • Adjusting the angle is always possible, in scan mode and freeze mode. 8.7.2 Artifact Suppression HD-Flow Artefact suppression reduces of movement artefacts in the image. For cardiac application it is recommended to switch off the artefact suppression. Switch on/off the artefact suppression in the Map section of the Submenu.
- Page 209 Doppler Modes Where the balance orientation line is on a gray step, the gray value will be displayed (only if a color value is present. For example: If the gray value is higher than 96 while a color value is present, the gray value will be displayed.
- Page 210 Doppler Modes 8.7.7.1 Ensemble for TD Select +/- on the [Ensemble] key and select the number of pulses per color line. max. value: 31 min. value: 3 step size: 1 8.7.8 Flow Resolution HD-Flow This function controls the axial resolution of color in the display. It adjusts the axial sample depth of color pixels.
- Page 211 Doppler Modes 8.7.10 Format HD-Flow The keys serve for selection of either one of two formats (Horizontal or Vertical) for display. Voluson® S6/S8 Basic User Manual 5433669-100 Revision 4 8-35...
- Page 212 Doppler Modes 8.7.11 Frequency HD-Flow The frequency setting controls the Transmit Frequency. It is common to work with the center frequency [Frequ. Mid] of the ultrasound crystal. With a higher Transmit Frequency [Frequ. High] lower flow velocities are displayed at a given PRF (advantage: better display of lower flow velocities), but the penetration depth is reduced.
- Page 213 Doppler Modes 8.7.12 Gently Colors HD-Flow Gently Color defines the transition between color and gray scale information. With [Gently Color] the embedding of the color into 2D mode is performed smoothly with less color flash. Switch on/off the Gently Color function. 8.7.13 Invert HD-Flow This function inverts the spectrum display in relation to the direction of flow.
- Page 214 Doppler Modes 8.7.15 Line Filter HD-Flow Especially the lateral resolution can be optimized with this correlation algorithm. With this process, the signals of neighboring pulses are less weighted for the image which improves detail resolution and signal-to-noise ratio. Eight steps are provided. Select the [Line F.] key and select the filtering.
- Page 215 Doppler Modes 3. Select the sensitivity of the envelope curve (to eliminate artefacts). Important note: The determination of the envelope curve requires a clear and low-noise recording of the Doppler spectrum. Otherwise, the reliability of the displayed measurement results may not be ensured! Remarks: Activating the Real Time Trace is only possible in scan mode.
- Page 216 Doppler Modes Select +/- on the [Smooth Fall] key to select the fall filter. FALL: This filter leads to prolongation of the displayed flow. Usage with quick pulses (short "color flashes") prolongates them for better evaluation on the monitor. Select +/- on the [Smooth Rise] key to select the rise filter. RISE: Filtering of the rise velocity leads to noise suppression.
- Page 217 Doppler Modes flow within the vessel to portray flow in the wrong direction. The disadvantage of using a higher PRF is a loss of sensitivity to low flow velocities. Use the [PRF] control to adjust the velocity range. Selecting up - increases the PRF Selecting down - decreases the PRF If a selected PRF is unavailable for the selected depth the PRF will be automatically reduced.
- Page 218 Doppler Modes • The Wall Motion Filter is user-selectable but the actual cutoff frequencies vary depending on the [PRF] control setting. • The WMF-filter is calculated automatically and adjusted when the PRF is changed. 8.7.23.1 WMF for PW A Wall Motion Filter is used to eliminate Doppler “noise” that is caused by vessel wall or cardiac wall motion which is low in frequency but high in intensity.
-
Page 219: Chapter 9 - Volume Mode
Chapter 9 Volume Mode Describes the general functions of the Volume Mode. Image quality is the essential performance of the system. Please read this chapter carefully. Voluson® S6/S8 Basic User Manual 5433669-100 Revision 4... -
Page 220: Volume Acquisition With Volume Probes
Volume Mode General Description The Volume mode allows for scanning a tissue volume and subsequent analysis of sections of the volume in 3 dimensions. The liberal selection of sections within the volume and the simultaneous real-time 4D display of three orthogonal planes and a rendered 3D image represents a new dimension for e.g., the diagnosis of fetal abnormalities. - Page 221 Volume Mode Depending on what button you pressed before either the “3D Mode” menu or the 4D Mode menu appears on the menu area (scan mode). 3D Mode Screen(scan) 4D Mode Screen(scan) Voluson® S6/S8 Basic User Manual 5433669-100 Revision 4...
- Page 222 Volume Mode Select your settings. Then acquire a volume. After you have acquired the volume, the following menus will be displayed on the menu area: 3D menu (after Volume Acquisition) Voluson® S6/S8 Basic User Manual 5433669-100 Revision 4...
- Page 223 Volume Mode There are different possibilities for a 3D-Volume Acquisition, see: • on page 9-16 'Volume Acquisition: Static 3D Sectional Planes' • on page 9-48 'Volume Acquisition: Static 3D Render' 4D menu (after Volume Acquisition) Voluson® S6/S8 Basic User Manual 5433669-100 Revision 4...
- Page 224 Volume Mode There are different possibilities for a 4D-Volume Acquisition, see: • on page 9-78 'Real Time 4D Acquisition' • on page 9-99 'Volume Contrast Imaging: (VCI A-Plane)' • on page 9-102 'VCI-Omniview' • Upon [Freeze] a certain number of volumes will be stored in the cine memory. The sequence can be reviewed volume by volume.
- Page 225 Volume Mode represents the central 2D scan of the volume. The volume scan itself sweeps from one margin to the other margin of the volume to be acquired. 1. Central 2D scan 2. Start 2D scan 3. Range of VOL sweep The VOL BOX frames the Region of Interest (ROI) which will be stored during the volume sweep.
- Page 226 Volume Mode 9.1.3.1 What is Interactive? Interactive means that every operation/adjustment concerning the result of the rendering process can be followed in real time. The fast hardware and intelligent software enables calculation in real time rendered pictures. After an operation step the result is rendered with a lower resolution in order to speed up the interactive feedback, and when no further operation takes place the result is rendered in high resolution.
- Page 227 Volume Mode B image orientation: down -> up Resulting orientation of sectional planes (freeze mode). Voluson® S6/S8 Basic User Manual 5433669-100 Revision 4...
- Page 228 Volume Mode 9.1.5 Orientationhelp for 3D/4D data sets (Probe Orientation) In order to simplify orientation in a 3D or 4D data set the user can activate the display of directions like cranial, caudal, left, right, anterior, posterior at the border of the 3D or 4D data set.
- Page 229 Volume Mode Select the [More...] key at the top right corner of the menu area. The “3D/4D Sub Menu” appears. Select the [Probe Orientation] key to activate the Probe Orientation menu. The Probe Orientation menu appears and the system automatically switches to Quad-Screen display: Voluson®...
- Page 230 Volume Mode The lower right quadrant displays the body pattern and the probe marker, independent of the selected visualization mode. Position of body pattern (body view and body rotation) and probe marker are stored in the 3D/4D user program. Voluson® S6/S8 Basic User Manual 9-12 5433669-100 Revision 4...
- Page 231 Volume Mode The green point on the probe marker indicates the rotation of the probe (like Voluson® S6/S8- Logo on 2D image). Select this key to display the body pattern from front. The body pattern can be rotated in steps of 45˚. Select this key to display the body pattern from behind.
- Page 232 Volume Mode Following orientation markers are available: Anterior Posterior Left Right Cranial Caudal There are also combinations thereof possible e.g.: AL, PRCa etc. The orientation marks are visible if slices are present in T.U.I. mode (not in Render Full- Note Screen).
- Page 233 Volume Mode For more information see 'Render View Direction' on page 9-45. 9.1.7 General Advices to Obtain Good Rendered 3D Images B MODE • Poor quality of the volume scan will lead to a poor quality 3D image. • For a good 3D image quality, adjust high contrast in 2D mode of the interesting structures before starting the volume scan.
-
Page 234: Volume Acquisition: Static 3D Sectional Planes
Volume Mode • Smoothing Filter (Rise and Fall in 2D image) leads to smoother flow and a good color 3D display of vessels (e.g., filtering of high pulsatile vessels). Disadvantage: The higher the filter setting, the longer the acquisition time. •... - Page 235 Volume Mode 2. Select a 3D user setting (e.g., Default). The preset values are loaded. 3. Select [Render] or [Sectional Planes] 4. Select the display format desired. Note The selected format will be present in freeze mode after the acquisition is done. 5.
- Page 236 Volume Mode Press the upper trackball key to change the function of the trackball from position to size or vice versa. 6. Change the size of the Volume box by moving the trackball. Moving: ↑ decrease the box size in vertical direction ↓...
- Page 237 Volume Mode 9.2.1 3D Acquisition During Active High Resolution Zoom 1. Press the [Zoom] button, while still in 2D. 2. Place the zoom box over the region of interest The trackball has 2 functions: adjusting position and size of the zoom box. The activated function is displayed in the status bar area on the monitor.
- Page 238 Volume Mode 6. Press the [2D] button again to exit the High Resolution Zoom function. 9.2.2 During 3D Acquisition The system displays only the volume box area during the acquisition of a 3D Volume. After acquisition the system changes to freeze mode: 'After the Static 3D Sectional Planes on page 9-21 Acquisition' 1.
- Page 239 Volume Mode The acquisition stops and the “3D or 4D Mode” menu appears again. The recorded information will be deleted, except if more than 50% of the volume have already Note been acquired. 9.2.3 After the Static 3D Sectional Planes Acquisition After the 3D Sectional Planes acquisition the system automati-cally changes to the 3D menu.
- Page 240 Volume Mode Visualization modes: • on page 9-24 'Principle of Sectional Image Analysis' • on page 9-51 'After the Static 3D Render Acquisition' • 'After the Static 3D Sectional Planes Acquisition' on page 9-21 • 'VOCALII' on page 9-116 • 'Principle of Sectional Image Analysis' on page 9-24 •...
- Page 241 Volume Mode The orientation help image is only displayed in the lower right quadrant in Sectional Planes mode. To activate or deactivate the O.H. Graphic select the [Orient Help] key in the Sectional Planes mode. The help image figure shows the intersections of a plane within the volume body by lines as a section plane.
- Page 242 Volume Mode 9.2.3.4 Image Position By this function the position of a reference image A, B or C in relation to the display field is determined. First, press the ROI button, below the trackball. Press the upper trackball key to change the function from axis position to image position. By means of the trackball the reference image is shifted and positioned in X- and Y-direction, respectively.
- Page 243 Volume Mode 1. Display plane 3. Resultant image of plane within volume 2. Volume Center plane 4. Displacement Rotation of the volume body in relation to the display plane: The rotation can be around the X-axis or the Y-axis of the display plane, or the Z-axis which is perpendicular to the display plane.
- Page 244 Volume Mode non-conformance with the conventional customized orientation to the patient in 2D- sonography. An identification system - the automatic display of the direction of section - will clarify. Please note: Whenever a usual longitudinal section (of the patient) is selected for display field A, the usual orientation for longitudinal and transverse sections is valid.
- Page 245 Volume Mode By the clockwise rotation of the volume body in relation to the screen plane (as shown) the new sectional planes are calculated in real time and displayed on screen. For rotation around the Z-axis of a reference image (e.g. A): turn the [Z] rotary control clockwise: By rotation of the volume body in relation to the screen plane (as shown) the new sectional planes are calculated in real time and displayed on screen.
- Page 246 Volume Mode • Reference image e.g., A: X-axis: A ´ C Y-axis: A ´ B Z-axis: B ´ C • Before performing a rotation, position the center of rotation in the area of the image that you want to keep. 9.2.4.2 Translation The translation allows a displacement of the center of rotation along the intersection lines of the sectional planes A, B and C.
- Page 247 Volume Mode The center of rotation can be X/Y-positioned by the trackball. This causes also a parallel displacement of those planes presented by the non-reference images. The intersection line of the non-reference images with the reference image will undergo a parallel X or Y shift accordingly.
- Page 248 Volume Mode Directions: A - anterior (ventral) P - posterior (dorsal) Cr - cranial Ca - caudal R - right L - left Voluson® S6/S8 Basic User Manual 9-30 5433669-100 Revision 4...
- Page 249 Volume Mode Init condition of an abdominal probe: If the VOL-start image is a longitudinal section (Cr on the left of the screen below), the following Init positions are obtained: The sectional image A represents that 2D image A - anterior (ventral) ; P - posterior (dorsal) Cr - visible in the Vol preparation area.
- Page 250 Volume Mode Init condition of an small parts probe: If the VOL-start image is a longitudinal section (Cr on the left of the screen below), the following Init positions are obtained: The sectional image A represents that 2D image A - anterior (ventral) ; P - posterior (dorsal) Cr - visible in the Vol preparation area.
- Page 251 Volume Mode Init condition of an endocavity probe: If the VOL-start image is a median-sagittal section (left side of the screen is posterior), the following Init positions are obtained: The sectional image A represents that 2D image A - anterior (ventral) ; P - posterior (dorsal) Cr - visible in the Vol preparation area.
- Page 252 Volume Mode B: Positioning the Longitudinal Section Positioning the Transverse Positioning the Horizontal Section Section The sectional image A represents that 2D image visible in the Vol preparation area. If the VOL-start image is a transverse section of the prostate (right side of the patient is left side of the screen), the following Init positions are obtained: Monitor Display: 9.2.4.5 A,B,C - Sectional Plane Mode...
- Page 253 Volume Mode Pressing the [Single] screen format key will magnify x2 and display the reference image A, B or C. For the REF image plane selection the same rules as for sectional planes mode apply. The graphic display of the orientation help is not possible. 9.2.4.7 Niche Display Mode Parts of the orthogonal sections A, B and C are compiled to a 3D-section aspect.
- Page 254 Volume Mode 2. The Niche display mode appears on the monitor. 3. Select the reference image A, B or C by using left trackball key. The selected reference image is marked green. Voluson® S6/S8 Basic User Manual 9-36 5433669-100 Revision 4...
- Page 255 Volume Mode 4. Set the view direction for the niche mode. Use the [Niche Y-Rot] control to rotate around the Y-axis. Use the [Niche X-Rot] control to rotate around the X-axis. Voluson® S6/S8 Basic User Manual 5433669-100 Revision 4 9-37...
- Page 256 Volume Mode 5. Position the images in the niche mode display with the trackball. 6. Use the upper trackball key to change the function of the trackball from image position to axis position. Remarks: • Use the [Single] screen format key and the [Quad] screen format key to change from full to quad Niche display and vice versa.
- Page 257 Volume Mode 1. Select this key to display the “VCI Static” menu on the menu area. 9.2.5 Tomographic Ultrasound Imaging – TUI (Parallel Slices) Tomographic Ultrasound Imaging is an option. If this option is not installed, the [TUI] key is Note hidden.
- Page 258 Volume Mode Press the upper trackball key to change the function of the trackball from image position to axis position or vice versa. The activated function is displayed in the status bar area on the monitor. Add/Reduce number of slices and the distance between slices with digipots below the menu area.
- Page 259 Volume Mode 3. Select this key to select the number of slices displayed. on page 9-98 4. Select this key to display the “4D Volume Cine” menu. 'Volume Cine' Select this key to return into the initial position. 6. Select this key to select the reference image plane. The display on the monitor changes accordingly.
- Page 260 Volume Mode Select this key to select the number of slices displayed. Next/Previous plane is moved into view. Shift plane inside display area. Add/Reduce number of planes on the right and/or on the left side of the reference image and the adjust the distance between slices (29 possible slices) with buttons below the menu area.
-
Page 261: Sub Menus
Volume Mode Select this key to exit the “T.U.I. Adjust Slices” menu. Remarks: If VCI Static, which is a visualization mode, was engaged before entering T.U.I., the slices are displayed with VCI rendering,. The VCI settings cannot be changed in T.U.I. visualization mode. - Page 262 Volume Mode Remarks: • The Render View Direction keys are not available in Static 3D Sectional Planes mode. • The additional Sub Menu functions are not available in Static 3D Sectional Planes mode. • These keys are only available if a 3D+CFM, 3D+PD or a 3D+HD-Flow volume is acquired.
- Page 263 Volume Mode • '3D Gray Chroma Map' on page 9-47 • 'Tint Map' on page 6-23 • 'Contrast' on page 9-47 • on page 9-47 'Background' • on page 9-47 'Balance' • on page 9-48 'Power Threshold' 9.3.1 Render View Direction The 3D render box determines the ROI (region of interest) for the 3D calculation and determines the direction of view through the volume block.
- Page 264 Volume Mode Note If the volume was compressed using lossy image, a yellow Wxx”, where xx stands for the compression quality (e.g. 90) is displayed beneath the type line (e.g. 3D Static) A lossy compression can reduce image quality, which can lead to a false diagnosis! on page 13-30 'Connectivity' 9.3.3 3D Color Off...
- Page 265 Volume Mode 9.3.5 3D Gray Chroma Map 1. Select the [Gray 3D] key. 2. Select either a predefined Gray Curve (1-18). Note These settings require an alert observation of the influence on the 3D image! 3. With the Background function, the contrast between screen background and 2D image is set.
-
Page 266: Volume Acquisition: Static 3D Render
Volume Mode 9.3.9 Power Threshold This function eliminates low color noise of motion artefact signals in the sectional slices as well as in the rendered 3D image. A lower number cuts off fewer signals than a higher number. This key is only available if a 3D+CFM, 3D+PD or a 3D+HD image is acquired. Note 9.4 Volume Acquisition: Static 3D Render 1. - Page 267 Volume Mode 3. Select the display format desired. The selected format will be present in freeze mode after the acquisition is done. Note 4. Place the Volume box over the region of interest. The trackball has 2 functions: position and size of the Volume box. The activated function is displayed in the status bar area on the monitor.
- Page 268 Volume Mode low: Fast speed / low scan density This mode is selected only in case of expected movement artefacts. A loss of volume resolution will result. mid 2: Standard VOL scan / medium scan density max: Slow speed / high scan density 8.
- Page 269 Volume Mode 9. Select the [Render] key. Condition to activate 3D Image Rendering: 1. A “Static 3D Sectional Plane” volume scan is performed and in freeze mode. In the “3D/4D Mode” menu you can change to different “Visualization” modes. 2. A volume scan is performed with “Static 3D Rendering”. 9.4.1 After the Static 3D Render Acquisition After the 3D acquisition, the system switches automatically to the 3D menu.
