Siemens SINAMICS S120 Equipment Manual
Booksize cold-plate power units
Hide thumbs
Also See for SINAMICS S120:
- Function manual (1094 pages) ,
- Diagnostic manual (947 pages) ,
- Manual (848 pages)
Summary of Contents for Siemens SINAMICS S120
- Page 1 Equipment Manual, 03/2007 Edition SINAMICS S120 Booksize cold-plate power units SINAMICS S120 Booksize cold-plate power units sinamics...
- Page 3 Cold plate with external air heat sinks SINAMICS Cold plate with internal liquid cooling S120 Line connection SINAMICS S120 Booksize cold- Active line modules with cold plate power units plate Basic Line Modules with cold Manual plate Smart Line Modules (5 kW...
- Page 4 Trademarks All names identified by ® are registered trademarks of the Siemens AG. The remaining trademarks in this publication may be trademarks whose use by third parties for their own purposes could violate the rights of the owner.
-
Page 5: Foreword
Orientation SINAMICS S Sales Documentation Planning/configuration SIZER configuration tool Decision/ordering SINAMICS S Catalogs SINAMICS S120 Equipment Manual for Control Units and Installation/assembly • Supplementary System Components SINAMICS S120 Equipment Manual Power Modules Booksize • SINAMICS S120 Equipment Manual Power Modules Chassis •... - Page 6 Foreword Usage phase Tools SINAMICS S120 Commissioning Manual Usage/operation • SINAMICS S List Manual • SINAMICS S150 Operating Instructions • SINAMICS S120 Commissioning Manual Maintenance/servicing • SINAMICS S List Manual • SINAMICS S150 Operating Instructions • Target group This Manual addresses planners, installation technicians, design engineers.
- Page 7 ● in the Internet: http://support.automation.siemens.com under the Product/Order No. 15257461 ● with the responsible branch office of the A&D MC Business Division of Siemens AG. The EC Declaration of Conformity for the Low Voltage Directive can be found/obtained ● on the Internet http://support.automation.siemens.com...
- Page 8 Foreword ESD information CAUTION Electrostatic sensitive devices (ESDs) are individual components, integrated circuits, or boards that may be damaged by either electrostatic fields or electrostatic discharge. Regulations for handling ESD components: When handling components, make sure that personnel, workplaces, and packaging are well earthed.
- Page 9 Foreword DANGER Correct and safe operation of SINAMICS S units assumes correct transportation in the transportation packaging, correct long-term storage in the transport packaging, setup and installation, as well as careful operation and maintenance. The details in the catalogs and proposals also apply to the design of special equipment versions.
- Page 10 Foreword Explanation of symbols The symbols are in accordance with IEC 617-2. Table 2 Symbols Symbol Description Protective earth (PE) Ground (e.g. M 24 V) Functional ground (e.g. shield) Equipotential bonding Booksize cold-plate power units Manual, (GH4), 03.2007, 6SL3097-2AJ00-0BP4...
- Page 11 Foreword Residual risks of power drive systems When carrying out a risk assessment of the machine in accordance with the EU Machinery Directive, the machine manufacturer must consider the following residual risks associated with the control and drive components of a power drive system (PDS). 1.
-
Page 13: Table Of Contents
Table of contents Foreword ..............................5 Description............................... 21 Cold-plate cooling ........................21 System Data..........................23 Cold plate with external air heat sinks...................... 25 Overview ............................25 Example: cold plate with external air heat sink................26 2.2.1 Setup............................26 2.2.2 Sample setup: cold plate with external air heat sink..............26 Example: cold plate with external liquid heat sink ...............30 2.3.1 Design ............................30... - Page 14 Table of contents 4.6.4 Dimension drawings........................55 4.6.5 Technical Specifications......................60 Basic Line Filter for Basic Line Modules ..................61 4.7.1 Description ..........................61 4.7.2 Safety information ........................61 4.7.3 Interface description........................63 4.7.3.1 Overview ............................. 63 4.7.3.2 Line supply/load connection......................64 4.7.4 Dimension drawing........................
- Page 15 Table of contents 4.12.5 Technical specifications .......................99 4.13 Line connection variants ......................100 4.13.1 Methods of line connection ......................100 4.13.2 Operation of the line connection components on the supply network ........101 4.13.3 Operation of the line connection components via an autotransformer ........102 4.13.4 Operation of the line connection components via an isolating transformer.......104 4.13.5...