- Page 270 Volume Mode Note: If you want to return to the “3D/4D Volume Mode” menu press the right trackball key (Vol pre displayed in the status bar area on the monitor). Display of the rendered image: • on page 9-52 '3D ROI (Edit ROI) Mode' •...
- Page 271 Volume Mode [Single] screen format key illuminated. The rendered 3D image is magnified and displayed in a full-size format without the sectional planes A, B, and C. 9.4.1.2 Adjust Position, Size and Curvature of the Render Box The reference image selector will only be displayed if quad screen display is selected. Note 1.
- Page 272 Volume Mode The magnification of the entire 3D image without changing the contents of the box is only Note possible in 3D Pictogram (Accept ROI) Mode (chapter '3D Pictogram (Accept ROI) Mode' on page 9-54 ). 8. The Rotation controls rotate the contents of the box relative to the render box. Important: With the rotation controls the direction of view of the 3D image is selected.
- Page 273 Volume Mode Rotation around Y-axis Rotation around Z-axis Adjust the magnification of the rendered 3D image The 3D image as well as the sectional image can be varied by their aspect ratio by turning the [Zoom] control. Select a reference image A, B, C or 3D by using trackball The selected reference image is sectional plane A: The spatial position of plane A in relationship to the displayed 3D image is...
- Page 274 Volume Mode The position of image B and C in relationship to the reference image A is determined through the Y-axis (= intersection line for image B) and through the X-axis (= intersection line for image C). By positioning these two axes within the reference image the corresponding parallel planes of B- and C-images are displayed automatically.
- Page 275 Volume Mode Parallel shift control [Parallel shift] enables a parallel shifting (forward/backward) of plane C. The depth position of the image C in relationship to the Z-direction (perpendicular to the display) of the 3D image is indicated by the X-axis in image A and B. Adjust the position of image A and B with trackball The position of image A and B in relationship to the reference image C is determined through the Y-axis (= intersection line for image A) and through the X-axis (= intersection line for...
- Page 276 Volume Mode Select the appropriate button for the cine you prefer. Not all kinds of cine are available in all visualization modes, see table below. Note The following table shows the dependences 3D Rot. Cine 3D Transl. Cine Slice Cine Full View Quad View Full View...
- Page 277 Volume Mode Note that 3D Translational Cine and Slice Cine can be displayed either in Quad Screen Mode or in Full Screen Mode. To switch between the Modes use the hardkeys on the UI while the settings screen appears on the menu area. 9.4.2.1 3D Rotational Cine 3D rotation cine is the rotation of a volume around either X orY axis.
- Page 278 Volume Mode Select the Rotation Angle Alternatively use the [Start Image] and [End Image] control below the menu area to select the rotation angle desired. Select the step angle. Voluson® S6/S8 Basic User Manual 9-60 5433669-100 Revision 4...
- Page 279 Volume Mode The increment defines the amount of rotation between adjoining 3D images. Select the rotation axis. Select between X and Y rotation of the 3D Rotation Cine sequence. Start the calculation of the cine sequence. 9.4.2.2 3D Translational Cine A render box is moved in a translational movement through a volume.
- Page 280 Volume Mode Operation: Press the [3D Transl. Cine] key The settings screen appears on the menu area: Voluson® S6/S8 Basic User Manual 9-62 5433669-100 Revision 4...
- Page 281 Volume Mode Use the [Start Image] and [End Image] control below the menu area to select the starting point and endpoint desired. When you select the first image (either start image or end image) the lines denoting the images will be linked, when you select the second image the lines will be unlinked.
- Page 282 Volume Mode Operation: Press the [3D Slice Cine] key. The settings screen appears on the menu area: Voluson® S6/S8 Basic User Manual 9-64 5433669-100 Revision 4...
- Page 283 Volume Mode Use the [Start Image] and [End Image] control below the menu area to select the starting point and endpoint desired. When you select the first image (either start image or end image) the lines denoting the images will be linked, when you select the second image the lines will be unlinked.
- Page 284 Volume Mode Select of the [Break Cine calculation] key to stop the calculation. The images that have been calculated before the calculation has been stopped are displayed as a sequence. 9.4.2.5 During Display of a Cine If a Cine sequence is in the cine memory, the following menu appears: Voluson®...
- Page 285 Volume Mode The kind of cine is displayed in the first line: e.g. 3D Rot. Cine Select this key to start or stop the display of 3D cine sequence. Replay Mode Shows the sequence back and forth. Shows the sequence in an endless loop from start to end. Select the speed of the Cine sequence The speed of sequencing through the number of images can be varied between 6%, 12%, 25%, 50%, 100%, 200%, and 400%.
- Page 286 Volume Mode The 3D image magnification can be varied by turning the [Zoom] control. Select the render modes Choose between two render modes: Skin Surface or Smooth Selection of single images After selecting the [Start/Stop] key move the trackball horizontally and you can select each single image step by step.
- Page 287 Volume Mode • Press [Yes] and the menu changes to the Cine Calculation menu, from where you on page 9-57 proceed as described in 'Cine Calculation' 9.4.3 MagiCut This software has the ability to electronically edit the images, and makes it possible to cut away structures obstructing the view onto the ROI.
- Page 288 Volume Mode 2. Use the controls to rotate the rendered 3D image to a position where 3D artefacts or undesired information can be cut. For faster rotation press on the rotation control (switch function: slow rotation, fast rotation). Note 3. Select the “Cut Mode” and set the region of interest to be cut •...
- Page 289 Volume Mode Trace Inside: Structures within the contour will be discarded. Trace Outside: Structures outside the contour will be discarded. Use the trackball for tracing. Position the first point, enter it with right or left trackball key [SET] and move the cross along the desired trace, indicated by a red line. Press the right or left trackball key [SET] again.
- Page 290 Volume Mode Press the right or left trackball key [Done]. The region underneath the trace will be cut from the 3D rendered image. 6. Perform the next cut Rotate rendered image to another position and continue with points 2. to 4. again. 7.
- Page 291 Volume Mode 1. Select the [Render Mode] key. The following menu appears on the manu area. (chapter 'Gray Render Mode' on page 9-73 ) Color 2. Select image type among: Gray (chapter 'Color Render Mode' on page 9-75 ) Glass Body (chapter 'Glass Body Render on page 9-76 ) Inversion (chapter 'Inversion Render Mode' on page 9-77 ) Mode' 3.
- Page 292 Volume Mode Select the render algorithm desired: Surface Texture: A surface will be displayed in “texture” mode. The gray values of the Texture: surface are identical with the gray values of the original scan. Light: Light A surface will be displayed in “light” mode. Structures close to the viewer are displayed bright;...
- Page 293 Volume Mode Application: With this function small echoes or noise is removed, to have a “clear sight” from the start border of the render box to the desired Surface. 9.4.4.1.2 Transparency in Gray Render Mode small number = low transparency A higher number makes the gray scale information more transparent.
- Page 294 Volume Mode 9.4.4.2.1 Threshold Control in Color Render Mode In case Surface mode is selected, it will normally be necessary to adjust the low threshold for the border recognition of the surface. These threshold values do not apply for the Transparent modes! Threshold low (Reject): Normally this threshold always has to be adjusted properly for a good appearance of the 3D surface image.
- Page 295 Volume Mode In case Surface mode is selected, it will normally be necessary to adjust the low threshold for the border recognition of the surface. These threshold values do not apply for the Transparent modes! For adjustment of Threshold low and Transparency, review Color Render mode: •...
-
Page 296: Real Time 4D Acquisition
Volume Mode If the measurement function is activated in Render mode, the symbol appears. This symbol reminds the user that UNINTENDED USE of this feature could lead to measurement inaccuracy. For more information see 'Measurement Accuracy of the System' on page 11-23. This symbol will also be shown on the patient report (in the report header), if the performed Render Mode measurements are stored in the report. - Page 297 Volume Mode 2. Select a 4D user setting (e.g., Default). The preset values are loaded. 3. Select the display format desired. The selected format will be present in freeze mode after the Real Time 4D acquisition is done. Note The [Dual] screen format key is only available in Real Time 4D Render mode! 4.
- Page 298 Volume Mode Press the upper trackball key to change the function of the trackball from position to size or vice versa. 5. Change the size of the Volume box by moving the trackball. Moving: ↑ decrease the box size in vertical direction ↓...
- Page 299 Volume Mode 10. Select the [Render], [Sectional Planes] or [TUI] key. 9.5.1 Possible Display Adjustment before a Real Time 4D Acquisition (chapter 'Real Time 4D Acquisition During Active Display of Sectional Planes on page 9-82 ) High Resolution Zoom' (chapter 'Real Time 4D Acquisition During Active High Display of REF -Image on page 9-82 ) Resolution Zoom'...
- Page 300 Volume Mode 9.5.2 Real Time 4D Acquisition During Active High Resolution Zoom 1. Press the [Zoom] control, while still in 2D. 2. Place the zoom box over the region of interest. The trackball has two functions: adjusting position and size of the zoom box. The activated function is displayed in the status bar area on the monitor.
- Page 301 Volume Mode 7. Press the right trackball key to start volume acquisition. Remarks: • Real Time 4D Acquisition is not possible in PD-, HD- and CFM mode. Turn the [Zoom] control to adjust magnification. Press the [Zoom] control to return to the default value.
- Page 302 Volume Mode on page 9-92 To use the controls during the Real Time 4D acquisition: '4D Controls' 9.5.2.2 Display of REF-Image In continuous 4D volume acquisition, it is possible to display the reference sectional plane in full screen format. Voluson® S6/S8 Basic User Manual 9-84 5433669-100 Revision 4...
- Page 303 Volume Mode The monitor displays only the REF image plane during a Real Time 4D. on page 9-92 To use the controls during the Real Time 4D acquisition: '4D Controls' Voluson® S6/S8 Basic User Manual 5433669-100 Revision 4 9-85...
- Page 304 Volume Mode 9.5.2.3 Display of ROI 4D Continuous volume sweep (Real Time 4D) Quad display of a rendered 3D image + sectional planes The monitor displays the ROI and 4D image during acquisition of Real Time 4D. Voluson® S6/S8 Basic User Manual 9-86 5433669-100 Revision 4...
- Page 305 Volume Mode on page 9-92 To use the controls during the Real Time 4D acquisition: '4D Controls' 9.5.2.4 Display of 4D Continuous volume sweep (Real Time 4D) Full size display of a rendered image The monitor displays only the 4D image during the acquisition of Real Time 4D. Voluson®...
- Page 306 Volume Mode on page 9-92 To use the controls during the Real Time 4D acquisition: '4D Controls' 9.5.2.5 Display of A-ROI 4D Continuous volume sweep (Real Time 4D) Dual display of a rendered image + reference image A. Voluson® S6/S8 Basic User Manual 9-88 5433669-100 Revision 4...
- Page 307 Volume Mode The monitor displays the REF and 4D image during acquisition of Real Time 4D. on page 9-92 To use the controls during the Real Time 4D acquisition: '4D Controls' Voluson® S6/S8 Basic User Manual 5433669-100 Revision 4 9-89...
- Page 308 Volume Mode 9.5.2.5.1 4D ROI (Edit ROI) Mode This is the mode for the adjustment of the volume render box. The volume render box determines the ROI for the 4D calculation which is inserted in the orthogonal planes A, B, C. The rendering result is displayed in the lower right quadrant.
- Page 309 Volume Mode 9.5.3.1 MagiCut 4D Operation 1. Select the [MagiCut] key to switch on the MagiCut function. The following menu appears on the menu area. 2. Use the controls to rotate the rendered 4D image to a position where 4D artefacts or undesired information can be cut.
- Page 310 Volume Mode 9.5.4 4D Controls 9.5.4.1 Available Controls before the acquisition Note: To return to the “4D Mode” menu, press the right trackball key (Volpre displayed in the status bar on the monitor). Image Position, Size of the Volume box and Curved render start The trackball has 3 functions.
- Page 311 Volume Mode For Example: To produce a better, smoothed surface by mixing surface smooth and light mode. Set the Threshold low (Reject) Normally this threshold must always be adjusted for a good appearance of the 3D surface image. By changing the threshold all echoes below the level are enhanced in pink color for a certain interval.
-
Page 312: Sono Render Start
Volume Mode If the [ROI] key is highlighted, you have to press [Curve] key first and then [Reset]. Note Select the Init position Select the [More...] key at the top right corner of the menu area. The “3D/4D Sub Menu” appears This key resets the rotations of a volume section to the initial (start) position. -
Page 313: Volume Cine
Volume Mode If no valid render start area can be found following message appears: No valid Sono Render start found. 9.7 Volume Cine The 4D VolCine function allows the user to save and work with the acquired Volumes. Depending on the memory and volume size up to 128 volumes can be displayed. The advantage of working with 4D VolCine is that during the acquisition the user can concentrate on the acquisition itself. - Page 314 Volume Mode Upon [Freeze] a certain number of volumes will be stored in the cine memory. The sequence can be reviewed volume by volume. To Display Auto Cine Select this key to display the “4D Volume Cine” menu. To review the Volume Cine Sequence: on page 9-98 'Volume Cine' Voluson®...
- Page 315 Volume Mode Press the left trackball key to Start / Stop the stored cine sequence. Move the trackball to display the volumes of the stored sequence one by one. Alternatively use the [Vol Cine #] control to select the desired volume. The selected Volume number will be displayed also in the monitor’s status bar area.
- Page 316 Volume Mode Use the [X], [Y] and [Z] mode controls to rotate around the X-, Y- and Z-axis. Use the [Parallel Shift] mode control to shift along the Z-axis. For further controls and possible adjustments: '4D Controls' on page 9-92 9.7.1 Volume Cine 1.
-
Page 317: Volume Contrast Imaging: (Vci A-Plane)
Volume Mode By selecting [Exit] the menu area changes to the “Vol. Cine” menu. 9.8 Volume Contrast Imaging: (VCI A-Plane) Volume Contrast Imaging is an option. If this option is not installed, the [VCI A-Plane] key is Note hidden. By setting a small volume sweep angle you scan a limited number of slices with a relatively high volume rate. - Page 318 Volume Mode 3. Select a VCI-A user setting (e.g., Default). The preset values are loaded. 4. Select the “Slice Thickness” by selecting one of the keys on the menu area. Note The actual values for slice thickness may vary from probe to probe. 5.
- Page 319 Volume Mode The trackball has two functions: position and size of the Volume box. The activated function is displayed in status bar area on the monitor. Press the upper trackball key to change the function of the trackball from position to size or vice versa.
-
Page 320: Vci-Omniview
Volume Mode 9.8.2 After the VCI-A Acquisition After [Freeze] the system switches automatically to freeze mode and the “Vol. Cine” menu appears. The selected format and the last acquired volume will be present on the monitor. Upon [Freeze] a certain number of volumes will be stored in the cine memory. The sequence on page 9-95 can be reviewed volume by volume. - Page 321 Volume Mode 3. Select the [VCI-OmniView] key. 4. Select a VCI-OmniView user setting (e.g., Default). The preset values are loaded. 5. Move the horizontal green dotted line with the trackball to the desired position of the ultrasound image on the screen. 6.
- Page 322 Volume Mode 8. Select the Quality. This function changes the line density against acquisition speed. low: Fast speed / low scan density (A loss of volume resolution will result) This mode is selected only in case of expected movement artefacts. mid: Standard VOL scan / medium scan density high:...
- Page 323 Volume Mode Use the left trackball key to start a new VCI line. Use the [Z] rotary control to rotate the VCI-Omni View position line (+/- 45º). on page 9-92 For further controls and possible adjustments, '4D Controls' 9.9.2 VCI-Omni View Curve Line To adjust the VCI-Omni View Curvature Line press the [Omni View Curve Line] button on the menu area.
- Page 324 Volume Mode Polyline: add multiple angles to the starting line of the renderbox. 9.9.3 After the VCI-Omni View Acquisition After [Freeze] the system switches automatically to freeze mode and the “Vol. Cine” menu appears. The selected format and the last acquired volume will be present on the monitor. Upon [Freeze] a certain number of volumes will be stored in the cine memory.
-
Page 325: Stic (Spatio-Temporal Image Correlation)
Volume Mode Press the Quad-screen-format button to activate Omni View Ref. Line view. Press the Dual-screen-format button to activate Omni View dual view. Press the Single-screen-format button to switch back to Omni View full format view. 9.10 STIC (Spatio-Temporal Image Correlation) General: STIC is an option. - Page 326 Volume Mode • Asynchronous movement in different parts of the image: e.g., the left part of the image is contracting and the right part is expanding at the same time. • The color does not fit the structures displayed in gray mode: The color is displayed above or below the actual vessel.
- Page 327 Volume Mode When using STIC CFM (2D+CFM), STIC PD (2D+PD) or STIC HD-Flow (2D+ HD-Flow) Note adjustment of the Color settings is possible. Adjustment “Use 2D Color for STIC: 'General' on page 13-15 For further details, review: ‘CF Sub Menu’ on page 8‐17 PD Sub Menu 'PD Sub on page 8-21 HD-Flow Sub Menu 'HD-Flow Sub Menu' on page 8-26 Menu' STIC can also be used with M-Mode,...
- Page 328 Volume Mode 7. Set the volume sweep angle by using the control below the menu area. 8. Select the Acquisition time. In order to archive a good result, try to adjust the volume box and the sweep angle to be as Note small as possible.
- Page 329 Volume Mode During the acquisition following message will be displayed on the menu area: The user must be sure that no one of the participating persons (mother, fetus, user) moves Note during the acquisition. A movement of anyone will cause a failure of the acquisition. Omni View Ref.
- Page 330 Volume Mode 9.10.2 After STIC Calculation After the calculation, the Estimated Heart Rate is shown on the menu area. The previously selected format and the last acquired 4D sequence will be shown on the monitor. Note Guidance and precautions for interpretation of STIC-images: •...
-
Page 331: Real Time 4D Biopsy
Volume Mode 9.10.2.1 Measurements in the STIC-image If the measurement function is activated in mode STIC, the symbol appears. This symbol reminds the user that UNINTENDED USE of this feature could lead to measurement chapter 'Measurement Accuracy of the System' on inaccuracy (below accuracy mentioned in page 11-23 ). - Page 332 Volume Mode 4. Select a 4D Biopsy user setting (e.g., Default). The preset values are loaded. 5. Select the desired “Biopsy Mode”:2D image + volume box are shown on the screen. (no biopsy line) 2D image + biopsy line + volume box are shown on the screen. 2D image + volume box are shown on the screen.