- Page 16 Table of contents 7.3.2 Connection example ......................... 165 7.3.3 X1 line connection........................166 7.3.4 X21 terminals: smart line module....................167 7.3.5 X22 terminals: smart line module....................168 7.3.6 X24 24 V terminal adapter ......................168 7.3.7 Meaning of the LEDs on the smart line module with cold plate ..........169 Dimension drawing........................
- Page 17 Table of contents 11.1.3 Interface description........................219 11.1.3.1 Overview ............................219 11.1.3.2 Connection example ........................220 11.1.3.3 Braking resistor connection X1 ....................220 11.1.3.4 X21 digital inputs/outputs......................221 11.1.3.5 Meaning of the LEDs on the braking module................222 11.1.4 Dimension drawing ........................223 11.1.5 Installation ..........................224 11.1.6 Technical specifications ......................225 11.1.7 Braking resistors for Braking Module..................226...
- Page 18 Table of contents 13.2.2 Safety Information ........................270 13.2.3 Interface description........................272 13.2.3.1 Overview ........................... 272 13.2.3.2 DC link connection ........................273 13.2.4 Dimension drawings........................274 13.2.5 Installation ..........................276 13.2.6 Electrical Connection ........................ 280 13.3 DC link adapter ......................... 281 13.3.1 Description ..........................
- Page 19 Table of contents 14.3.3 Typical 24 V Component Current Consumption ................312 14.3.4 Overcurrent Protection.......................314 14.4 Arrangement of Components and Equipment ................317 14.4.1 General ............................317 14.4.2 Drive Line-Up ..........................317 14.4.3 Three-tier configuration......................321 14.4.4 Information on connecting the cooling water ................322 14.5 Electromagnetic Compatibility....................324 14.5.1 General ............................324...
-
Page 21: Description
Description Cold-plate cooling Cold-plate cooling is a cooling method for SINAMICS S120 booksize power sections. On the rear of the device is a flat aluminum cold plate, which acts as a thermal interface. There are three methods of cooling the SINAMICS power sections: 1. - Page 22 Description 1.1 Cold-plate cooling Figure 1-1 Overview: Cold-Plate Booksize cold-plate power units Manual, (GH4), 03.2007, 6SL3097-2AJ00-0BP4...
-
Page 23: System Data
1.2 System Data System Data Technical data Unless explicitly specified otherwise, the following technical data are valid for components of the SINAMICS S120 booksize drive system. Electrical data Line connection voltage 3-ph. 380 V to 480 V AC ±10 % (-15 % <... - Page 24 Description 1.2 System Data Environmental conditions Permissible coolant temperature (air) and installation 0 °C to +40 °C and an installation altitude of up to 1000 m altitude during operation without derating, >40 °C to +55 °C see the characteristic for current derating. Installation altitude >1000 m up to 4000 m see characteristic for current derating or reduction of the ambient temperature by 3.5 K per 500 m.
-
Page 25: Cold Plate With External Air Heat Sinks
Cold plate with external air heat sinks Overview This chapter provides a number of examples to illustrate various cooling methods with external heat sinks that are screwed onto the cold plate. The following cooling methods are available: ● Air cooling by means of ribbed heat sink ●... -
Page 26: Example: Cold Plate With External Air Heat Sink
Cold plate with external air heat sinks 2.2 Example: cold plate with external air heat sink Example: cold plate with external air heat sink 2.2.1 Setup This chapter describes the conditions that you must take into account when setting up the cold plate and external air heat sink. - Page 27 Cold plate with external air heat sinks 2.2 Example: cold plate with external air heat sink Front view of cabinet Figure 2-1 Example: cabinet setup with powers ections, cold plate, and external air heat sink In the cabinet, a fan is installed above the power sections. To optimize usage of the external air heat sink, it is best to arrange the components in such a way that the heat is dissipated equally over the surface of the external heat sink.
- Page 28 Cold plate with external air heat sinks 2.2 Example: cold plate with external air heat sink Rear view of cabinet Figure 2-2 Rear view of cabinet In this example, two axial fans with a diameter of 150 mm ensure forced convection. The ribbed heat sink, which is attached to the rear, is located in an air duct (approx.
- Page 29 Cold plate with external air heat sinks 2.2 Example: cold plate with external air heat sink Example: external air heat sink Figure 2-3 Example of an air heat sink Aluminum air heat sinks are recommended. The heat sinks and fans must be dimensioned for the power loss to be dissipated. For the component-specific power loss in rated operation, refer to "Technical data".
-
Page 30: Example: Cold Plate With External Liquid Heat Sink
Cold plate with external air heat sinks 2.3 Example: cold plate with external liquid heat sink Example: cold plate with external liquid heat sink 2.3.1 Design When an external liquid heat sink is used, the power sections are all mounted on a plate through which cooling water flows to cool the power sections. -
Page 31: Sample Setup: Cold Plate With External Liquid Heat Sink
Cold plate with external air heat sinks 2.3 Example: cold plate with external liquid heat sink 2.3.2 Sample setup: cold plate with external liquid heat sink Figure 2-4 Example: cold plate drive line-up with external liquid cooling Setup: ● Supply: Active line module 55 kW ●... -
Page 33: Cold Plate With Internal Liquid Cooling
Cold plate with internal liquid cooling Principle of internal liquid cooling With internal cold-plate liquid cooling, connectors ("connection adapters") are required directly on the cold plate for connecting the water supply. These connection adapters are available for 300 mm wide power units (see section "Connection adapters"). The following principle applies: Inlet below, outlet above Figure 3-1... -
Page 35: Line Connection
Line connection 4.1 Introduction Line connection Introduction The line connection for a SINAMICS booksize drive line-up comprises an optional line filter and a line reactor: ● Line filter variants: – Basic Line Filter for Active Line Modules with line reactor –... - Page 36 Figure 4-2 Overview: line connection with Active Interface Module Using line filters not approved by SIEMENS for SINAMICS can lead to damage/interference to the Line Modules and line-side harmonics that can interfere with or damage other loads operated by the network.
-
Page 37: Overview: Line Filter
4.2 Overview: line filter Overview: line filter A separate line filter (see catalog) must be used for the SINAMICS S120 drive line-up. An additional line filter must be used to suppress interference in other loads. To prevent mutual interference, this line filter must not be equipped with line-side capacitors with respect to ground. - Page 38 Line connection 4.2 Overview: line filter Basic Line Filter for Smart Line Modules Basic Line Filters for Smart Line Modules are specified for total cable lengths of up to 150 m (shielded) of category C2 to EN 61800-3. Basic Line Filters 16 kW and 36 kW for Smart Line Modules are specified for total cable lengths of up to 350 m (shielded) of category C2 to EN 61800-3.
-
Page 39: Combining Line Reactors And Line Filters
Line connection 4.3 Combining line reactors and line filters Combining line reactors and line filters Figure 4-3 Combining line reactors and line filters Booksize cold-plate power units Manual, (GH4), 03.2007, 6SL3097-2AJ00-0BP4... -
Page 40: Basic Line Filter For Active Line Modules With Line Reactor
Line connection 4.4 Basic Line Filter for Active Line Modules with line reactor Basic Line Filter for Active Line Modules with line reactor 4.4.1 Description The Basic Line Filters for Active Line Modules are designed for limiting the cable-borne interference in accordance with the specifications of the EMC legislation. The machine manufacturer must certify the machines that he plans to launch on the market in accordance with the EU EMC Directive. - Page 41 Line connection 4.4 Basic Line Filter for Active Line Modules with line reactor DANGER The line filters listed conduct a high leakage current via the PE conductor. A permanent PE connection for the line filter or control cabinet is required due to the high leakage current of the line filters.
-
Page 42: Interface Description
Line connection 4.4 Basic Line Filter for Active Line Modules with line reactor 4.4.3 Interface description 4.4.3.1 Overview Figure 4-4 Basic Line Filter for Active Line Modules (example: 36 kW) NOTICE The line/load connection must not be interchanged. Booksize cold-plate power units Manual, (GH4), 03.2007, 6SL3097-2AJ00-0BP4... -
Page 43: Line/Load Connection
Line connection 4.4 Basic Line Filter for Active Line Modules with line reactor 4.4.3.2 Line/load connection Table 4-2 Type of connection Terminals Designations Line supply connection (line supply) L1, L2, L3, PE Load connection (load) L1´, L2´, L3´, PE Basic Line Filter for Active Line Modules 16 kW Screw terminal: 10 mm 3-pin/1.5 -1.8 Nm (see Screw Terminals chapter) -
Page 44: Technical Specifications
Line connection 4.4 Basic Line Filter for Active Line Modules with line reactor 4.4.5 Technical Specifications Table 4-4 Technical data of Basic Line Filter for Active Line Modules with line reactor 6SL3000 0BE21-6DAx 0BE23-6DAx 0BE25-5DAx unit Rated power Connection voltage: Supply voltage 380 3 AC -10% (-15% <... -
Page 45: Basic Line Filter For Active Line Modules With Active Interface Module
Line connection 4.5 Basic Line Filter for Active Line Modules with Active Interface Module Basic Line Filter for Active Line Modules with Active Interface Module 4.5.1 Description Basic Line Filters are mainly effective in the frequency range from 150 kHz to 30 MHz; this is the range relevant to ensure compliance with the appropriate standard. - Page 46 Line connection 4.5 Basic Line Filter for Active Line Modules with Active Interface Module NOTICE The associated Line Module must only be connected to the SINAMICS line filter via the associated line reactor. Additional loads must be connected upstream of the SINAMICS line filter (if required, via a separate line filter).