- Page 333 Volume Mode 7. Change the size of the Volume box by moving the trackball. Moving: ↑ decrease the box size in vertical direction ↓ increase the box size in vertical direction → increase the box size in horizontal direction ← decrease the box size in horizontal direction 8.
-
Page 334: Vocalii
Volume Mode 9.11.2 After the Real Time 4D Biopsy After [Freeze] the system switches automatically to freeze mode and the “4D Image Cine” menu appears. The last acquired volume will be present on the monitor. Upon [Freeze] a certain number of volumes will be stored in the cine memory. The sequence (chapter 'Volume Cine' on page 9- can be reviewed volume by volume. - Page 335 Volume Mode • Manual or Semi automatic Contour detection of structures (such as tumor lesion, cyst, prostate, etc.) and subsequent volume calculation. The accuracy of the process can be visually controlled by the examiner in multi-planar display. • Construction of a virtual shell around the contour of the lesion. The wall thickness of the shell can be defined.
- Page 336 Volume Mode Definition of a Shell Contour (Geometry) Shell Contour is, to define a “thickness”’ of the “reference”’ surface The basic idea of a geometry. The “’parallel” contours shown in the image define the “parallel” surface geometry (describing the shell). The “parallel” contours are either defined symmetrically to the reference contour or Shell Geometry consists of one outside and one limited to one direction, inside or outside.
- Page 337 Volume Mode (Shell) Volume Calculation The (shell) volume is defined as the difference between the volume defined by the outer surface (of the shell geometry) and the volume defined by the inner surface (of the shell geometry). (Shell) Niche presentation The niche presentation allows the visualization of slices and the shell contour in one image.
- Page 338 Volume Mode 2. Select the [Volume Analysis] and press [VOCAL] key. The “VOCAL settings” menu appears on the menu area. 3. Select the desired contour generation mode. (chapter 'Selection of a VOCAL For details see: Selection of a VOCAL Generation Mode on page 9-122 ) Generation Mode' If desired, change the [VOCAL Settings] of the chosen VOCAL Generation Mode.
- Page 339 Volume Mode 4. To start defining a new contour, select the [Start] key. 9.12.3 VOCAL Settings Selection of Rotation Steps The “Rotation Steps” define, how many contours have to be generated. The decision, which rotation step should be chosen depends on the shape of the ROI. For example: An angle setting of [30˚] means that after the fist trace has been done, the volume data set is rotated 30˚...
- Page 340 Volume Mode 9.12.4 Selection of a VOCAL Generation Mode The main contour axis should pass the center of the 3D lesion. (The 3D object should be centered with respect to the rotation axis.) All defined contours (in different planes) cross the main contour axis at the position of the green arrows.
- Page 341 Volume Mode 4. Select the next image plane by means of this control below the menu area, or select the [Next] key. The contour is copied to the next image plane and can be redefined by drawing a new contour. Every time you start to outline a contour, the new contour in this image plane replaces the old one.
- Page 342 Volume Mode If necessary, edit the contour, review: VOCAL - Edit (chapter 'VOCAL - Edit' on page 9-124 ) , otherwise select this key to accept the computer-assisted contour. 9.12.4.3 Save VOCAL After accepting the ROI the VOCAL image can be stored in the archive by using the P-keys. Chapter 14 To customize the P-keys, 9.12.5 VOCAL - Edit...
- Page 343 Volume Mode In the “VOCAL - Edit” menu: (chapter 'Modifying a the contours can be manipulated; review: Modifying a Contour on page 9-125 ) Contour' (chapter 'Defining a Shell a shell contour is generated; review: Defining a Shell contour on page 9-126 ) contour (shell geometry)' The shell contour is accepted and stored.
- Page 344 Volume Mode 3. Select the next image plane by using the [Next] or [Back] key of the “Rotation Ref.:” function. (chapter 4. Select the desired Shell mode. For details, review: Defining a Shell contour on page 9-126 ) 'Defining a Shell contour (shell geometry)' 5.
- Page 345 Volume Mode Shell [Sym.] (symmetric) • half The outside surface (1) is the surface geometry of the outer ’parallel’ contours with distance Shell Thickness in mm. • half The inside surface (1) is the surface geometry of the inner ’parallel’ contours with distance Shell Thickness in mm.
- Page 346 Volume Mode Return to the “VOCAL Modes” menu, where you can define a new contour. Return to the “VOCAL - Edit” menu, where you can readjust the defined contour. To choose the Reference image The rotary buttons and the trackball are assigned to the selected reference image for adjusting the position, magnification and rotation of the shell image.
- Page 347 Volume Mode Depending on the “Render Mode” setting, the skin (of the shell contour) or the rendered volume image within the shell contour is displayed in the lower right quadrant. review: Render (chapter 'Render Mode and Display of the Shell Mode and Display of the Shell Geometry on page 9-129 ) Geometry'...
- Page 348 Volume Mode 2. Select the desired Render Mode (e.g., Inversion). If you have select [Vocal Surface] Render Mode you can change the display of the Shell Geometry among [Skin] or [Wire Mesh]. Select this key to change the “Surface Color” of the Shell Geometry. 9.12.5.6 Threshold Volume After volume calculation via the VOCAL program, it is possible to display an automatically calculated Threshold volume.
-
Page 349: Sonoavc Follicle
Volume Mode The same applies for the Threshold Volume result window see (chapter 'Threshold Volume' on page 9-130 ) 9.12.5.8 Volume Histogram After volume calculation via the VOCAL program, it is possible to display an automatically calculated (Color Angio) Histogram of the volume. Select the [Volume Histogram] key in the Vocal menu. - Page 350 Volume Mode 9.13.2 Operation Create a 3D Static Volume of the desired Organ, see 'Volume Acquisition: Static 3D on page 9-48 . Render' Select a Region of Interest or create a VOCAL, see 'After the Static 3D Render on page 9-51 Acquisition' Press the [Volume Analysis] Button on the menu area.
- Page 351 Volume Mode 9.13.2.1 Table of low echogenic objects The calculation results are displayed in the top right corner. The objects are listed according to size. All different objects are colorcoded i.e. the colour surrounding the number of the object also denotes the object on the image. If the mousecursor hovers over a specific item on the list the respective object in the image is highlighted and vice versa.
- Page 352 Volume Mode • Edit ROI Select this key to edit the ROI again, see 'After the Static 3D Render Acquisition' page 9-51 • Init Select this key to reset the rotations and translations of a volume section to the initial on page 9-24 (start) position, see'Principle of Sectional Image Analysis' •...
- Page 353 Volume Mode • Select the [3D Frame] to turn the 3D frame around the SonoAVC areas off or on. • Select the [Filled] button to highlight the segments by filling the area of the segment with color. • Select [More...] to see more options. •...
-
Page 354: Vcad Heart - Volume Computer Aided Display
Volume Mode 1. Press the left trackball key to start drawing a path along the area you want to cut out. 2. Press again to set the path’s endpoint. If the path is not closed, the software will connect the start and end point with a straight line. 3. - Page 355 Volume Mode 9.14.1 General Description VCAD is a technology that automatically generates a number of views of the fetal heart to make diagnosis easier. 9.14.2 Operation Acquire a 3D/4D view of the fetal heart. Ideally, the acquisition should start with a four- chamber-view.
- Page 356 Volume Mode If you can already see the heart template on the monitor you can start adjusting. If you cannot see the heart template on the monitor, press the [Plane Graphic] button. The heart template appears. Adjust the US image, using the X-, Y-, Z-rotary controls and the zoom button so that it For more information see 'Principle fits the template.
- Page 357 Volume Mode Press [Cardiac 1] to view the left outflow tract. Or press [Cardiac 2] to view the right outflow tract, or press [Cardiac 3] to view the fetal stomach. or press [Cardiac 6] to view the fetal aortic arch Voluson®...
- Page 358 Volume Mode or press [Start Plane] to view the Start Plane again. Voluson® S6/S8 Basic User Manual 9-140 5433669-100 Revision 4...
- Page 359 Volume Mode 9.14.3 Before VCAD Operation Plane Graphic Press this key to switch on and off the heart template Set Starting Plane Press this key to display the VCAD application menu, on page 9-142 see'During VCAD Operation' More... Press the [More...] button to go to submenu, see 'Sub Menus' on page 9-43 Cephalic/ Breech Press this key to turn the image 18º...
- Page 360 Volume Mode 9.14.4 During VCAD Operation Select [ 1 x 2], [ 2 x 2], [ 2 x 3], [ 3x 3], [ 3 x 4] and [ 4 x 4] to display number of slices. Set Starting Plane Press the [Set New Plane] button to get back to the VCAD Heart Main on page 9-141 menu, see'Before VCAD Operation' on page 9-43...
-
Page 361: Sonovcad Labor
Volume Mode Cardiac 1 Press the [Cardiac 1] button to view the left outflow tract. Cardiac 2 Press the [Cardiac 2] button to view the right outflow tract. Cardiac 3 Press the [Cardiac 3] button to view the fetal stomach. Cardiac 4 Press the [Cardiac 4] button to view Venous. - Page 362 Volume Mode Menu item Description Click this menu item to set the skull contour as described in 'Set fetal on page 9-146 . The checkbox controls whether or not the contour contour' line is displayed in the ultrasound image. Click this menu item to set the head direction as described in 'Set head on page 9-146 .
- Page 363 Volume Mode 9.15.3 Mark pubis position - manual Bring the volume in the correct position using rotation, translation and zoom. Align image plane A to the Pubis Longitude mark and image plane B to the Pubis Transverse mark. Confirm the correct alignment by clicking the Set Position menu item.
- Page 364 Volume Mode 9.15.4 Set fetal contour Trace the position of the fetal head point by point. 9.15.5 Set head direction Draw a line of two points along the maximum head diameter. Then mark the most distant point of the head contour. The head direction is automatically calculated as a line orthogonal to the Voluson®...
- Page 365 Volume Mode max diameter passing through the distal point 9.15.6 Set midline Mark the position of the midline with a line of two points. The measurement result is the calculated angle between the vertical axis and the midline. As the rotation can be to the left or to the right it is necessary to start measuring at the occiput to get acurate results.
- Page 366 Volume Mode 9.15.7 Head progression distance Perform this measurement in image plane A. The measurement’s point of origin is vertically locked to the pubis. Mark the distal point of the fetal head to measure the distance between the pubis and the head in millimeters. 9.15.8 Head progression angle Perform this measurement in image plane A.
- Page 367 Volume Mode dihedral angle between the pubis and the defined line. Voluson® S6/S8 Basic User Manual 5433669-100 Revision 4 9-149...
- Page 368 Volume Mode This page was intentionally left blank. Voluson® S6/S8 Basic User Manual 9-150 5433669-100 Revision 4...
-
Page 369: Chapter 10 - Elastography Mode
Chapter 10 Elastography Mode Describes the general functions of the Elastography Mode. Image quality is the essential performance of the system. Please read this chapter carefully. Voluson® S6/S8 Basic User Manual 5433669-100 Revision 4 10-1... -
Page 370: Gui Elements
Elastography Mode Elastography Mode: • on page 8-2 'Pulsed Wave Doppler Mode (PW Mode)' • on page 10-3 'Elastography Main Menu' • on page 8-17 'Power Doppler Mode (PD Mode)' General Description Elastography shows the spatial distribution of tissue elasticity properties in a region of interest by estimating the strain before and after tissue distortion caused by external or internal forces. -
Page 371: Elastography Main Menu
Elastography Mode 10.1.1 Quality bar Quality steps (squares) Color 1.) Steps 1 - 2 2.) Steps 3 - 4 Yellow 3.) Steps 5 - 6 Green 10.2 Elastography Main Menu Elastography mode key (hard key) Press the [Elasto] key on the user interface to activate the Elastography mode. Voluson®... - Page 372 Elastography Mode When the [Elasto] key is pressed the Elastography main menu appears on the screen: Change the size and the position of the Elastography box by using the trackball key. Change between size and position by using the upper trackball key. 10.2.1 SRI on page 9-46 'Speckle Reduction Imaging (SRI)'...
-
Page 373: Elastography Sub Menu
Elastography Mode ORange: 0 (full transparent) - 255 (not transparent); 5 steps 10.2.4 Frequency For more information see 'Frequency' on page 8-36. 10.2.5 PRF For more information see 'Velocity Range (PRF)' on page 8-40. 10.3 Elastography Sub Menu Access the Elastography Sub menu by pressing the [Sub Elasto] key on the menu area. Following menu appears on the menu area: 10.3.1 Elasto Map Elastography color maps. -
Page 374: Elastography Sub Menu 2
Elastography Mode 10.3.4 Window Length Range: 8-25; Step size: 1 10.3.5 Window Step Range: 4 - 49; Step size: 1 10.3.6 Filter Axial Range: 1 - 9; Step size: 1 10.3.7 Filter Lateral Range: 1 - 21; Step size: 2 10.3.8 Frame Reject Range: 0 - 255;... - Page 375 Elastography Mode 10.4.1 AGC Filter Axial Range: 1 - 63; Step size: 2 10.4.2 AGC Filter Lateral Range: 1 - 63; Step size: 2 10.4.3 AGC Threshold High Range: 1 - 10; Step size: 1 10.4.4 AGC Threshold Low Range: 1 - 10; Step size: 1 10.4.5 Frame Averaging Range: 1 - 9;...
- Page 376 Elastography Mode This page was intentionally left blank. Voluson® S6/S8 Basic User Manual 10-8 5433669-100 Revision 4...
-
Page 377: Chapter 11 - Measurements And Patient Worksheets (Reports)
Chapter 11 Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) Describes the general functions of generic measurements, calculations and patient worksheets. Voluson® S6/S8 Basic User Manual 5433669-100 Revision 4 11-1... -
Page 378: Generic Measurements
Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) 11.1 Generic Measurements Generic Measurement - Caliper key (hard key) By pressing the [Caliper] key the Generic Measurement functions are switched on and a cursor appears in the image area. (chapter 'Basic For description of Generic Measurement functionality review: Basic Operations on page 11-3 ) . - Page 379 Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) • M Mode measurements (chapter 'M-Mode Measurements' on page 11-14 ) • D Mode measurements (chapter 'D-Mode Measurements' on page 11-16 ) Additional functions in the “Generic Measurement” menu: • (chapter 'To Change the Measurement To Change the Measurement Applications on page 11-20 ) Application'...
- Page 380 Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) To delete all measurement results of the selected “Study” from the monitor as well as from the corresponding Worksheet, select the [Clear Study] item on the menu area. When [Clear Study] runs, it shows below message. Note To erase measurement results: •...
- Page 381 Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) Depending on the setting in the Measure Setup: • all previously set measuring marks are erased when activating cine mode, or the measurement results are kept on screen. • a new cursor appears to repeat the measurement, or not •...
- Page 382 Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) (chapter (chapter 'Area Trace' on page 11-8 ) Area Trace (chapter 'Area Point' on page 11-8 ) 'Generic Area Area Point (chapter 'Area 2 Distances' on page Measurements' Area 2 Distances on page 11- 11-9 ) Ellipse (chapter 'Ellipse' on page 11-9 ) Stenosis %Area (chapter 'Stenosis %Area' on page 11-9 )
- Page 383 Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) 11.1.2.1.1 Distance 2 Points To measure the distance between two points, select the [Dist. 2Point] item in the menu area. A cursor appears on the screen. Use the trackball to move the cursor to the start point of the measurement and press the right or left trackball key [Set] to fix the marker.
- Page 384 Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) Remark: The results (such as outer and inner distance and the Stenosis %) appear automatically. 11.1.2.2 Generic Area Measurements 11.1.2.2.1 Area Trace To measure circumference and area using trace, select the [Area Trace] item in the menu area.
- Page 385 Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) Move the trackball again to adjust the next line between two points and then press [Set] again. To re-adjust a line, press the upper trackball key [Undo] repeatedly. Note Set as many points as necessary, around the shape to be measured. When you press the [Set] key once again, a straight line automatically completes the trace.
- Page 386 Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) 11.1.2.3 Generic Volume Measurement 11.1.2.3.1 3 Distances To measure volume of an ovoid using three distances, select the [3 Dist] item in the menu area. A cursor appears on the screen. Move the cursor to the start point of the measurement and press the right or left trackball key [Set] to fix the marker.
- Page 387 Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) 11.1.2.3.2 Ellipse The measurement procedure is the same than the measurement of the Generic Area - Ellipse (chapter 'Ellipse' on page 11-9 ) . Remark: After the measurement, the volume of the ellipse is displayed. 11.1.2.3.3 1 Distance + Ellipse To measure volume of an ovoid using one distance and ellipse, select the [1 Dist Ellipse] item in the menu area.
- Page 388 Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) To measure volume using the Multplane method in 3D Mode: Select the reference image in which the measurement is to be performed. (A, B or C) Activate the Multiplane volume measurement by selecting the [Multiplane] key. The menu area changes to the Multiplane menu.
- Page 389 Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) • The different sections can be chosen liberally, it is not necessary to follow a certain order. • The volume measurement is only possible in 3D static mode 3D static mode will be activated automatically when switching on the measurement. Full size format active: A render image will be replaced by the current reference section plane image during the 3D Multiplane measurement and is shown again when you exit the 3D Multiplane measurement.
- Page 390 Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) Remark: The angle between the two lines is displayed. 11.1.2.4.2 Angle 2 Line To measure the angle between to lines, select the [Angle 2 Line] item in the menu area. A cursor appears on the screen. Move the cursor to the start point of the angle measurement and press the right or left trackball key [Set] to fix the marker.
- Page 391 Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) 11.1.3.1 Generic Measurements 11.1.3.1.1 Distance 2 Points This measures the vertical distance (tissue depth) between two points. The measurement procedure is the same as the distance measurement in 2D Mode. review: Distance 2 Points (chapter '2D Mode Measurements' on page 11-5 ) . 11.1.3.1.2 Slope To measure the time and slope, select the [Slope] item in the menu area.
- Page 392 Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) To re-adjust the start point, press the upper trackball key. A second line (parallel to the first Note one) appears. Move this line using the trackball to the end point of the measurement and then press [Set].
- Page 393 Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) 11.1.4.1 Generic Measurements 11.1.4.1.1 Auto Trace 1. To trace the Doppler spectrum automatically and to display the results (according to the setting in the Measure Setup), select the [Auto Trace] item in the menu area. 2.
- Page 394 Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) The status bar shows the current function of the trackball. 5. Press the right or left trackball key [Set] to finish the measurement. Remark: To select the Doppler measuring results, which should be displayed after an Auto Trace measurement.
- Page 395 Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) Move the line to the peak of the systole and press the right or left trackball key [Set]. A second line appears. Move the second line to the end of the diastole and press [Set] again. 11.1.4.1.6 PI (Pulsatility Index) To measure the pulsatility index, the time averaged maximum velocity as well as the peak-systolic and end-diastolic velocity in Spectral-Doppler mode, select the [PI] item on...
- Page 396 Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) 11.1.4.2 PG (Pressure Gradient) Measurements 11.1.4.2.1 PG max (Pressure Gradient maximum) To measure the maximum velocity and the maximum pressure gradient in Spectral- Doppler mode, select the [PG max] item on the menu area. A cursor appears on the screen.
- Page 397 Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) 2. Select another application. If desired, change also the Preset and Sub Category. Note 3. Press [Exit] item to return to the Generic Measurement menu without a change. When changing to another measurement application, the main application (chosen in the “Probe Selection”...
- Page 398 Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) The display of the worksheet depends on the currently selected measurement application (e.g., Worksheet Obstetric). 2. Select the [Generic] key to review all previously calculated generic measurement results. By means of this flip control, additional worksheet pages can be selected. For further descriptions, possible adjustments and functions, review: Basic Patient Report (chapter 'Basic Patient Worksheet Functions' on page 11-101 ) .
-
Page 399: Calculations And Worksheets
Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) 11.1.7 Measurement Accuracy of the System Measurements must never be made in a hurry, accurate positioning of the measuring cross or measuring dots is necessary especially with area/circumference measurements. Despite the high technical accuracy of the scan geometry and the measuring system of the Voluson® S6/S8 equipment one must, however, be aware of inaccuracies caused by the ultrasound beam properties and the physiological properties of the scanned structures, tissues and fluids. - Page 400 Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) To change the current measurement application (and/or the Sub Category), press the [Calc] hardkey and select this key on the menu area. (chapter 'Basic Calculation Functionality' on page For Basic Calculation Functionality, review: 11-98 ) The system supports following application-oriented Patient Worksheets (Reports): (chapter 'Abdomen Calculations' on page 11-24 ) Abdomen - Worksheet...
- Page 401 Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) 11.2.2.2 Before starting Abdomen Calculations 1. Press the [Patient] key on the control panel, select the [ABD] page and enter all patient (chapter information for Abdomen calculations. For details refer to: Entering Patient Data on page 4-10 ) 'Entering Patient Data' To cancel all calculations performed before and to start new measurement, press this key and Note...
- Page 402 Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) Press the [Calc] key on the control panel. Select the desired item. For example: select [Liver]. Select the desired measurement parameter. For example: select [Length]. Use the trackball to move the cursor to the start point of the measurement and press the right or left trackball key [Set] to fix the marker.
- Page 403 Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) Press the [Calc] key on the control panel. Select the desired item. For example: select [Left Renal Artery]. Select the appropriate measurement parameter [Vessel Area] or [Vessel Diameter]. Use the trackball to move the cursor to the start point of the measurement and press the right or left trackball key [Set] to fix the marker.
- Page 404 Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) 11.2.2.6 Stenosis Area/Stenosis Diameter To calculate the Stenosis Area or the Stenosis Diameter in 2D mode: Press the [Calc] key on the control panel. Select the desired item. For example: select [Left Renal Artery]. Select the appropriate measurement parameter [Stenosis Area] or [Stenosis Diameter]. To measure the outer area (resp.
- Page 405 Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) • Stenosis Diameter (chapter 'Stenosis Diameter' on page 11-29 ) • Time (chapter 'Time' on page 11-29 ) • HR (Heart Rate) (chapter 'HR (Heart Rate)' on page 11-30 ) 11.2.2.8 Vessel Diameter To measure the Vessel Diameter in M Mode: Press the [Calc] key on the control panel.
- Page 406 Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) 11.2.2.11 HR (Heart Rate) To measure the Heart Rate (HR) in M Mode: 1. Press the [Calc] key on the control panel. 2. Select the desired item. For example: select [Left Renal Artery]. 3. Select the [HR] key on the control panel. A line appears on the screen. 4.
- Page 407 Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) • Manual Trace (chapter 'Manual Trace' on page 11-32 ) • Measurement of Each Item (chapter 'Measurement of Each Item' on page 11-32 ) • Measurement of PSV/EDV RI+SD (chapter 'Measurement of PSV/EDV RI+SD' on page 11-32 ) •...
- Page 408 Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) 5. If necessary, adjust the [Angle] and the [Baseline]. A green line appears at the left of the spectrum. Press the upper trackball key [Change] to move the line and readjust the start cycle (the line changes to yellow). Press the right or left trackball key [Set] to fix the line.
- Page 409 Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) Perform the EDV measurement using the trackball and press the right/left trackball key [Set] again. The measurement results of PSV, EDV, RI and S/D are displayed and stored in the report. Note 11.2.2.17 Time To measure the Time in Spectral Doppler Mode: Press the [Calc] key on the control panel.
- Page 410 Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) With this flip control additional worksheet pages can be selected. To close the worksheet, select the [Exit] key on the menu area. For additional description please refer to Basic Patient Worksheet Functions (chapter 'Basic Patient Worksheet Functions' on page 11-101 ) .
- Page 411 Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) 11.2.3.3 Before starting Small Parts Calculations 1. Press the [Patient] key on the control panel, select the [SM P] page and enter all patient information for Small Parts calculations. For details refer to: Entering Patient Data (chapter 'Entering Patient Data' on page 4-10 )
- Page 412 Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) • Manual Trace • Measurement of Each Item • Measurement of PSV/EDV RI+SD • Time • HR (Heart Rate) The measurement procedures in Spectral Doppler Mode are the same than in application (chapter 'Abdomen “Abdomen”. review: Abdomen Calculations in Spectral Doppler Mode on page 11-24 ) .
- Page 413 Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) With this flip control additional worksheet pages can be selected, e.g. the BiRADS Page. To close the worksheet, select the [Exit] key on the menu area. For more information see 'Basic Patient Worksheet Functions' on page 11-101. 11.2.4 Obstetric Calculations - Subcategory: Biometry Application “Obstetric”, (Factory - Sub Category: Biometry) allows measurements/calculations in 2D/3D mode, M mode and Spectral-Doppler mode, using various measure items.
- Page 414 Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) For some obstetric measurements there are different methods how perform these. These Note different methods can be selected by the rotary control, which is on the left side. Which method is currently active, is displayed in the lower, left corner. 11.2.4.2 Before starting Obstetric Calculations 1.
- Page 415 Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) If a Fetus number has been entered, several fetuses can be measured on one patient. Select this flip switch control to change from fetus A to B or C or fetus D. 2. Make sure that the probe and application are selected properly. If another application is selected, press the [Probe] key on the control panel, and change it to Obstetric.
- Page 416 Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) 11.2.4.4 Distance Measurements Press the [Calc] key on the control panel. Select the study for the corresponding item. For example: select [Fetal Biometry]. Select the desired measurement parameter. For example: select [BPD]. Use the trackball to move the cursor to the start point of the measurement and press the right or left trackball key [Set] to fix the marker.
- Page 417 Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) Select [Early Gestation] and then [GS] on the menu area. A cursor appears. Select “Triple Caliper” by turning the left rotary control. Use the trackball to move the cursor to the start point of the measurement and press the right or left trackball key [Set] to fix the marker.
- Page 418 Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) 11.2.4.6 Circumference Measurements Press the [Calc] key on the control panel. Select the study for the corresponding item. For example: select [Fetal Biometry]. Select the desired measurement parameter. For example: select [HC]. If HC or AC have been selected, you can select the desired way to perform the measurement, Note using the left rotary control.
- Page 419 Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) 11.2.4.7 AFI Calculation To calculate AFI, the Amniotic Fluid Index (distances are measured in several images): Press the [Calc] key on the control panel. Select the [AFI] key and then select [Q1]. Use the trackball to move the cursor to the start point of the measurement and press the right or left trackball key [Set] to fix the marker.
- Page 420 Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) • Manual NT: Same as standard distance measurement: '2D Mode Measurements' page 11-5 ) • SonoNT: Switch to SonoNT by using the [NT Method] flipswitch and follow the instruction: Press the [Calc] key on the control panel and choose [Early Gest.]. Select the [NT] key.
- Page 421 Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) NT Methode Switch between “Manual” or “Sono” NT. Face up/ Switch between “Face up” or “Face down”. Select according to scanned down image. i-i, i-m NT calculation algorithm i-i: inner - inner i-m: inner - middle Key is hidden if on page 11-109 ) not activated in system setup:.
- Page 422 Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) Display of the Standard Deviation (e.g., 0.6SD) e.g. Mean: 0.00 SD Min./Max.: -2SD / +2SD out of range: < SD / > SD Selection of the field “Growth Dev. Display” in the Measure Setup is “SD”. For further details, Note review: Global Parameters (chapter 'The Measure Setup Pages' on page 11-109 ) Display of the growth percentile (e.g., 71.9%)
- Page 423 Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) Note Selection of the field “Growth Dev. Display” in the Measure Setup is “%”. For further details, review: Global Parameters (chapter 'The Measure Setup Pages' on page 11-109 ) 11.2.4.10 Obstetric Calculations in M Mode •...
- Page 424 Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) 5. Select the number of heart rate cycles for measurement with the rotary control. 6. If necessary, adjust the [Angle] and the [Baseline]. 7. Press the right or the left trackball [Set] key again. The Heart Rate is displayed. 11.2.4.13 Obstetrics - Subcategory Z-Scores This subcategory contains measurements that help you to obtain the Z-scores needed for analysation of the fetal heart.
- Page 425 Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) If a Fetus number has been entered, several fetuses can be measured on one patient. Select this flipswitch to change from fetus A to B or C or fetus D. 2. Press the [GA] key on the menu area to enter the Gestational Age. Alternatively the GA can be calculated by entering the LMP the DOC or the EDD.
- Page 426 Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) 11.2.4.17 Distance Measurements Press the [Calc] key on the control panel. Select the [Meas. Applicat.] key Select [Fetal Echo] Select a study for the corresponding item. For example: select [Aortic arch]. Select the desired measurement parameter. For example: select [Anulus]. Use the trackball to move the cursor to the start point of the measurement and press the right or left trackball key [Set] to fix the marker.
- Page 427 Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) FL...femur length; GA...gestational age in completed weeks; BPD...biparietal diameter; m...multiplier; c...intercept 11.2.4.18 To obtain Z-Scores The Z-scores compare either GA, BPD or FL with any fetal echo parameter (i.e.: Aortic valve, RV area, LV area). So in order to obtain Z-scores on your report, you either need to measure BPD or FL, or have the GA calculated from your LMP;...
- Page 428 Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) 11.2.4.20 Fractional Limb This measurement is for calculating the fetal limbs. Based on this partial volume-calculation the fetal weight can be estimated. Figure: Fractional limb volume. Fractional Arm (AVol) and Thigh (TVol) volumes are based on 50% of the humeral (A) or femoral (B) diaphysis length.
- Page 429 Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) Define the reference line, using the trackball. Accept with left or right trackball. Measure the all areas. When the measurement is done the next line will be highlighted. If the last area is measured press the Done button. If necessary correct the measurements.
- Page 430 Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) The worksheet appears as follows (e.g., summary report “Calc”). With this flip control additional worksheet pages of the measured Fetus (e.g., Fetus A) can be selected. Select this flip switch control to change from the 1 (A) fetus to the 2 (B) or 3 (C) or 4...
- Page 431 Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) Note It is now possible to switch between Gyn and OB worksheets (if both worksheets exists). Review: First Trimester OB in application GYN (chapter 'The Measure Setup Pages' on page 11-109 ) (chapter 'Basic For additional functions please refer to Basic Patient Worksheet Functions on page 11-101 ) .
- Page 432 Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) All the values in the checklist are set to “Normal”. All the values in the checklist are cleared. 11.2.4.26 Summary Report - Graph By selecting this key on the control panel any stored measurement can be viewed in a Graph display.
- Page 433 Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) To view the stored measurement graphs, select the desired item using the trackball and trackball keys. In multiple gestations, the growth of each fetus is indicated with a different mark. The “check marks” indicate the measurement graphs which will be printed. Use the trackball and the trackball keys to select/deselect the graphs.
- Page 434 Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) Bar - Display The Bar graph display can also be included on the report. Note Single - Display Voluson® S6/S8 Basic User Manual 11-58 5433669-100 Revision 4...
- Page 435 Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) Quad - Display 11.2.4.27 Summary Report - Fetus Compare Select this key to compare all measurement results of the measured fetuses. 11.2.4.28 Summary Report - Generic This “Summary report” is only active if generic measurements were performed. For further (chapter ‘Generic Measurements’...
- Page 436 Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) 11.2.4.29 Summary Report - Exam Comment Select this key to enter a comment using the keyboard, or to enter a previous defined comment by selecting the [Comment A], [Comment B] or [Comment C] key. For further details (chapter 'Basic Patient Worksheet Functions' on page 11-101 ) .
- Page 437 Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) 1. Press the [Patient] key on the control panel, select the [CARD] page and enter all patient (chapter information for Cardio calculations. For details refer to: Entering Patient Data on page 4-10 ) 'Entering Patient Data' To cancel all calculations performed before and to start new measurement, press this key and Note select [End Exam] or [Clear Exam].
- Page 438 Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) 11.2.5.4 LV Simpson To calculate the left ventricular (end diastolic or end systolic) volume in 2D mode: Press the [Calc] key on the control panel. Select the item [LV Simps.]. Select the desired measurement parameter. For example: select [A4C Dias.]. Perform the circumference measurement of the left ventricle by using the trackball key and then press the right or left trackball key [Set].
- Page 439 Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) Press the [Calc] key on the control panel. Select the item [Vol A/L]. Select the desired measurement parameter. For example: select [LV Vol. Dias.]. Perform the circumference measurement of the left ventricle by using the trackball key and then press the right or left trackball key [Set].
- Page 440 Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) 11.2.5.6 LV (Left Ventricle) To calculate the distances IVSd, IVSs, LVDd, LVDs, LVPWd, LVPWs and RVDd in 2D mode: Press the [Calc] key on the control panel. Select the item [LV]. Select the desired measurement parameter. For example: select [IVSd]. Use the trackball to move the cursor to the start point of the measurement and press the right or left trackball key [Set] to fix the marker.
- Page 441 Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) 1. Press the [Calc] key on the control panel. 2. Select the item [LV Mass]. 3. Select the desired measurement parameter. For example: select [Epi Area]. Perform the measurement of the Epicardial Area, Endocardial Area and Epicardial Length Note prior to the LV mass measurement.
- Page 442 Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) Press the [Calc] key on the control panel. Select the item [LVOT] or [RVOT]. Select the corresponding measurement parameter. For example: select [LVOT Diam]. Use the trackball to move the cursor to the start point of the measurement and press the right or left trackball key [Set] to fix the marker.
- Page 443 Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) 11.2.5.9 MV (Mitral Valve) (Mitral Valve) in 2D mode: To measure Distance A, Distance B or Area of the MV Press the [Calc] key on the control panel. Select the item [MV]. Select the appropriate measurement parameter. For example: select [Dist A]. Use the trackball to move the cursor to the start point of the measurement and press the right or left trackball key [Set] to fix the marker.
- Page 444 Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) 11.2.5.11 AV/LA (Aortic Valve/Left Atrium) To measure the Aortic Diameter or the Left Atrium Diameter in 2D mode: Press the [Calc] key on the control panel. Select the item [AV/LA] and then the desired measurement parameter [Ao Root Diam] or [LA Diam].
- Page 445 Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) After obtaining a feasible Color Doppler image, press the [Calc] key on the control panel. Select the appropriate item. For example: select [MV]. Select the measurement parameter [PISA]. The cursor appears on the screen. Perform the distance measurement using the trackball and press the right or left trackball key [Set].
- Page 446 Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) 11.2.5.17 To measure all Items at a Time To calculate all the items of the Left Ventricle in M mode at a time: 1. Press the [Calc] key on the control panel. 2. Select the item [LV] and then select [LV Study]. A vertical line with a cursor appears in the M Mode trace display.
- Page 447 Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) Additionally also [RVDd] and [HR] can be measured. If the Heart Rate is measured, also the Note Cardiac Output is calculated and shown in the worksheet. IVSd: Interventricular Septum - diastolic LVDd: Left Ventricle Diameter - diastolic LVPWd: Left Ventricular Posterior Wall - diastolic IVSs: Interventricular Septum - systolic LVDs: Left Ventricle Diameter - systolic LVPWs: Left Ventricular Posterior Wall - systolic 11.2.5.18 To measure the Items One by One...
- Page 448 Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) Move the second cursor to the second point of the measurement and press [Set] again. Note To re-adjust the start point, press the upper trackball key [Change] before completing the measurement. This alternates the control from one cursor to the other. Aortic Root Diameter: distance between the anterior aortic wall and the posterior aortic wall Left Atrial Diameter: distance between posterior aortic wall echo and posterior left atrial wall Aortic Cusp Separation: distance between the coronary cusp and the non coronary cusp...
- Page 449 Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) The + cursor appears on the screen. Move the cursor to the E point and press the right or left trackball key to fix the mark. The + cursor appears on the screen. Move the cursor to the F point and press the right or left trackball key to fix the mark.
- Page 450 Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) 1. Press the [Calc] key on the control panel. 2. Select the item Heart Rate [HR] on the screen. A vertical line appears on the screen. 3. Move the line to the start point of the period and press the right or left trackball key [Set]. The second line appears.
- Page 451 Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) • Pulmonary Veins (chapter 'Pulmonary Veins' on page 11-79 ) • PAP (Pulmonary Artery Pressure Measurement) (chapter 'PAP (Pulmonary Artery on page 11-80 ) Pressure Measurement)' • HR (Heart Rate) (chapter 'HR (Heart Rate)' on page 11-81 ) 11.2.5.25 MV (Mitral Valve) There are different methods to perform measurements and calculations of the Mitral Valve in the Spectral-Doppler mode:...