-
Page 47: Interface Description
Line connection 4.5 Basic Line Filter for Active Line Modules with Active Interface Module 4.5.3 Interface description 4.5.3.1 Overview Figure 4-6 Interface description: Basic Line Filter 55 kW Booksize cold-plate power units Manual, (GH4), 03.2007, 6SL3097-2AJ00-0BP4... - Page 48 Line connection 4.5 Basic Line Filter for Active Line Modules with Active Interface Module Figure 4-7 Interface description: 80 kW and 120 kW Basic Line Filter NOTICE The line/load connection must not be interchanged. Booksize cold-plate power units Manual, (GH4), 03.2007, 6SL3097-2AJ00-0BP4...
-
Page 49: Line/Load Connection
Line connection 4.5 Basic Line Filter for Active Line Modules with Active Interface Module 4.5.3.2 Line/load connection Table 4-5 Connection type Terminals Designations Line supply connection (line supply) L1, L2, L3, PE Load connection (load) L1´, L2´, L3´, PE Basic Line Filter for Active Line Module with Active Interface Module 55 kW Screw terminal: 95 mm PE connection: M6/6 Nm... -
Page 50: Technical Specifications
Line connection 4.5 Basic Line Filter for Active Line Modules with Active Interface Module Figure 4-9 Dimension drawing: 80 kW and 120 kW Basic Line Filter Table 4-7 Dimensions: Basic Line Filter for Active Line Modules Basic Line Order number W [mm] w [mm] a [mm]... -
Page 51: Wideband Line Filter For Active Line Modules
Line connection 4.6 Wideband Line Filter for Active Line Modules Wideband Line Filter for Active Line Modules 4.6.1 Description The damping characteristics of Wideband Line Filters for Active Line Modules not only conform with the requirements of EMC standards for the frequency range of 150 kHz to 30 MHz but also include low frequencies as of 2 kHz. - Page 52 Line connection 4.6 Wideband Line Filter for Active Line Modules DANGER The line filters listed conduct a high leakage current via the protective ground conductor. A permanent PE connection for the line filter or control cabinet is required due to the high leakage current of the line filters.
-
Page 53: Interface Description
Line connection 4.6 Wideband Line Filter for Active Line Modules 4.6.3 Interface description Figure 4-10 Wideband Line Filter for Active Line Module (example: 16 kW) NOTICE The line/load connection must not be interchanged. Booksize cold-plate power units Manual, (GH4), 03.2007, 6SL3097-2AJ00-0BP4... -
Page 54: Line/Load Connection
Line connection 4.6 Wideband Line Filter for Active Line Modules 4.6.3.1 Line/load connection Table 4-9 Type of connection Terminals Designations Line supply connection (line supply) L1, L2, L3, PE Load connection (load) U, V, W Wideband Line Filter for Active Line Modules 16 kW Screw terminal: 10 mm 3-pin/1.5 -1.8 Nm (see Screw Terminals chapter) -
Page 55: Dimension Drawings
Line connection 4.6 Wideband Line Filter for Active Line Modules 4.6.4 Dimension drawings Figure 4-11 Dimension drawing: 16 kW Wideband Line Filter for Active Line Modules Booksize cold-plate power units Manual, (GH4), 03.2007, 6SL3097-2AJ00-0BP4... - Page 56 Line connection 4.6 Wideband Line Filter for Active Line Modules Figure 4-12 Dimension drawing: 36 kW Wideband Line Filter for Active Line Modules Booksize cold-plate power units Manual, (GH4), 03.2007, 6SL3097-2AJ00-0BP4...
- Page 57 Line connection 4.6 Wideband Line Filter for Active Line Modules Figure 4-13 Dimension drawing: 55 kW Wideband Line Filter for Active Line Modules Booksize cold-plate power units Manual, (GH4), 03.2007, 6SL3097-2AJ00-0BP4...