- Page 452 Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) Remark: To select the Doppler measuring results, which should be displayed after the measurement (= “Auto/Manual Trace”) and to select if the envelope curve will be performed with a continuous trace line or by setting points (= “Manual Trace Mode”), review: Application (chapter 'The Measure Setup Pages' on page 11-109 ).
- Page 453 Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) 11.2.5.29 TV (Tricuspid Valve) There are different methods to perform measurements and calculations of the Tricuspid Valve in the Spectral-Doppler mode. The measurement methods are similar to those of the Mitral Valve. For further details, review: MV (Mitral Valve) (chapter 'MV (Mitral Valve)' on page 11-75 ) Voluson®...
- Page 454 Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) 11.2.5.30 PV (Pulmonary Valve) There are different methods to perform measurements and calculations of the Pulmonary Valve in the Spectral-Doppler mode. The measurement methods are similar to those of the Mitral Valve. (chapter 'MV (Mitral Valve)' on page 11-75 ) For further details, review: MV (Mitral Valve) Voluson®...
- Page 455 Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) 11.2.5.31 LVOT- or RVOT Doppler There are different methods to perform measurements of LVOT (Left Ventricle Outflow Tract) or RVOT (Right Ventricle Outflow Tract) in the Spectral-Doppler mode. The measurement methods are similar to those of the Mitral Valve. (chapter 'MV (Mitral Valve)' on page 11-75 ) For further details, review: MV (Mitral Valve) 11.2.5.32 Pulmonary Veins...
- Page 456 Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) Press the [Calc] key on the control panel. Select the appropriate item. For example: select [Dias. V]. If necessary, select the [Angle] and the [Baseline]. Perform the measurement by using the trackball and the right or left trackball key [Set]. 11.2.5.33 PAP (Pulmonary Artery Pressure Measurement) To measure the items such as VPD (protodiastolic velocity) or VTD (telediastolic velocity) in Spectral-Doppler mode:...
- Page 457 Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) Press the [Calc] key on the control panel. Select the item [PAP]. Select the appropriate measurement parameter. For example: select [VPD]. If necessary, select the [Angle] and the [Baseline]. Perform the measurement by using the trackball and the right or left trackball key [Set]. 11.2.5.34 HR (Heart Rate) The method of the measurement is the same as that of measuring the Heart Rate in M mode.
- Page 458 Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) With this flip control additional worksheet pages can be selected. To close the worksheet, select the [Exit] key on the menu area. (chapter 'Basic For additional description please refer to Basic Patient Worksheet Functions on page 11-101 ) . Patient Worksheet Functions' 11.2.6 Urology Calculations Application “Urology”, (Factory - Sub Category: Default) allows measurements/calculations in...
- Page 459 Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) 11.2.6.2 Before starting Urology Calculations 1. Press the [Patient] key on the control panel, select the [URO] page and enter all patient (chapter information for Urology calculations. For details refer to: Entering Patient Data on page 4-10 ) 'Entering Patient Data' To cancel all calculations performed before and to start new measurement, press this key and Note...
- Page 460 Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) • Manual Trace • Measurement of Each Item • Measurement of PS/ED RI+SD • Time • HR (Heart Rate) The measurement procedures in Spectral Doppler Mode are the same than in application “Abdomen”. review: Abdomen Calculations in Spectral Doppler Mode 'Abdomen Calculations' on page 11-24 .
- Page 461 Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) The methods for obtaining measurements in the Vascular Calculations menu are similar to the generic measurement functions in 2D, M and Spectral Doppler mode. 11.2.7.1 Items of Vascular Calculations The items of vascular calculations in each mode are as follows: (Common Carotid Artery) , Left/Right ECA (External Carotid 2D/3D Mode Left/Right CCA...
- Page 462 Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) The measurement procedures in 2D Mode are the same than in application “Abdomen”. on page 11-24 . Review: Abdomen Calculations in 2D Mode in 'Abdomen Calculations' 11.2.7.4 Vascular Calculations in M Mode • Vessel Diameter •...
- Page 463 Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) With this flip control additional worksheet pages can be selected. Vessel Summary Select the Vessel Summary button or select the corresponding page in the report to access the Vessel Summary. This feature makes it possible to select custom Doppler values for calculating the ICA/CCA value.
- Page 464 Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) 11.2.8.1 Items of Gynecology Calculations The items of gynecology calculations in each mode are as follows: 2D/3D Mode Uterus (UT-Trace), Left/Right Uterine Artery, Left/Right Ovary, Left/Right Follicle, Fibroid, Pelvic Floor, Early Gestation (Fetal Heart Rate) M Mode: Left/Right Ovarian Artery, Left/Right Uterine Artery, FHR Doppler Mode:...
- Page 465 Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) 1. Press the [Patient] key on the control panel, select the [GYN] page and enter all patient information for Gynecology calculations (e.g., expected Ovulation). For details refer to: (chapter 'Entering Patient Data' on page 4-10 ) Entering Patient Data To cancel all calculations performed before and to start new measurement, press this key and Note...
- Page 466 Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) The measurement procedures in Spectral Doppler Mode are the same than in application “Abdomen”. Review: Abdomen Calculations in Spectral Doppler Mode in 'Abdomen on page 11-24 . Calculations' • FHR (Fetal Heart Rate) The measurement procedure of the Fetal Heart Rate in Spectral Doppler Mode is the same than in application “Obstetrics”.
- Page 467 Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) For additional description please refer to Basic Patient Worksheet Functions (chapter 'Basic on page 11-101 ) . Patient Worksheet Functions' 11.2.9 Pediatric Calculations Application “Pediatrics”, (Factory - Sub Category: Default) allows measurements/calculations in 2D/3D mode, M mode and Spectral-Doppler mode, using various measure items. For details (chapter 'The Measure Setup Pages' about settings, review: Measure Setup - Measure &...
- Page 468 Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) 11.2.9.4 Hip Joint The [Hip Joint] calculation assists in assessing the development of the infant hip. In this calculation, three straight lines are aligned with the anatomical features as shown in the figure below. The two angles are computed, displayed, and can be used by the physician in making a diagnosis.
- Page 469 Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) Select the measurement parameter [Hip Joint]. A cursor appears on the screen. Use the trackball to move the cursor to the start point of the line 1 measurement (a-b) and press the right or left trackball key [Set] to fix the marker. A second cursor appears. Move the second cursor to the second point of the line 1 measurement (a-b) and press [Set] again.
- Page 470 Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) With this flip control additional worksheet pages can be selected. To close the worksheet, select the [Exit key on the menu area. (chapter 'Basic For additional description please refer to Basic Patient Worksheet Functions Patient Worksheet Functions' on page 11-101 ) .
- Page 471 Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) 11.2.10.2 Before starting Neurology Calculations 1. Press the [Patient] key on the control panel, select the [NEURO] page and enter all patient (chapter information for Neurology calculations. For details refer to: Entering Patient Data on page 4-10 ) 'Entering Patient Data' To cancel all calculations performed before and to start new measurement, press this key and Note...
- Page 472 Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) • Manual Trace • Measurement of Each Item • Measurement of PS/ED RI+SD • Time • HR (Heart Rate) The measurement procedures in Spectral Doppler Mode are the same than in application “Abdomen”. Review: Abdomen Calculations in Spectral Doppler Mode in 'Abdomen on page 11-24 .
- Page 473 Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) 11.2.11 MSK Calculations There are no measurements/calculations specified for application “MSK”. 11.2.11.1 Items of MSK Calculations There are no items specified for application “MSK”. 11.2.11.2 Before starting MSK Calculations 1. Press the [Patient] key on the control panel, select the [MSK] page and enter all patient (chapter 'Entering information for MSK calculations.
-
Page 474: Basic Calculation Functionality
Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) 11.3 Basic Calculation Functionality Calculation key (hard key) By pressing on the [Calc] key the Calculation function is switched on and a caliper appears within the frozen image area. Measurements are possible in freeze mode only. Note Positioning of measuring marks is done with the trackball. - Page 475 Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) To erase results: • select the [Clear Study] item in the menu area • or Select the [Delete Last] item in the menu area To exit the Calculation program: • press the [Calc] key on the control panel •...
- Page 476 Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) For further details, review: Application Parameters (chapter 'The Measure Setup Pages' on page 11-109 ) • Depending on the setting in the Measure Setup: • all previously set measuring marks are erased when activating cine mode. •...
-
Page 477: Basic Patient Worksheet Functions
Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) 11.4 Basic Patient Worksheet Functions All calculation results are recorded in the “application dependent” patient worksheets. By pressing the [Report] key on the control panel, the Worksheet of the selected Measurement Application is switched on. (Always start with first page of worksheet.) •... - Page 478 Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) With this flip control different worksheet pages can be selected. To close the worksheet, select the [Exit] key on the menu area. Note It is now possible to switch between Gyn and OB worksheets (if both worksheets exists). Review: First Trimester OB in application GYN (chapter 'The Measure Setup Pages' on page 11-109 ).
- Page 479 Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) If a patient worksheet contains measurements that were performed in the XTD-View mode chapter 'XTD-View (Extended View)' on page 6-26 ), this symbol will be shown in the (review worksheet header. 11.4.2 To edit a Worksheet Any stored measurements in a patient worksheet can be edited.
- Page 480 Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) Select the [Exam Comment] key, to view the “Exam Comment” summary report, to enter a comment using the keyboard, or to enter a previous defined comment by selecting the [Comment A], [Comment B] or [Comment C] key on the menu area. If a comment is already saved: Voluson®...
- Page 481 Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) • type in the comment desired using the alphanumeric keyboard, or • Select the [Comment A], [Comment B] or [Comment C] key to enter a previous defined comment If no comment is saved, and you want to save one: Type in the comment desired using the alphanumeric keyboard Select the [Save as] key on the menu area.
- Page 482 Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) Select the desired Date. Click the [View] button to show the selected patient worksheet on the screen. 11.4.7 To print a Report 1. Select the “Print report” menu for the printout. Display depends on selected Application. Note A checkmark marks each summary report that is included in the printout report.
-
Page 483: Measure Setup
Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) Following window appears: Select whether to print only the current report or all available reports (all applications). Selection also affects “Print” Button in Worksheet Menu. Print all/Print Print all available reports or just the currently displayed report. Depends on setting above. - Page 484 Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) upper trackball key (right mouse button): no function in system desktop right trackball key (left mouse button): sets, fixates markers and activates pages/buttons etc. marked by the pointing device There is a National Language Support for the whole measurement package (generic and Note calculation measurements, Measurement setup and worksheets/reports).
- Page 485 Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) 11.5.2 To Exit from the Measure Setup Select the [Exit] button on the screen; select the [Exit] item on the menu area, or press [Exit] on the control panel. Setup changes are cancelled and not saved. Select the [Save] button with the mouse pointer (arrow) and press [Set] (right trackball key) to save the settings and exit the Measure Setup.
- Page 486 Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) Measure Preset = User 1 Measure Mode = Calc Sub Category = Biometry Imaging Mode = 2D/3D Study = Early Gestation Measure = YS (is the highlighted, relevant item) Application: Select the desired Application (e.g., Obstetric). Setting: Select a measure setting (e.g., User 1).
- Page 487 Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) 11.5.3.1.1 To Add a Sub Category, Study or Measure Item 1. Select the relevant item in (all) the digest column(s) and then highlight the one where you want to add an entry. For example: Biometry - 2D/3D - Early Gest. - Measure (= column where you add an entry) 2.
- Page 488 Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) To add an existing preset, select the desired entry (marked blue) from the sub window and then click on the [Add] button and then click on [Close]. To create a new entry, click on the [New] button. 4.1 When creating a new “Sub Category”...
- Page 489 Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) 3. In the “New Measure / Calc Item” window, select the item desired and then click [OK]. 4. In the displayed screen, select resp. enter: Measure Name: Either select a parameter from the drop down menu or enter it directly.
- Page 490 Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) Fetal Age These are normal ranges for estimating an unknown gestational age from the sonographically measured variable. Fetal Growth These are normal ranges for sonographically determined variables as a function of gestational age. Therefore, the Last Menstruation Period (LMP) must be entered first, otherwise the Growth Curve [Graph] won’t be shown in the worklist.
- Page 491 Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) - Move the mouse pointer to the field desired and press the [Set] key (right trackball key). - Type in the value and confirm with the [Enter] or the [Tab] key (keyboard). Click [+] to add additional lines. Click [-] to delete unwanted lines.
- Page 492 Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) 2. New Equation: (e.g., Fetal Growth) - Move the mouse pointer to the field desired and press the [Set] key (right trackball key). - Type in the equation using the keyboard. Use only the available symbols and abbreviations! Note + Addition ( left parenthesis...
- Page 493 Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) 11.5.3.1.2 To Delete a Sub Category, Study or Measure Item 1. Select the relevant item in (all) the digest column(s) and then highlight the entry to be deleted. For example: Biometry - 2D/3D - Early Gest. - GS 2.
- Page 494 Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) 2. Select the [Reorder] button. 3. Select the item desired (that have to be moved). 4. By means of these buttons, you can change the position of the selected item. 5. To finish, click the [OK] button. 11.5.3.1.4 To Edit a Sub Category, Study or Measure Item 1.
- Page 495 Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) Measurement Tool: If available, choose the desired Measurement Tool. For example: Select, if the GS (Gestational Sack) is to be measured using one Distance (value = GS diameter), or by using 3 Distances (mean value = GS diameter) “Selection Field”: Adjust the display in the worksheet and the measure result field.
- Page 496 Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) 2. To display the exact Fetal Age / Fetal Growth Table or Equation of the selected measurement parameter, click on the [Edit] button of corresponding field. Note To display the exact table, click on this button. 11.5.3.1.5 To Copy Settings 1.
- Page 497 Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) 2. If it is desired, select “Use Report Order” (check mark visible). 3. Choose the desired measurement parameter (e.g., BPD). 4. Use [Move Up] and [Move Down]. 5. To finish, click the [OK] button. 11.5.3.1.7 First Trimester OB in application GYN Additional study “Early Gestation”...
- Page 498 Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) Following “Add Measurement” menu appears in Gyn application: It is possible to select the application “OB” from the pull down menu and add OB measurements to the Gyn measurements menu. Results of OB measurements taken in the application Gyn are still displayed in the OB Report! Note There are two Reports when measuring Gyn and OB items in the application Gyn! 11.5.3.1.8 EFW (Estimated Fetal Weight)
- Page 499 Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) Estimation 1. Click on [Estimation] (the display is illuminated and the display about [New] key shows “Estimation”. 2. Click on [New] key. Following window appears: The procedure is the same as in “New Equation”, review Page 18-10 , except that “Author’s Note name”...
- Page 500 Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) Remark: Factory preseted tables/equations cannot be edited! EFW GP/SD 1. Click on [EFWGP/SD] (the display is illuminated and the display about [New] key shows “EFW GP/SD”). 2. Click on [New] key. Following window appears: 3. Select “EFW Table” or “EFW Equation”. The procedure is the same as in “New Table”...
- Page 501 Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) Rename To rename the selected term, click this button. On freeze 2D/3D start: Select the status on freeze in 2D/3D mode • None • Calc: Calculation menu appears automatically on Freeze • Generic: Generic measurement menu appears automatically on Freeze...
- Page 502 Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) Auto/Manual Trace: Select the Doppler measuring results, which should be displayed after each Auto Trace, Manual Trace and Real Time Trace measurement. Calculation - Ratio: Select either: Off or On If Ratio is “On” (check mark visible), select the desired ratio calculations that should be displayed in the Patient worklist.
- Page 503 Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) 11.5.3.3 Global Parameters Some parameters and possible adjustments depend on the “Table Preselection”. Table Preselection: Select the desired combination of measurements that fulfil the needs of the respective country. CUA/AUA for Hadlock: Select to use CUA (Composite Ultrasound Age) or AUA (Average Ultrasound Age) as default.
- Page 504 Measurements and Patient Worksheets (Reports) Fix Caliper by Print key: Select if the last measurement caliper of the currently performed measurement should also be fixed automatically, when • you press the [Freeze] key • you press the [Print A] or [Print B] key •...
-
Page 505: Chapter 12 - Archive
Chapter 12 Archive Describes the general functions of the archive, like image history, patient archive and exams. Voluson® S6/S8 Basic User Manual 5433669-100 Revision 4 12-1... - Page 506 Archive The Voluson® S6/S8 provides an Image Management System that allows fast and extremely easy image management. It allows users to view, print and transfer images stored in the Voluson® S6/S8. In addition, it allows users to send and receive DICOM images over the DICOM Network.
-
Page 507: Current Patient Dialog
Archive 12.1 Current Patient Dialog Press this key to shift from scan mode to Current Patient Dialog. Press this key to save the temporarily stored images from the Clipboard to the Archive. Patient Dialog The four parts of the Patient Dialog are: on page 12-4 Patient Data Area, see 'Patient Data Area' on page 12-4... - Page 508 Archive 12.1.1 Patient Data Area Patient ID: ID number max. 32 characters Last Name: patient’s last name max. 32 characters First Name: patient’s first name max. 15 characters Middle Name: patient’s middle name max. 15 characters DOB (Day of Birth) patient day of birth patient age ---- , female, male (selection in pull down menu)
- Page 509 Archive Picture Action Current Patient Opens "Current Patient” Screen, on page 12-3 see'Current Patient Dialog' Image History Opens the "Image History" Screen, see 'Image History' on page 12-30 Exam Opens the "Exam Review" Screen, see on page 12-31 'Exam Review' Review Worklist Changes to Worklist Dialog.
-
Page 510: Clipboard
Archive Picture Action Exit Closes the "Exam Review" dialog and returns to the running exam without saving any changes. Search To conduct a search enter the required criteria and press the [Search] button or the [Return] key on the keyboard, see on page 'Searching for a Particular Exam' 12-13... - Page 511 Archive • Saving Files to Archive, see'Saving Files to Archive' on page 12-9 12.2.1 Appearances of the Clipboard 12.2.1.1 Changing pages You can save a number of images onto clipboard that is only limited by the hardware. However, a maximum of 8 images can be displayed on one page of the clipboard. If a page is full, Archive automatically opens another page.
- Page 512 Archive • Pressing [OK] evokes the Current Patient Dialog and you can enter a Patient immediately. After entering the patient data and returning to scan mode using the [Start Exam] button the image or cine will be stored automatically and a message will show in the message window.
- Page 513 Archive Deletion using the trackball also works in the Exam Review. Note 12.2.3 Saving Files to Archive In Standard Configuration, the images and cines on the clipboard are automatically saved to Archive upon ending an exam. However, you can easily alter this. To alter, see 'End Exam on page 14-10 Button' Press the [End Exam] hardkey to save an exam and all its images.
-
Page 514: Patient Archive
Archive 12.2.4.3 Deletion Mark When you want to delete an image from the clipboard, mark it using the trackball, and a red cross appears in the image. The actual deletion will be performed upon pressing the [End Exam] hardkey. 12.2.4.4 Open Image For adding measurements or text to an image the image needs to be opened i.e. - Page 515 Archive 2.Archive Screen (Exam Only table) 12.3.1 Trackball allocation Press the left or right trackball key to set. Press the lower, left trackball key to send and image to dicom. For more details, see 'Data on page 12-25 Transfer Menu' Voluson®...
- Page 516 Archive Press the lower, middle trackball key to print an image.'Data Transfer Menu' on page 12-25 For more details, see Press the lower, right trackball key to export an image. For more details, see 'Data Transfer on page 12-25 Menu' Doubleclick on the left trackball key will open the Exam Review menu.
- Page 517 Archive If patient(s), exam(s) or image(s) are selected to be deleted, the following warning messages may appear if locked exams are involved: Message Description Your selection contains Exams that are locked and cannot be deleted! Your selection contains Exams that are locked and cannot be deleted! Do you want to delete the unlocked Exams?
- Page 518 Archive or show all patients and exams. Using the radio button below you can change the display format. You can choose to display Patients and exams or the exam list only. In System Setup - General - Patient Info Display there is a checkbox “Automatically List Note Patients”...
- Page 519 Archive and enter its value in the neighbouring field. Finally press the [Search] key to perform the search using the entered criteria. You can also start a search from the Current Patient Data Menu. See 'To Search in the Patient Note on page 4-26 List'...
- Page 520 Archive • If you select an exam, all its images will be displayed in the Exam Image area. • To select more than one patient, hold down the [Ctrl] key on the keyboard and select the patients with the left trackball key. 12.3.3.4 Image Area Use the arrow keys on the right-side margin to skim through the images.
- Page 521 Archive Operation: Select search criteria category from the reduced search drop down. Enter search criteria. Note Searching with “or” is not possible in this mode. Press [Query Patients]. This is only possible in "Patients&Exams" View. Note The list of Patients is filled with the patients from the DICOM Server that match the given criteria.
- Page 522 Archive Select one ore more patients from the list. (In the Archive - Patient Area, all buttons, except data transfer, are disabled.) Press [Query Exams]. This is only possible in "Patients&Exams" View. Note The list of exams is filled with the exams of the selected patient. If more than one patient was selected, exams for these patients are available when switching between patients.
- Page 523 Archive In the "Archive - Image" part of the menu, all buttons are now enabled. Go to Data Transfer. The "Import" button is now available. Select a patient or exam and press "Import" to import the selected data into the local archive.
- Page 524 Archive Picture Action Current Patient Opens "Current Patient” Screen, on page 12-3 see'Current Patient Dialog' Image History Opens the "Image History" Screen, see 'Image History' on page 12-30 Exam Review Opens the "Exam Review" Screen, see on page 12-31 'Exam Review' Use as Current Uses the currently selected patient as the current patient and changes back to the...
- Page 525 Archive Use the Filing Card tabs to navigate between the application areas, see 'Application Area' page 12-4 . To exit the Edit Data Menu press either: [Save&Return] to save the modified data and return to previous operating mode. or [Cancel&Return] to discard the modified data and return to previous operating mode. 12.3.4.3 Data Transfer Menu The options in the data transfer menu depend on what is selected on screen.
- Page 526 Archive Picture Action Current Patient Opens "Current Patient” Screen, on page 12-3 see'Current Patient Dialog' Image History Opens the "Image History" Screen, see 'Image History' on page 12-30 Exam Review Opens the "Exam Review" Screen, see on page 12-31 'Exam Review' Reopen Exam Allows you to reopen old exams, see on page 12-22 .
- Page 527 Archive • Reload a data set, change it (rotation, color,...) and save it again using the programmable keys • Create a new acquisition (2D, 3D, 4D) and save it using the P-buttons. 12.3.5.2 Exam Details Exam Details: Allows you to view the Exam Details. Use the scroll bar on the left to scroll up and down.
- Page 528 Archive 12.3.5.4 Data Transfer Menu The options in the data transfer menu depend on what is selected on screen. The options available, when the exam table is active, are listed below and described in 'Data Transfer on page 12-25 Menu' •...
- Page 529 Archive 12.3.6.2 Data Transfer Menu The options in the data transfer menu depend on what is selected on screen. The options available, when the image area is active, are listed below. For a detailed account of functionality, please, refer to: Data Transfer Menu 'Data Transfer Menu' on page 12-25 •...
- Page 530 Archive The selected images of the exam(s) will be sent to the selected DICOM storage destination. Press [DICOM Config] to customize your DICOM server. For more details, see 'Connectivity' on page 13-30 12.3.7.2 Print After selecting the exam(s) to be printed using the trackball and the left or right trackball key [Set], click the [Print] button.
- Page 531 Archive [Properties] will open the DICOM printer confige menu. 12.3.7.3 Export This enables the export of images in BMP, JPG, TIFF; Cines in AVI, MOV or MPG ; Images and Cines can be exported in PC format (JPG & AVI) or MAC format (JPG & MOV) and Volumes in VOL or RAW to a DVD/CD+(R)W, an MO disk or a mapped Network drive.To save all Patient Data and images use either compressed or uncompressed 4DV.
- Page 532 Archive Depending on the file format, the (image) size, quality and AVI-codec can be adjusted. The AVI will be saved as a loop (start -> end -> start) Set the “Anonymize” checkbox, to hide patient information from the header of US images.
- Page 533 Archive • Include SR: Includes structured report • Anonymize function: Anonymize patient data 12.3.7.4 Fast Export Fast export is only possible if an USB storage device is connected and will only save on the Note last connected USB drive. For Fast Export of JPEG images, press the [Prt Sc] key on the keyboard: 12.3.7.5 Import Choose, where to import your image from, type in a filename, or select your file from the displayed ones in your selected folder.
-
Page 534: Image History
Archive Press [Import] again and the selected exams or images and patients will be copied onto the harddisk. 12.3.7.6 Delete After selecting the patient(s), exam(s) or image(s) to be deleted by using the trackball and the right trackball key [Set], click the [Delete] button. Select a patient from the Patient List and the following dialog appears: (1) This filed shows the number and type of items you have selected to delete! Choose your desired answer. - Page 535 Archive Picture Action Exam Buttons Used to select an exam and indicate the selected exam (button pressed). Displays the Exam Date and Time and the string “Current Exam” to mark the current Exam. Left/Right Arrows Used to scroll through the individual images.
- Page 536 Archive Picture Action Repro Reproduce a scan. on page 12-36 'Repro' Data Transfer Switches to Data Transfer Menu, see 'Data on page 12-25 Transfer Menu' End Exam Closes the active exam. This button is only available, if the exam displayed in "Exam Review"...
- Page 537 Archive Picture Action Image Comment Adds an image comment to the according image. Button looks differently, if an image comment already exists for the according image, see 'Commenting' on page 12- 37 . Acquisition Type Displays the acquisition type of the according image and changes it, on page 12-38 .
- Page 538 Archive 12.5.1.1 Exam Review Screen 12.5.2 End Exam 12.5.2.1 Setup Switch “End Exam Dialog” OFF End Exam function is done immediately when pressing the above buttons. 12.5.2.2 Setup Switch “End Exam Dialog” ON • If an incomplete measurement exists, a dialog window appears on screen: •...
- Page 539 Archive 12.5.3 Reload When the "Reload" button is pressed, the selected image is reloaded into the system. This also means that the exam that the image belongs to is reopened. The other images belonging to the exam are displayed on the clipboard and can also be reloaded to the clipboard.
- Page 540 Archive Gray/ chroma in all modes OTO, L/R and U/D in 2D Mode Base line and Invert in PW and CW Color Display Mode, Color Invert, Gently Color, Color Maps, Color On/Off are available as during examination. Reload of DICOM data: It is possible to perform the following functions after a reload of DICOM data (=Bitmaps) from internal archive into the system: Make new measurements...
- Page 541 Archive The repro can now be loaded: • Without new patien/exam • with new exam • with new patient 12.5.5 Commenting 12.5.5.1 Exam Comment Press the [Exam Comment] key. The following window pops up, asking for an exam comment: This is the same comment as in the comment field in the current patient dialog. If an exam comment already exists, the dialog displays the current exam comment, which can then be edited or deleted (max.
- Page 542 Archive The image comment is different from the exam comment in that it can differ for each image. If an image comment already exists, the dialog displays the current image comment, which can then be edited or deleted (max. 40 characters). Press [OK] to save and exit.
-
Page 543: Selecting Exams
Archive Note If the current exam is still active, a warning message will be displayed before loading the 3D or Real Time 4D volume dataset. For details about Raw Format and Multiframe review: Archive Configuration'Connectivity' on page 13-30 . One Image Forward One Image Back Display: Displays image numbers according to the following format (current Image number/total number of images) - Page 544 Archive • To Delete Exams 'Data Transfer Menu' on page 12-25 • To Send Exams 'Data Transfer Menu' on page 12-25 • To Print Exams 'Data Transfer Menu' on page 12-25 • on page 12-25 To Export Exams 'Data Transfer Menu' •...
-
Page 545: Settings
Archive • The user can confirm the capacity of an appropriate medium. The number of all exams of the exam list; the number of currently selected exams, the number of images and the capacity of selected exams are displayed automatically at the right and upper part of the Exams List. - Page 546 Archive This page was intentionally left blank. Voluson® S6/S8 Basic User Manual 12-42 5433669-100 Revision 4...
-
Page 547: Chapter 13 - Utilities And System Setup
Chapter 13 Utilities and System Setup Describes the general functions of the utilites and system setup, like setup procedures and backups. Voluson® S6/S8 Basic User Manual 5433669-100 Revision 4 13-1... -
Page 548: Utilities
Utilities and System Setup 13.1 Utilities [Utilities] hardkey . After selecting [Utilities], the screen changes to the “Utilities” menu. In the Utilities menu you find keys for programming the System and keys to switch on functions. Voluson® S6/S8 Basic User Manual 13-2 5433669-100 Revision 4... - Page 549 Utilities and System Setup To leave the Utilities Menu for the previous operating state press the [Exit] key. for programming review: ( 'System Setup' on page 13-12 ) Measure Setup ( 'Measure Setup' on page System Setup 11-107 ) Biopsy Setup ( 'Biopsy Setup' on page 5-13 ) switch on functions review: on page 13-3 ) Monitor ('Monitor'...
- Page 550 Utilities and System Setup 3 pre-defined monitor settings can be set: Dark Room, Semi-Dark Room and Light Room. The monitor can also be adjusted in brigthness and contrast using the flipswitches. For detailed adjustment press the [OSD Controls] button on the screen. The OSD menu will appear on the screen: Adjust Brightness, Contrast, Backlight and Adjust the monitor colors.
- Page 551 Utilities and System Setup All values can be set back to default values when selecting a default monitor setting. Note 13.1.3 Histogram With this function the gray scale or color distribution within a marked Region of Interest (ROI) will be graphically displayed. Three histograms may be shown on the screen simultaneously. There are three possibilities to calculate the gray scale or color distribution: •...
- Page 552 Utilities and System Setup 5. The upper trackball key changes from position to size of the ROI and back. 6. Select the [Calculate] key on the menu area or press the right or left trackball key. The histogram and corresponding number (left below the box) will be calculated and displayed. Remarks: •...
- Page 553 Utilities and System Setup To exit the Histogram select [Exit] on the menu area. 13.1.3.2 3D Histogram Operation: 1. Store a 3D, a 3D/PD or a 3D/CFM mode image. 2. By selecting the [Utilities] and the [Histogram] key the Histogram menu appears on the screen.
- Page 554 Utilities and System Setup The selected Thermal Index is displayed in the [TI select] key. Remarks: • While you are scanning, notice the index numbers you are using and which controls affect the readings. • Try to keep the index numbers as low as you can, while maintaining diagnostic information within the image.
- Page 555 Utilities and System Setup Lock Screen is a security function. It protects the system by password against unwanted intruders. There are two ways to activate Lock Screen: • by pressing the [Lock Screen] softkey • as soon as the screensaver starts When Lock Screen is active, a full-screen dialog with no title bar or menu appears.
- Page 556 Utilities and System Setup A valid password must be at least 6 characters long and has a maximum length of 80 Note characters. A password must contain at least 2 non-letter characters, 0..9 or ! @ # $ % ^ * ( ). Confirm that you want Lock Screen enabled with [Save &...
- Page 557 Utilities and System Setup Press [Lock Screen] to activate the Lockscreen function. 13.1.6.3 Emergency Mode When Lock Screen is active, there are two possibilities to enter the system again. Firstly you can gain full access by typing in the password or secondly you can click the [Emergency] softkey to enter in Emergency Mode.
-
Page 558: System Setup
Utilities and System Setup 13.1.6.4 Changing Password When Lock Screen is active, you can also change the existing password. Press the the [Change PWD] button. The following dialog appears: Enter the current password. Then enter and retype the new password. A valid password must be at least 6 characters long and has a maximum length of 80 Note characters. - Page 559 Utilities and System Setup System setup desktop: for example the opened page: “General” In general operations are done with the trackball and the trackball keys (mouse emulation). Trackball (mouse position): positions the pointing device (arrow) on the desktop left trackball key (left mouse button): sets, fixates markers and activates pages/buttons etc. marked by the pointing device upper trackball key (right mouse button): no function in system desktop right trackball key (left mouse button): sets, fixates markers and activates pages/buttons etc.
- Page 560 Utilities and System Setup 13.2.1 To invoke the Setup Procedure To invoke the Setup procedures select the [System Setup] key in the menu "Utilities" to activate the setup desktop on screen. Select the [Utilities] Hardkey. The menu area changes to the Utilities menu. Then select [System Setup]. 13.2.2 To Exit from the Setup Procedure Select the [Exit] key on the menu area.
- Page 561 Utilities and System Setup Select the [Exit] button with the mouse pointer (arrow) and press [Set] (right/left trackball keys). Setup changes are cancelled and not saved. Select the [Save&Exit] button with the mouse pointer (arrow) and press [Set] (right/left trackball keys). Setup changes are saved. 13.2.3 General 13.2.3.1 General filing card 13.2.3.1.1 To Enter Date, Time and Time Zone...
- Page 562 Utilities and System Setup Close the sub-window with [Ok] to save the changes or [Cancel] to return to the “Setup Page” without saving the changes. 13.2.3.1.2 To Change the Time Format • Select the [Time Format] button to activate a sub-dialog window to choose the preferred time format.
- Page 563 Utilities and System Setup 13.2.3.1.3 Date Format Activate the corresponding option button (only one can be active) to select the order of the date format desired (day-DD, month-MM and year-YY). 13.2.3.1.4 Display (each button is an on/off switch) Activate the desired option buttons. •...
- Page 564 Utilities and System Setup This selection is not influenced by general language selection and vice versa. Only languages Note available on the system are listed. If a new language is installed, it is automatically added to the list. 13.2.3.1.9 Presentation Mode Select the [Presentation Mode] button to evoke the following menu to configure and start the presentation mode.
- Page 565 Utilities and System Setup 13.2.3.2 User Settings Steering Angle: If the selected probe supports steering the possible angles are displayed. If the selected probe does not support steering, the input field remains gray (disabled). Overview Window: Position: Off, Left Top, Left Bottom (default), Right Top or Right Bottom Size: Large, normal (default) or small (chapter 'To Save a User Program' on page 13-...
- Page 566 Utilities and System Setup Clear text on If this checkbox has been selected all annotation will be cleared, when you untoggle Unfreeze: the [Freeze] key. Zoom Key: While in Zoom Pre Mode, select which Zoom Mode (Pan Zoom or HD Zoom) is activated automatically, if the Zoom hardkey is pressed again.
- Page 567 Utilities and System Setup It is possible to select which user program shall be started when a new exam is created. Note Setting – Application: Select a program button and press [Set] (labeling area and cursor are displayed inside). Enter a new program label using keyboard or overwrite the existing label or don’t change an existing program label, if the same term is desired.
- Page 568 Utilities and System Setup The “3D/4D Settings” menu appears on the monitor. 2. Select a program button and press [Set] (labelling area and cursor are displayed inside). 3. Enter a new program label using keyboard or overwrite the existing label or don’t change an existing program label, if the same term is desired.
- Page 569 Utilities and System Setup The “Auto Text” menu appears on the screen. 2. Select an Auto Text button and press [Set]. The cursor appears inside the selected button. 3. Enter the Text with the keyboard. 4. Select the next Text button and so on ..5.
- Page 570 Utilities and System Setup The “Auto text Application select” menu appears on the monitor. Operation: Open the Application window with the [Application] button. Choose the application desired (select the corresponding application button). After a selection the first Auto Text page of the selected application appears on the screen. Click [Return] to return to the previous Text Auto page, without saving changes.
- Page 571 Utilities and System Setup The “Trackball Speed” menu appears on the monitor. 2. Adjust the desired Trackball Speed for each function (low ´ high) using the trackball and the right or left trackball key [Set]. 3. Select [Save] or [Save&Exit]. The trackball speed settings are saved in the database. Exit: Back to the last active menu without saving.
- Page 572 Utilities and System Setup 13.2.3.3.1 Exam Table Columns Use the trackball to choose the contents of the last two columns of the Exam table: Place the cursor on the column heading you wish to change. Press the left/right trackball key to evoke a Drop down Menu. Select the information you wish to be displayed from the Drop Down List.
- Page 573 Utilities and System Setup 13.2.3.3.5 Automatically List Patients Setting this checkbox automatically displays all available patients when opening the Current Patient Search or the Archive dialog. If this box is not checked, the patients are only listed after the [Show all] button has been pressed in the worklist dialog.
- Page 574 Utilities and System Setup For further details and explanations refer to the Service Manual of the system. Note 13.2.4.2 System Info In the “System Info” page the Software/Hardware version that is installed in the system can be seen. Serial Number: Displays the serial number of the system. System Info Software: Display of the current software version of the system.