- Page 58 Line connection 4.6 Wideband Line Filter for Active Line Modules Figure 4-14 Dimension drawing: 80 kW Wideband Line Filter for Active Line Modules Booksize cold-plate power units Manual, (GH4), 03.2007, 6SL3097-2AJ00-0BP4...
- Page 59 Line connection 4.6 Wideband Line Filter for Active Line Modules Figure 4-15 Dimension drawing: 120 kW Wideband Line Filter for Active Line Modules Table 4-10 Wideband Line Filter For Active Line Modules Order no. 16 kW 6SL3000-0BE-21-6AAx 36 kW 6SL3000-0BE-23-6AAx 55 kW 6SL3000-0BE-25-5AAx 80 kW...
-
Page 60: Technical Specifications
Line connection 4.6 Wideband Line Filter for Active Line Modules 4.6.5 Technical Specifications Table 4-11 Technical data: Wideband Line Filter for Active Line Modules 6SL3000 0BE21-6AAx 0BE23- 0BE25- 0BE28- 0BE31- unit 6AAx 5AAx 0AAx 2AAx Rated power Connection voltages: Supply voltage 3-ph. -
Page 61: Basic Line Filter For Basic Line Modules
Line connection 4.7 Basic Line Filter for Basic Line Modules Basic Line Filter for Basic Line Modules 4.7.1 Description The Basic Line Filters for Basic Line Modules are designed for limiting the cable-borne interference in the frequency range in accordance with the specifications of the EMC legislation. - Page 62 Line connection 4.7 Basic Line Filter for Basic Line Modules DANGER The line filters listed conduct a high leakage current via the protective ground conductor. A permanent PE connection for the line filter or control cabinet is required due to the high leakage current of the line filters.
-
Page 63: Interface Description
Line connection 4.7 Basic Line Filter for Basic Line Modules 4.7.3 Interface description 4.7.3.1 Overview Figure 4-16 Line filters for Basic Line Modules (example: 40 kW) NOTICE The line/load connection must not be interchanged. Booksize cold-plate power units Manual, (GH4), 03.2007, 6SL3097-2AJ00-0BP4... -
Page 64: Line Supply/Load Connection
Line connection 4.7 Basic Line Filter for Basic Line Modules 4.7.3.2 Line supply/load connection Table 4-12 Connection type Terminals Designations Line supply connection (line supply) L1, L2, L3, PE Load connection (load) L1´, L2´, L3´, PE Basic Line Filter for Basic Line Modules 20 kW Screw terminal: 10 mm 3-pin / 1.5 - 1.8 Nm (see Screw Terminals chapter) -
Page 65: Technical Specifications
Line connection 4.7 Basic Line Filter for Basic Line Modules 4.7.5 Technical Specifications Table 4-14 Technical data for Basic Line Filter for Basic Line Modules 6SL3000 0BE21-6DAx 0BE23-6DA1 0BE31-2DAx unit Rated power Connection voltage: Supply voltage 380 3 AC -10% (-15% < 1 min) to 480 3 AC +10% Line frequency 47 to 63 Hz Rated current... -
Page 66: Basic Line Filter For Smart Line Modules
Line connection 4.8 Basic Line Filter for Smart Line Modules Basic Line Filter for Smart Line Modules 4.8.1 Description In conjunction with the associated line reactors, the Basic Line Filters for Smart Line Modules limit the cable-borne interference to a level in compliance with EN61800-3 category In conjunction with the line filters and the associated line reactors, drive line-ups with Smart Line Modules fulfill the requirements of category C2 to EN 61800-3. - Page 67 Line connection 4.8 Basic Line Filter for Smart Line Modules DANGER Risk of electric shock. Dangerous voltages are still present for up to 5 minutes after the power supply has been switched off. Note If a high-voltage test is conducted with alternating voltage in the system, the line filters must be disconnected in order to obtain accurate measurements.
-
Page 68: Interface Description
Line connection 4.8 Basic Line Filter for Smart Line Modules 4.8.3 Interface description 4.8.3.1 Overview Figure 4-18 Basic Line Filter for Smart Line Modules (example: 36 kW) NOTICE The line/load connection must not be interchanged. Booksize cold-plate power units Manual, (GH4), 03.2007, 6SL3097-2AJ00-0BP4... -
Page 69: Line/Load Connection
Line connection 4.8 Basic Line Filter for Smart Line Modules Line voltage 415 V 3 AC to 480 V AC + 10 % ● Controlled DC link voltage required, or ● limitation of the DC link voltage required due to motor isolation 4.8.3.2 Line/load connection Table 4-15... -
Page 70: Dimension Drawings
Line connection 4.8 Basic Line Filter for Smart Line Modules 4.8.4 Dimension Drawings Figure 4-19 Dimension drawing: Basic Line Filter for Smart Line Modules (5 and 10 kW) Table 4-16 Basic Line Filter for Smart Line Modules Basic Line Filter for Smart Line Modules Order number 5 kW 6SL3000-0HE15-0AAx... -
Page 71: Technical Specifications
Line connection 4.8 Basic Line Filter for Smart Line Modules Figure 4-20 Dimension drawing: Basic Line Filter for Smart Line Modules (16 kW and 36 kW) Table 4-17 Dimensions of Basic Line Filter for Smart Line Modules Basic Line Order number W [mm] b [mm] a [mm]... -
Page 72: Active Interface Module
Line connection 4.9 Active Interface Module Active Interface Module 4.9.1 Description Active Interface Modules are line-side interfaces for the Active Line Modules. They contain the following functional units: ● Line reactors ● Low-frequency/switching frequency filters ● Line filters to EN61800-3, category C3, max. total motor cable length 350 m (shielded) In conjunction with the associated Basic Line Filter and an EMC-compliant design, the following voltage interference limit values are observed: ●... -
Page 73: Interface Description
Line connection 4.9 Active Interface Module Note The Active Interface Modules must only be operated in a vertical position ("hanging"). 4.9.3 Interface description 4.9.3.1 Overview Figure 4-21 Interface description: Active Interface Module 55 kW Booksize cold-plate power units Manual, (GH4), 03.2007, 6SL3097-2AJ00-0BP4... - Page 74 Line connection 4.9 Active Interface Module Figure 4-22 Interface description: Active Interface Module (80 kW and 120 kW) Booksize cold-plate power units Manual, (GH4), 03.2007, 6SL3097-2AJ00-0BP4...
-
Page 75: Connection Example
Line connection 4.9 Active Interface Module 4.9.3.2 Connection example Figure 4-23 Connection example: Active Interface Module Booksize cold-plate power units Manual, (GH4), 03.2007, 6SL3097-2AJ00-0BP4... -
Page 76: Electronics Power Supply X124
Line connection 4.9 Active Interface Module 4.9.3.3 Electronics power supply X124 Table 4-19 Terminal block X124 Terminal Function Technical specifications Electronics power supply Voltage: 24 V DC (20.4 V - 28.8 V) Current consumption: max. 1.6 A Electronics power supply Max. -
Page 77: X121 Alarm Contacts For Temperature Switch
Line connection 4.9 Active Interface Module 4.9.3.5 X121 alarm contacts for temperature switch Table 4-21 Plug-in screw terminal X121 Terminal Designation Technical specifications +Temp Rated current at cosφ 1: 2.5 A (max. 5 A) Voltage: 12 - 250 V (12 - 100 V Temperature switch output -Temp Temperature switch output... -
Page 78: Dimension Drawings
Line connection 4.9 Active Interface Module 4.9.4 Dimension drawings Figure 4-24 Dimension drawing: Active Interface Module 55 kW Booksize cold-plate power units Manual, (GH4), 03.2007, 6SL3097-2AJ00-0BP4... - Page 79 Line connection 4.9 Active Interface Module Figure 4-25 Dimension drawing: Active Interface Module (80 kW and 120 kW) Table 4-22 Active Interface Modules Active Interface Module 6SL3100-0BE25-5ABx 6SL3100-0BE28-0ABx 6SL3100-0BE31-2ABx 55 kW 80 kW 120 kW Table 4-23 Shield connecting plates for Active Interface Modules Shield connecting plate 6SL3163-1AH00-0AAx 6SL3163-1AM00-0AAx...
-
Page 80: Installation
Line connection 4.9 Active Interface Module 4.9.5 Installation The Active Interface Modules are designed for installation in the control cabinet. The components are secured onto the control cabinet installation panel next to the line filter using four M6 screws (not hexagon-head screws). Figure 4-26 Mounting: Active Interface Module Table 4-24... - Page 81 Line connection 4.9 Active Interface Module Operating an Active Interface Module from an insulated network (IT system) When a 55 kW, 80 kW and 120 kW Active Interface Module is operated from an insulated supply (IT system), the connection bracket for the interference-suppression capacitor must be removed.