- Page 575 Utilities and System Setup 13.2.4.3 Options This page shows all available system options and their state Possible states are:. Demo Option is activated for demo and expires on the date shown in the “Valid” column. Inactive Option is not activated. Permanent Option is permanently activated (purchased).
- Page 576 Utilities and System Setup 13.2.5 Connectivity 13.2.5.1 Peripherals Recorder Type: Only internal DVR is possible. Add Printer: Allows you to install a new printer and opens the Windows” Add Printer Wizard”. Printer Settings Select a printer from the drop down menu and then press [Edit], to edit the printer settings under “Windows Properties”.
- Page 577 Utilities and System Setup 13.2.5.2 Device Setup For detailed description review: • (chapter 'DICOM DICOM Configuration on page 13-31 ) Configuration' • (chapter 'DICOM Queue DICOM Queue Status Status' on page 13-37 ) • (chapter 'Network Network Configuration on page 13-39 ) Configuration' •...
- Page 578 Utilities and System Setup Press the [Add] button to add another server to the list. The following menu will appear: • Edit Press the [Edit] button to edit the selected server from the list. The following menu will appear: Make your edits, then press [Save&Exit] to save them. Press [Exit] to discard them. •...
- Page 579 Utilities and System Setup Press the [Delete] button to delete the selected server from the list. The following dialog will appear: Confirm this dialog with OK. To Specify a DICOM Address Select the [DICOM Configuration] button (in the System Setup - Network page) to display the DICOM Configuration window.
- Page 580 Utilities and System Setup Services: Select [STORE] to send screen images, 2D cine sequences and 3D/4D data to a DICOM server (e.g., Radworks Server). Select [STORE 3D] to send 3D/4D data only (volumes and cine sequences) to a different store server (e.g., PC with Software 4D View installed) than screen images and 2D cine sequences.
- Page 581 Utilities and System Setup Colorselect either Color, Image Sizeselect either Original or 640x480 Grayscale or Automatic 2D Compressionselect either 2D JPEG Qualityselect the desired JPEG-compression factor NONE or JPEG Cine Compressionselect either Cine JPEG Qualityselect the desired JPEG-compression factor NONE or JPEG Volume Compr.
- Page 582 Utilities and System Setup By selecting Service [PRINT] the Printer Setup fields are available to adjust the printer configuration. WORKLIST With a [WORKLIST] service a filter (mask) can be selected especially for patient data marked with Modality "Ultrasound". Enable Private Tags for communication with a ViewPoint system. The Merge option determines if data from a worklist server should be merged with locally stored patient data.
- Page 583 Utilities and System Setup Note “Associated Storage” provides a list of all available STORE or STORE3D destinations. Select the destination that the image data is sent to. If images are sent to more than one STORE or STORE3D destination, on ST. COMMIT destination is necessary for each STORE/STORE3D destination.
- Page 584 Utilities and System Setup If the transfer was successful, but a storage commitment request was not yet successful, the Note images receive the status “sent”. As soon as the storage commitment was successful the entries (both images and storage commit) are deleted from the list. Select the [Retry] button to retry selected exam.
- Page 585 Utilities and System Setup As soon as the [Process Queue] button is selected, the system continues to send the data. Show Information: With this function more information about the failed DICOM transfer can be requested. This button is enabled if a failed DICOM transfer is selected in the Queue list and than the following window pops up if the button is pressed: If Image is stored in archive the additional button “Go to Archive”...
- Page 586 Utilities and System Setup 13.2.5.2.4 Archive Configuration Select the [Archive Configuration] button to display the following window. Image Compressionselect either NONE 2D JPEG Qualityselect the desired or JPEG JPEG-compression factor Img. Cine Compressionselect either Img. Cine JPEG Qualityselect the NONE or JPEG desired JPEG-compression factor Volume Compr.
- Page 587 Utilities and System Setup Ultrasound images are consuming a lot of the system’s memory resources. Therefore, the JPEG-compression method can be applied to the images to reduce their size. When selecting the JPEG-compression less than 100% a message appears. Volume Wavelet Quality is only enabled if Volume Compression is wavelet lossy. Note Whenever lossy compression is activated the following dialog appears: If the volume contains color information, the color part of the volume is compressed with a...
- Page 588 Utilities and System Setup The configuration process will start automatically, and after a few seconds waiting, the field “Connection Info” on screen should say “connected” and the other values should have been entered automatically. If not ask your local system administrator for help! The WLAN security has to be adjusted to prevent viruses and to ensure data protection.
- Page 589 Utilities and System Setup Define and switch between different network settings for all your work environments to further improve Voluson© S6/S8’s portability. The following settings are stored in a network profile: • All DICOM settings and configurations • Static IP address, gateway, network mask, DNS •...
- Page 590 Utilities and System Setup After clicking the New button the following dialog appears: Profile Name textfield. There are to options to Specify a name for the network profile in the Copy Settings from: • Current Settings The current network setup of the system is stored in the network profile. •...
- Page 591 Utilities and System Setup Press the [Stop Device] button. To Map the Network Drive Press the [Map Network Drive] button. The following window appears: This button displays a dialog, which is used to map a network drive to the system. (NW 1 - NW 5).
- Page 592 Utilities and System Setup If a USB device was not recognized you can reinstall it. Select the USB device from the list. Press the [Reinstall Drive] Button . The following message appears. Confirm with [OK]. The following dialog appears. After the rescan, the following message appears. Confirm with [OK].
- Page 593 Utilities and System Setup When both modes are possible and the user changes from complete mode to fast mode a Note dialog will appear, saying: It is highly recommended to use complete erase mode to avoid problems with the DVD/CD. Do you really want to use the fast erase mode? 13.2.6 Backup There are 2 tabs on the Backup page.
- Page 594 Utilities and System Setup 13.2.6.1.1 Save Image Settings • With this function the internal database is saved to the selected read/write device. The Image Settings contain: • Image settings • Auto Text • Setup settings (language, date format, screensaver on/off, etc.) •...
- Page 595 Utilities and System Setup 1. Click on the [Load] button of the “Image Settings Only” group in the System Setup - Backup page. The Load/Save window is displayed. 2. Choose the media (e.g., DVD/CD+(R)W) and click the [Load] button. 3. Select the appropriate file and click [OK]. The Load option window appears. 4.
- Page 596 Utilities and System Setup Click the plus [+] sign to open the content tree. User Progra ms: Select the appropriate group (all probes, probe & all applications, etc..) down to the final single program within the displayed tree. Click the [Arrow] button to copy the selected item into the Load Data field.
- Page 597 Utilities and System Setup • Measure Setup Settings (user specific measure settings) • Voluson® S6/S8 settings (general settings such as language, time/date format and the enabled options) • Windows Network Settings (network settings including the computer name) • Serviceplatform (state of the serviceplatform) •...
- Page 598 Utilities and System Setup After copying the data,confirm the next message with [OK] to reboot the system and start the application again. EXIT: Exit without saving a backup. Remarks: • It is possible to store more than one backup on a destination. The backups reside in fullbackup ”-folder found at the root of the drive (e.g., z: subfolders of the main “...
- Page 599 Utilities and System Setup 13.2.6.1.4 Load Full System Configuration There are circumstances where it is not possible to load (restore) all the data. The following rules specify the restrictions: Generally, only restoring data from an older to a newer software version is possible. Loading a backup into a system that has a lower software version than the system the backup was created on is prohibited.
- Page 600 Utilities and System Setup Select the [Next] button. The following window will be displayed. Select the data to be restored to the Voluson® S6/S8 system. For description of the checkbox names review: 'Save Full System Configuration' on page 13-50 The data from the backup always replaces the corresponding data on the Voluson® S6/S8 system! Select the [Next] button again to start the restore process.
- Page 601 Utilities and System Setup After copying the data, the system reboots and the application starts again. 13.2.6.1.5 Delete Full System Configuration To delete an existing backup, click on the [Delete] button of the “Full System Configuration” group in the System Setup - Backup page. The Full System Configuration Delete window is displayed.
- Page 602 Utilities and System Setup 13.2.6.1.6 Working with external USB-Devices When an external USB-storage device is connected to the system, such as a memory stick or a hard disk, Windows detects the device and automatically installs a driver. Afterwards the device is accessible using the drive letter the system assigned to it (e.g., G:). Before an external USB-device (e.g., USB-memory stick) can be disconnected, the system has to be informed about the removal of the device! For this purpose every last dialog of “Full System Configuration Save”...
- Page 603 Utilities and System Setup Choose the location by clicking one of the radiobuttons. Then select the file, you desire. Confirm your choice with [Next]. The following window appears. Here you can choose between [Patient View] and [Exam View]. Depending on which view you choose you can select patients or exams to load from the archive.
- Page 604 Utilities and System Setup After selecting the patients or exams you desire confirm with [Next]. The following dialog appears: Confirm with [Yes]; (If you do not want to restore the backup now, press [No].) The Process bar appears. As soon as the loading procedure is finished the following window appears. Confirm with [OK].
- Page 605 Utilities and System Setup 13.2.6.2.2 How to Save an Archive Press the [Save] button. The following menu appears: Check the checkbox “Remove Local Images after Backup”, if you want to save hard disk space and remove the backed-up exams from your local hard disk. Then choose the exams, you wish to backup, according to date.
- Page 606 Utilities and System Setup If you want to choose exams or patients arbitrarily, press [Advanced]. The following window appears: Here you can choose between [Patient View] and [Exam View]. Depending on which view you choose you can select patients or exams to save in your backup. It is also possible to choose a singular patient or a singular exam.
- Page 607 Utilities and System Setup If you have chosen CD/DVD as your saving destination, then the following dialog will come up, asking you to label your CD or DVD. Confirm with [OK]. Confirm with [Yes]; (If you do not want to start the backup now, press [No].) The Process bar appears.
- Page 608 Utilities and System Setup 13.2.8 Scan Assistant Settings 1. Choose the application that is required 2. Shows all created Scan Assistant lists. To edit or add Scan Assistant list, see (5) 3. Items in the selected Scan Assistant. 4. Load Factory and Load Last Saved: Load Factory Load the saved Factory Scan Assistant, see Save Factory Load Last Saved...
- Page 609 Utilities and System Setup 8. Add annotation: When pressing the [Abc] key. See 'Image Annotation' on page 4-27 . The annotation will appear on the selected position. 9. Position of the Scan assistant annotation. Choose between “Top-Left” and “Bottom-Left”. Voluson® S6/S8 Basic User Manual 5433669-100 Revision 4 13-63...
- Page 610 Utilities and System Setup This page was intentionally left blank. Voluson® S6/S8 Basic User Manual 13-64 5433669-100 Revision 4...
-
Page 611: Chapter 14 - Programmable Keys
Chapter 14 Programmable Keys Describes the general function of the programmable keys. Voluson® S6/S8 Basic User Manual 5433669-100 Revision 4 14-1... -
Page 612: Where To Program The Keys
Programmable Keys There are three different kinds of keys which are programmable, P1, P2, P3, P4; Start Exam and End Exam. So there are six keys altogether. They are all programmable for printing, sending and saving data. How to use the P1, P2, P3, P4 key Use the trackball and the trackball buttons to press a P-key. - Page 613 Programmable Keys 1. Keys: Select the key you would like to program. 2. Key actions: Choose the action(s) you want the key to do. There are different actions for different keys. The tab “Detailed Settings” is only available for Note the P-keys.
-
Page 614: P-Keys
Programmable Keys 14.2 P-keys There are 4 different actions which can be programmed onto a P-key. Each P-key (P1-P4) can be programmed to perform several actions, except when you choose “4. Record on an DVR Recorder”. Save to Clipboard: If the P-Button is configured to save the image to the clipboard, the current image or cine (depending on the settings in the button configuration page) is moved to the clipboard. - Page 615 Programmable Keys Control Button Description DVR button At the first push: The DVR menu appears. At the second push: The DVR menu disappears. Programmed P- At the Px key push: • button If the DVR is not recording: Recording is started. •...
- Page 616 Programmable Keys Sends a volume cine to external destination. Sends the selected item to a black&white printer. Sends the selected item to a color printer. DVR REC mode DVR REC-PAUSE mode DVR status: Disabled Confirm Scan Assistant. If an option is not possible, a little red cross is displayed in front of the icon. e.g.:when a 2D Cine can not be saved as a 3D Volume.
- Page 617 Programmable Keys Send: There are three checkboxes. You can choose up to three different destinations, where to send your images or cines to. Choose the destination from the drop-down list. on page 13-30 To alter the drop-down list, see'Connectivity' Print: There are three checkboxes. You can choose up to three different destinations, where to print your images or cines or reports.
- Page 618 Programmable Keys Automatic: Basically, save the data that is displayed on screen. In Freeze Mode: save a single 2D image In Auto Cine Mode: save Cine as defined in Auto Cine Menu In write mode save Cine according to “Default Cine Length”...
-
Page 619: Start Exam Button
Programmable Keys 14.3 Start Exam Button On Start Exam activate: There are two checkboxes. • Auto Start Acquisition: If you check, the system automatically starts with predefined setting. a. Probe: Select the Probe in the probe drop down list. This list contains all probes currently connected to the system. -
Page 620: End Exam Button
Programmable Keys 14.4 End Exam Button Archive: This checkbox is set per default. If set, it moves the complete content of the clipboard to the Internal archive. Note If this checkbox is not set, there is no possibility to save the clipboard content, apart from entering Utilities - System Setup - Connectivity - Button Configuration and setting this checkbox again! Transfer Worksheet: There are three checkboxes. - Page 621 Programmable Keys Send: There are three checkboxes. You can choose up to three different destinations, where to send your images or cines to. Choose the destination from the drop-down list. on page 13-30 To alter the drop-down list, see'Connectivity' Print: There are three checkboxes. You can choose up to three different destinations, where to print your images or cines or reports.
- Page 622 Programmable Keys This page was intentionally left blank. Voluson® S6/S8 Basic User Manual 14-12 5433669-100 Revision 4...
-
Page 623: Chapter 15 - Connections
Chapter 15 Connections Describes the external devices and how to install / connect them. Voluson® S6/S8 Basic User Manual 5433669-100 Revision 4 15-1... -
Page 624: How To Connect Auxiliary Devices Safely
Peripherals, that have been ordered simultaneously with the Voluson® S6/S8, are usually already mounted and connected. The first mounting and connecting will usually be performed by a GE system technician. Basic Concept: Video Copy Processors (VCP) and Video tape recorders (VTR) are to be connected here as described in the chapter Connections. -
Page 625: To Connect Internal And External Accessories
Auxiliary equipment with direct mains connection requires galvanic separation of the signal and / or control leads. Only accessories explicitly approved by the system manufacturer GE Healthcare shall be used in connection with this ultrasound system. 15.2 To Connect Internal and External Accessories... -
Page 626: Connection Between Internal I/O And External I/O
Connections 15.3 Connection between Internal I/O and External I/O 15.3.1 Internal and external I/O Voluson® S6/S8 Basic User Manual 15-4 5433669-100 Revision 4... - Page 627 Connections 15.3.2 Power Supply (rear side) Mains IN Mains voltage according to rating plate. Voluson® S6/S8 supports the free voltages. Potential equilibrium connection Protective earth (ground) connection 15.3.3 Power Supply (for on-board peripherals) There is one connectors for on-board peripherals: The outlet voltage is identical on the mains voltage.
- Page 628 Connections Connector Name Description Main Monitor Out Connector for main monitor. OPIO Connector Connector for User console. USB 2.0 x 3 USB port connectors, used for peripherals (e.g.printer) Speaker Connector for system speaker SATA Connector for System DVD Drive Serial Serial port (DMC, Foot switch) DVI Output DVI output connector for external Monitor.
-
Page 629: Connection Of Peripherals
Connections 15.3.4.2 Upper OPIO Panel The Upper OPIO panel can be found on the upper side of User Interface. Connector Name Description USB 2.0 User accessible USB 2.0 port review also: Technical data/ Information: Interfaces (chapter 'External Inputs and Outputs' page 16-29) . - Page 630 Connections 15.4.2 Foot Switch (GP 26) Connection (chapter 'Peripherals' on page 16- To adjust the Foot Switch see: System Setup: Peripherals 30 ) . Voluson® S6/S8 Basic User Manual 15-8 5433669-100 Revision 4...
-
Page 631: External Monitor
Connections 15.4.3 WLAN Adapter on page 13-30 To configure the WLAN adapter see'Connectivity' 15.5 External Monitor The External Monitor can be mounted with a special wall mount. For connection and wall mount installation please see Installation Manual deliverd with the external monitor. -
Page 632: Isolating Transformer Noratel Imed 300Wr
Connections 15.6 Isolating transformer Noratel IMED 300WR 15.7 ECG Module • The ECG kit consists of a ECG module and a patient connection cable. • The connector of the patient connection cable is on the right side beneath the keyboard. Voluson®... - Page 633 Connections • The ECG Module is used for acquiring an ECG signal to be displayed with the ultrasound image. • The signal input of the ECG module is equipped with a protection against high voltages used for defibrillation. (Type CF) 15.7.1 Handling 1.
- Page 634 The socket must be equipped with a grounded conductor. If necessary a potential equilibrium must be connected. • Only the patient cable provided by GE Healthcare may be used. Consequently, only push-button electrodes may be used. • Take care that neither bare parts of one of the electrodes nor the patient can get in contact with conductive parts (e.g., metal parts of the examination bed, trolley, or...
- Page 635 Connections 15.7.3 Care and Maintenance, Repairs • Electrodes and the cables should be handled with the usual care. Refer to manufacturer"s instructions in concerns of cleaning and maintenance. • Refer to manufacturer"s instructions concerning sterilization. • Necessary repairs must be performed by authorized service personnel only! 15.7.4 ECG Display This function inserts an ECG line in the display of the image.
- Page 636 Connections Adjust ECG amplitude (0 to 100 in 10 steps). Return to the main menu. The ECG function remains active. Freeze the image. The most recent information is always on the right edge of the image. When moving the trackball a indicator (small vertical line) is inserted on the ECGcurve and indicates the temporal position of the 2D image in relation to the recordedECG line.
- Page 637 Connections • The green ECG line indicates to which image the trigger mark is related. • The Cine-Split Function is also possible in Auto Cine. Press [ECG Line] to switch off the ECG Display function. The button is inactivated. Press [ECG Line] again to switch on the ECG Display function. The button is activated.