- Page 82 Line connection 4.9 Active Interface Module Replacing the fan in an Active Interface Module DANGER Before replacing the fan, you must switch off the power supplies (24 V DC and 400 V AC). Risk of electric shock. Dangerous voltages are still present for up to 5 minutes after the power supply has been switched off.
-
Page 83: Technical Specifications
Line connection 4.9 Active Interface Module 4.9.6 Technical specifications Table 4-26 Technical data Active Interface Module 6SL3100- 0BE25-5ABx 0BE28-0ABx 0BE31-2ABx 55 kW 80 kW 120 kW rated Current requirements of the 24 V DC electronics power supply Mains voltage 380 V 3 AC to 480 V 3 AC ±10% Line frequency 47 - 63 Cooling air requirement... -
Page 84: Line Reactors For Active Line Modules
Only the line reactors or Active Interface Modules described in this Manual should be used. The following can occur if line reactors are used that have not been approved for SINAMICS S120 by SIEMENS: - The Line Modules may become damaged/faulty. -
Page 85: Connection Description
Line connection 4.10 Line reactors for Active Line Modules 4.10.3 Connection description Figure 4-27 Line reactor (example: 16 kW) 4.10.3.1 Line/load connection Table 4-27 Connection types for line reactors Terminals Designations Line supply connection 1U1, 1V1, 1W1, PE Load connection 1U2, 1V2, 1W2 Line reactors for Active Line Modules 16 kW... -
Page 86: Dimension Drawings
Line connection 4.10 Line reactors for Active Line Modules 4.10.4 Dimension drawings Figure 4-28 Dimension drawing: line reactor for Active Line Modules (up to 55 kW) Table 4-28 Dimensions of the line reactor for Active Line Modules Order number L [mm] W [mm] h [mm] w [mm]... -
Page 87: Technical Specifications
Line connection 4.10 Line reactors for Active Line Modules Figure 4-29 Dimension drawing: line reactor for Active Line Modules (as of 80 kW) Table 4-29 Dimensions of the line reactor for Active Line Modules Order L [mm] W [mm] h1 [mm] h2 [mm] H [mm] w [mm]... -
Page 88: Line Reactors For Smart Line Modules
Only the line reactors or Active Interface Modules described in this Manual should be used. The following can occur if line reactors are used that have not been approved for SINAMICS S120 by SIEMENS: - The Line Modules may become damaged/faulty. -
Page 89: Connection Description
Line connection 4.11 Line reactors for Smart Line Modules 4.11.3 Connection description 4.11.3.1 Overview Figure 4-30 Line reactors for Smart Line Modules (example: 36 kW) 4.11.3.2 Line supply/load connection Table 4-31 Connection types for line reactors Terminals Designations Line supply connection 1U1, 1V1, 1W1, PE Load connection 1U2, 1V2, 1W2... -
Page 90: Dimension Drawings
Line connection 4.11 Line reactors for Smart Line Modules 4.11.4 Dimension Drawings Figure 4-31 Dimension drawing: line reactor for Smart Line Modules (5 and 10 KW) Table 4-32 Dimensions of the line filter for Smart Line Modules Order number W [mm] b [mm] H [mm] D [mm]... - Page 91 Line connection 4.11 Line reactors for Smart Line Modules Figure 4-32 Dimension drawing of line reactor for the Smart Line Module 16 kW Booksize cold-plate power units Manual, (GH4), 03.2007, 6SL3097-2AJ00-0BP4...
- Page 92 Line connection 4.11 Line reactors for Smart Line Modules Figure 4-33 Dimension drawing of the line reactor for the Smart Line Module 36 kW Table 4-33 Line reactor for the Smart Line Modules 16 kW and 36 kW Order No. 16 kW 6SL3000-0CE-21-6AAx 36 KW...