- Page 638 Connections This page was intentionally left blank. Voluson® S6/S8 Basic User Manual 15-16 5433669-100 Revision 4...
-
Page 639: Chapter 16 - Technical Data / Information
Chapter 16 Technical Data / Information All technical data of the ultrasound device. Voluson® S6/S8 Basic User Manual 5433669-100 Revision 4 16-1... -
Page 640: Safety Conformance
Technical Data / Information 16.1 Safety Conformance TYPE: Voluson MODEL: Voluson® S6/S8 SERIAL NUMBER Position: Rear side of the system on the identification plate. Rating plate Example: • Listed to UL 60601 by a Nationally Recognized Test Lab • Certified to CSA 22.2, 60601.1 by an SCC accredited Test Lab •... -
Page 641: Physical Attributes
Technical Data / Information • IEC*61000-4-4: 2kV burst on power lines • IEC*61000-4-4: 1kV burst on data lines, length above 3m • IEC*61000-4-5: 1kV differential mode 2kV common mode • IEC*61000-4-6: 150 kHz-80 MHz, 0.1V (80% AM, 1kHz) • IEC*61000-4-8: Power frequency magnetic field •... - Page 642 Technical Data / Information Height: min. 975 mm (38.4 in); max. 1725 mm (67.9 in)adjustable with electrical motor Weight: Basic system (without accessories) approx. 90 kg 16.2.2 Power Supply Power 220V - 240VAC; 100V - 120 V AC requirements: Frequenzy: 50 Hz, 60 Hz (± 2%) Power nominal 900VA including all optionsTypical power consumption with 500VA load consumption:...
-
Page 643: System Overview
Technical Data / Information 16.2.6 Monitor Flat panel monitor: 19’’ high-resolution LCD display with DVI interface Resolution: SXGA 1280 x 1024 pixel Tilt/Rotate: tilt: + 10˚ / -90˚ rotate: +/- 90˚ Controls: Digital brightness & contrast adjustment Dark Room, Semi Dark Room and Bright Room Safety UL60601-1 and IEC60601-1 classification:... -
Page 644: Screen Formats
Technical Data / Information High PRF Doppler Mode Color Flow Doppler Mode(CFM) CW Doppler Mode(CW) Power Doppler Mode (PD) HD-Flow Doppler Mode (HD-Flow) Tissue Doppler Mode (TD) B Flow Mode (BF) Elastography mode XTD-Mode Contrast Agent Mode (Contrast) M-Color Flow Modes (M/CF, M/HD-Flow, M/TD) Volume Modes (3D/4D): 3D Static 4D Real Time... -
Page 645: Display Modes
Technical Data / Information 16.5 Display Modes Real time in combination with SRI and/or CRI: simultaneous capability: B/CF, B/PD, B/HD-Flow, B/TD, B+AMM,2D/CF+AMM, 2D/PD+AMM, 2D/HD-Flow +AMM, 2D/TD+AMM3D/CF, 3D/PD, 3D/HD-FlowSTIC/CF, STIC/PD, STIC/HD-Flow, STIC/TDB+B, B+B/CF, B+B/PD or B+B/HD-Flow in combination with SRI: 2D+M, 2D+PW, 3D/BF, 3D/Contrast, 4D/Contrast Real time Triplex in combination with SRI: capability:... - Page 646 Technical Data / Information Frame Rate Zoom Factor • B-Mode User program • Receiver Frequency • Acoustic Power • Gain • Dynamic Contrast • Gray Map • Edge Enhance • Persistence • SRI, CRI • Focal Zone Markers • Depth Scale Marker •...
-
Page 647: System Standard Features
TIB: Thermal Index Bone • MI: Mechanical Index • Power output Biopsy Guide Line ECG Line Record Status Trackball function GE Logo Zoom overview image (zoom box position) 16.7 System Standard Features Operating modes: M (Conventional M) PW/CW CFM (Color Flow Doppler Mode) -
Page 648: System Options
Program presets), 10 default programs (one for each application, not programmable by the user) 3D/4D sub Support 3D/4D Sub Programs programs 16.8 System Options 16.8.1 Voluson® S6/S8 Software Options Voluson S6 Voluson S8 Anatomical M-mode Option Option B-Flow Option Option... - Page 649 Technical Data / Information Options Voluson S6 Voluson S8 Interface for DICOM 3 standard Option Option 3D/4D Advanced Option 3D/4D Expert Option SonoAVC follicle Option Option SonoVCAD heart Option SonoVCAD labor Option Option Coded Contrast Imaging Option Elastography Option Option...
-
Page 650: System Parameters
Technical Data / Information 16.9 System Parameters 16.9.1 System Setup Pre-programmable Categories date format User Programmable Preset Capability, User program etc. Languages: English, French, German, Spanish, Italian, Danish, Dutch, Finnish, Norwegian, Swedish, Russian, Simplified Chinese, Japanese EUM Languages: English, German, Spanish, Italian, French, Russian Up to 400 Programmable Annotations organized in 10 anatomical groups Free programmable Scan assistant lists including Add, Delete, Edit and Reorder of checklist items Four programmable Px buttons for documentation preferences like Save, DICOM Send, Print, Check, Cine... - Page 651 Technical Data / Information 16.9.4 Pre-Processing • B/M-Mode • Write Zoom up to 8x • Gain • • Dynamic Range • Acoustic Output • Transmission Focus Position • Transmission Focus Number • Transmission Frequency • Edge Enhancement • Persistence Control •...
- Page 652 • Dyn. Contr. 16.9.6 Image Processing and Presentation Digital Beamformer 226626 (Voluson S6) and 335127 (Voluson S8) system processing channel technology Minimum Depth of Field: 1 cm (Zoom, probe dependent) Maximum Depth of Field: 36 cm (probe dependent) Transmission Focus:...
- Page 653 Technical Data / Information 256 shades of gray 16,8 Mio Colors 24 bit > 261 dB Dynamic. Range adjustable by selecting 12 Dynamic Contrast Curves Image Reverse: Right/ Left Rotation: 0˚, 180˚ 16.9.7 2D Features/Length Cine Features: Dual/Quad Image CINE Display CINE Gauge and CINE Image number display CINE Review Loop Selectable CINE Sequence for CINE Review (by Start Frame and End Frame)
-
Page 654: Scanning Parameters
Technical Data / Information Sequence of Bitmaps: BMP, AVI, MOV DICOM Files: DCM, DICOM Files with DICOMDIR 3D Raw Data: conversion to Cartesian format possible AVI Codec: MPEG 4, MS Video 1, FullFrames Export to: DVD+/- R(W) /CD-R(W), Network, USB devices Exp. - Page 655 Technical Data / Information Line Density steps (pre) low, norm, high Reject: 51 steps (pre) from0 to 225 Enhance: 6 steps (pre) 0 to 5 Gray maps: Tint maps: Dynamic: 12 different dynamic curves C1-C12 Display modes: B, XTD Screen formats: 2D imaging: Single (B), Dual (B+B), Quad (B+B+B) XTD View: Single (XTD), Dual (B+XTD) 16.10.2 M-Mode...
- Page 656 Technical Data / Information Angle correction: - 85º ... 0º ... + 85º Power control range: 1 - 100% GAIN range: + 15 to - 25dB (PW) + 15 to - 15dB (CW) WMF (wall motion filter): PW: 30 - 500Hz CW: 30 - 1000Hz Zero line shift: ±...
- Page 657 Technical Data / Information V-P (velocity + power) T (turbulence) P-T (power + turbulence) CF window size: axial: 0 to B scan range lateral: 0 to B scan range Baseline shift: 17 steps (independent from spectral Doppler) Inversion of color direction: yes Wall Motion Filter: 8 steps (low1, low2, mid1, mid2, high1, high2, max1, max2) Smoothing Filter:...
- Page 658 Technical Data / Information falling edge: 12 steps Gain control: +15dB to -15dB, 0.2dB steps PD Ensemble: 7 to 31 PD Line Density: 10 steps Pulse repetition frequency: 150 Hz to 20.5 kHz PD Map: 8 different color codes for each probe Frequency range: 1 to 16 MHz depending on the probe, adjustable in 3 steps (low, mid, high) Flow Resolution:...
- Page 659 Technical Data / Information TD coding steps: 65536 color steps Depth range: axial: 0 to B-scan range lateral: 0 to B-scan-range Zero line shift: 17 steps Inversion of color direction: yes Smoothing Filter: 12 steps rising time 12 steps falling time Gain control: +15dB to -15dB, 0.2dB steps Line Density (color line...
- Page 660 Technical Data / Information 3D/CF (incl. CRI) 3D/HD-FLow incl. CRI) 3D B-Flow 3D Contrast: 3D/Contrast (Coded PI, CCIS) 4D Real Time 4D Biopsy VCI-A VCI- OmniView STIC: Fetal Cardio STIC Angio: B/Power Doppler (incl. CRI) STIC CF: B/Color Doppler (incl. CRI) STIC HD-FLow: B/HD-Flow (incl.CRI) STIC B-Flow STIC TD...
- Page 661 Technical Data / Information maxmin-and X-ray Gradient Light Inversion Glass Body Mix Mode of two Render Modes Display graphics: Rotation axis, center pointROI box, 3D Frametemporary display of onscreen controls (rotation, translation) Gray maps: Slices: 18 3D Image: one general map adjustable with Low Tones (-50 bis+50) & High Tones (-50 to +50) Tint maps: Tint 2D : 15...
- Page 662 Technical Data / Information Coded PI Coded PI: CIS Coded PI: CCIS Acc. power range: 1 - 100% Scan angle: taken from 2D GAIN range: +15 to -15 dB Gray scale values: 32 bit taken from 2D Persistance filter: 8 steps (pre) S./PRI 1.00, 1.50, 2.00, 3.00, 4.00....15.00 Line Density...
-
Page 663: Generic Measurements And Measurements/Calculations
Technical Data / Information AGC Filter lateral: Range: 1-63; step size 2 AGC Threshold High: Range: 1-10; step size 1 AGC Threshold Low: Range: 1-10; step size 1 Frame Averaging: Range: 1-9; step size 1 16.11 Generic Measurements and Measurements/Calculations 16.11.1 Generic Measurements 2D Mode and 3D: Distance: Distance (Point to Point), Distance (Line to Line), 2D... - Page 664 Technical Data / Information Gestational Age Calculation, Gestational Growth Calculation, Fetal Weight (FW) Estimation, Fetal Trend Graph, Multi-Gestational Calculation & Fetal Compare, Calculation and Ratios, Fetal Qualitative Description (Anatomical survey), Fetal Environmental Description (Biophysical profile);all included in Summary Reports Obstetrics: 4-Chamber-view, Thorax, Outflow Tract, Aortic arch, Venous, LVOT, RVOT Fetal Echo:...
- Page 665 Technical Data / Information TCD: ACA, MCA, PCA, Basilar, A Comb.A, P Comb.A, Vertebral, Basilaris all included in Summary Reports Gynecology: Uterus, Right/Left Ovary Right/Left Follicle, Fibroid, Endometrial thickness, Cervix Length, Left/Right Ovarian Artery, Left/Right Uterine Artery, Vessels, Pelvic Floor, FHR; all included in Summary Reports Pediatrics: Left/Right Hip Joint;...
- Page 666 Technical Data / Information ASUM, CFEF, Chitty, Hadlock_82, Hadlock_84, Hansmann, Jeanty, Johnsen, Kurmanavicius, Merz, Nicolaides, Siriraj ASUM, Hobbins, Jeanty, Merz, OSAKA Tokyo MAD: EIK-NES, Kurmanavicius OFD: ASUM, Chitty, Hansmann, Jeanty, Kurmanavicius, Merz, Nicolaides RAD: Jeanty, Merz TIB: Jeanty, Merz TAD: CFEF, Merz, Chitty, Goldstein, HILL, Hobbins, Nicolaides, Hansmann ULNA: Jeanty, Merz...
-
Page 667: External Inputs And Outputs
Technical Data / Information ASUM, CFEF, Chitty, Hadlock, Hansmann, Jacot-Uillarmod, Jeanty, Kurmanavicius, Lessoway, Merz, Nicolaides, Siriraj, Verburg ASUM, Chitty, Jeanty, Merz, OSAKA, Siriraj Tokyo MCA PI, RI: JSUM, Bahlman MCA PV: Mari MAD: EIK-NES, Kurmanavicius MV E/A: HARADA NBL: BUNDUKI, SONEK OFD: ASUM, Chitty, Hansmann, Jeanty, Kurmanavicius, Merz, Nicolaides MainPA... - Page 668 Technical Data / Information 16.12.2 Connectivity behind rear panel (accessible after opening) DVI-D out: 1x DVI-D for OUT Resolution: SXGA Audio out L/R: Cinch, LF-signal 1.2Vss Cinch, RF-signal 1.2Vss USB (1x): RS 232. optional (via USB to RS232 converter) 16.12.3 Peripherals Remote BW Printer: via USB Remote Color Printer:...
-
Page 669: Guidance And Manufacturer´s Declaration
Technical Data / Information 16.12.6 Internal Battery Type CR2450 Note Engraved “+” marking shall be on top position. 16.13 Guidance and manufacturer´s declaration Guidance and manufacturer´s declaration - electromagnetic emissions The Voluson® S6/S8 is inteded for use in electromagnetic enviroment specified below. The customer or the user of the Voluson®... - Page 670 Technical Data / Information Guidance and manufacturer´s declaration - electromagnetic emissions Voltage dips, short < 5% UT < 5% UT Mains power quality should be that of a interruptions and typical commercial or hospital (> 95 % dip in UT) (>...
- Page 671 Technical Data / Information Guidance and manufacturer´s declaration - electromagnetic emissions Radiated RF 3 V/m; 80MHz to 2.5 GHz E1=3 V/m IEC 61000-4-3 80MHz to 800 MHz 800MHz to 2.5GHz where P is the maximum output power rating of the transmitter in watts (W) according to the transmitter manufacturer and d is the recommended separation distance in meters (m).
- Page 672 Technical Data / Information Recommended separation distances between portable and mobile RF communications equipment and the Voluson© S6/S8 11.07 0.37 0.74 35.00 1.17 2.33 110.68 3.70 7.40 350.00 11.70 23.30 For transmitters rated at a maximum output power not listed above, the recommended separation distance d in meters (m) can be estimated using equation applicable to the frequency of transmitter, where P is the maximum output power rating of the transmitter in watts (W) according to the transmitter manufacturer.
-
Page 673: Chapter 17 - Annex- Abbreviations
Chapter 17 ANNEX- Abbreviations Description of abbreviations, sorted alphabetically Voluson® S6/S8 Basic User Manual 5433669-100 Revision 4 17-1... - Page 674 ANNEX- Abbreviations • • ‘A’ on page 17‐2 ‘M’ on page 17‐6 • • ‘B’ on page 17‐3 ‘N’ on page 17‐7 • • ‘C’ on page 17‐3 ‘O’ on page 17‐7 • • ‘D’ on page 17‐4 ‘P’ on page 17‐7 •...
- Page 675 Body Surface Area Bulb lat. Bulbus = engl carotid (artery) bulb Common Carotid Artery Coded Excitation CEPH lat. Cephalica = engl. Cephalic CFEF Collège Français d’Echographie Foetale Color Flow Mode Calculated Gestational Age Cephalic Index CLAV Clavicle Cisterna Magna Cardiac Output...
- Page 676 ANNEX- Abbreviations Abbreviation Designation DEEP FEM V deep femoral vein Inner (reduced) distance Dout Outer (original) distance Day of Birth Day of Conception Dor. PenA Dorsal Penile Artery DORS PED A lat. arteria dorsalis pedis = engl. Dorsal pedis artery Duration DV PI Ductus Venosus PI (=Pulsatility Index)
- Page 677 ANNEX- Abbreviations Abbreviation Designation Fetal Weight Gestational Age Gmean Mean Gradient Growth Percentile Gpeak Peak Gradient Gravida Number of pregnancies GRAFT vacular implant Gestational Sac GSAPH V Great saphenous vein Head Circumference -Flow High Definition Flow Hemisphere Harmonic Imaging Heart Rate HSVa Hemisphere Ventricle anterior HSVp...
- Page 678 ANNEX- Abbreviations Abbreviation Designation Length of Vertebra Left Ventricle LV Vol. Left Ventricle Volume Left Ventricular Area Left Ventricle Diameter Left Ventricular Mass LVOT Left Ventricle Outflow Tract LVPW Left Ventricle Posterior Wall M&A Measurement & Analysis Middle Abdominal Diameter MainPA Vmax Main pulmonary artery Vmax Middle Cephalic Artery...
- Page 679 ANNEX- Abbreviations Abbreviation Designation Posterior Cerebral Artery PERON A peroneal artery PERON V peroneal vein Power Doppler Pressure Gradient Pressure Half Time Pulsatility Index PISA Proximal Isovelocity Surface Area PPSA Predicted PSA (see also: PSA) POPL A popliteal artery POPLIT V popliteal vein POST TIB A posterior tibial artery...
- Page 680 ANNEX- Abbreviations Abbreviation Designation Standard Deviation SEGM A segmental artery Spine Length Speckle Reduction Imaging STIC Spatio-Temporal Image Correlation SUBC A subclavian artery SUBC V subclavian vein Subclav subclavian SUP FEM A superior femoral artery Stroke Volume Transverse Abdominal Diameter TAmax Time Averaged maximum velocity TAmean...
- Page 681 ANNEX- Abbreviations Abbreviation Designation Verteb Vertebral Volume Contrast Imaging Velocity diastolic (= minimum velocity or end-diastolic velocity) (see also: ED and MD) Vmax maximum Velocity (see also: PS) Vmean mean Velocity Vmin minimum Velocity (see also: MD) Vert. A. Vertebral Artery Vp/Hem posterior horn of lateral ventricle / hemisphere Protodiastolic Velocity...
- Page 682 ANNEX- Abbreviations This page was intentionally left blank. Voluson® S6/S8 Basic User Manual 17-10 5433669-100 Revision 4...
- Page 684 GE Ultrasound Korea, Ltd. 65-1, Sangdaewon-dong, Jungwon-gu, Seongnam-si, Gyeonggi-do, 462-120 Republic of Korea www.gehealthcare.com GE imagination at work...