-
Page 93: Technical Specifications
Line connection 4.11 Line reactors for Smart Line Modules 4.11.5 Technical specifications Table 4-34 Technical data of line reactors for the Smart Line Module 6SL3000 0CE15-0AAx 0CE21-0AAx 0CE22-0AAx 0CE24-0AAx unit Power Rated current Power loss Weight 1 For an overview, see the power loss tables in chapter Cabinet Design Booksize cold-plate power units Manual, (GH4), 03.2007, 6SL3097-2AJ00-0BP4... -
Page 94: Line Reactors For Basic Line Modules
Only the line reactors described in this Manual must be used. The following can occur if line reactors are used that have not been approved for SINAMICS S120 by SIEMENS: - The Line Modules may become damaged/faulty. - Line reactions can occur that can damage or interfere with other loads powered from the same network. -
Page 95: Connection Description
Line connection 4.12 Line reactors for Basic Line Modules 4.12.3 Connection description 4.12.3.1 Overview Figure 4-34 Line reactor for Basic Line Module (20 kW) Figure 4-35 Line reactor for Basic Line Module (40 kW) Booksize cold-plate power units Manual, (GH4), 03.2007, 6SL3097-2AJ00-0BP4... -
Page 96: Line/Power Connection
Line connection 4.12 Line reactors for Basic Line Modules Figure 4-36 Line reactor for Basic Line Module (100 kW) 4.12.3.2 Line/power connection Table 4-35 Connection types for line reactors Terminals Designations Power connection L1, L2, L3 Load connection 1L1, 1L2, 1L3 Line reactors for Basic Line Modules 20 kW Max. -
Page 97: Dimension Drawings
Line connection 4.12 Line reactors for Basic Line Modules 4.12.4 Dimension drawings Figure 4-37 Dimension drawing: Line reactor for Basic Line Module (20 kW) Booksize cold-plate power units Manual, (GH4), 03.2007, 6SL3097-2AJ00-0BP4... - Page 98 Line connection 4.12 Line reactors for Basic Line Modules Figure 4-38 Dimension drawing: Line reactor for Basic Line Module (40 kW) Booksize cold-plate power units Manual, (GH4), 03.2007, 6SL3097-2AJ00-0BP4...
-
Page 99: Technical Specifications
Line connection 4.12 Line reactors for Basic Line Modules Figure 4-39 Dimension drawing: Line reactor for Basic Line Module (100 kW) 4.12.5 Technical specifications Table 4-36 Technical specifications of line reactors for the Basic Line Modules 6SL3000 0CE22-0AAx 0CE24-0AAx 0CE31-0AAx unit Power Rated current... -
Page 100: Line Connection Variants
Line connection 4.13 Line connection variants 4.13 Line connection variants 4.13.1 Methods of line connection A distinction is made between: ● Direct operation of the line connection components on the supply ● Operating line connection components via an autotransformer ● Operating line connection components via an isolating transformer Figure 4-40 Overview of line connection versions Booksize cold-plate power units... -
Page 101: Operation Of The Line Connection Components On The Supply Network
Line connection 4.13 Line connection variants 4.13.2 Operation of the line connection components on the supply network The SINAMICS S Booksize converter system is rated for direct operation on TN, TT, and IT line supply systems with a rated voltage of 380 V 3 AC to 480 V 3 AC. Figure 4-41 Direct operation on the line supply Booksize cold-plate power units... -
Page 102: Operation Of The Line Connection Components Via An Autotransformer
Line connection 4.13 Line connection variants 4.13.3 Operation of the line connection components via an autotransformer An autotransformer can be used to adapt the voltage in the range up to 3-ph. 480 V AC +10 %. DANGER To ensure protective separation an isolating transformer must be used for voltages greater than 3-ph. - Page 103 Line connection 4.13 Line connection variants Figure 4-42 Autotransformer Booksize cold-plate power units Manual, (GH4), 03.2007, 6SL3097-2AJ00-0BP4...
-
Page 104: Operation Of The Line Connection Components Via An Isolating Transformer
Line connection 4.13 Line connection variants 4.13.4 Operation of the line connection components via an isolating transformer The isolating transformer converts the network configuration of the system (e.g. IT/TT system) to a TN system. Additional voltage adaptation to the permissible voltage tolerance range is possible. - Page 105 Line connection 4.13 Line connection variants Figure 4-43 Isolating transformer Booksize cold-plate power units Manual, (GH4), 03.2007, 6SL3097-2AJ00-0BP4...
-
Page 106: Line Connection Via A Ground-Fault Circuit Interrupter
Line connection 4.13 Line connection variants 4.13.5 Line connection via a ground-fault circuit interrupter In addition to the implemented protective measures against direct and indirect contact, selectively tripping AC/DC-sensitive residual-current circuit-breakers (Type B) can be used. DANGER Residual-current circuit-breakers alone are not permissible to provide protection against direct and indirect contact. - Page 107 Recommendation SIEMENS selectively switching AC/DC-sensitive residual-current circuit-breakers in accordance with EN 61009-1 of the 5SM series (e.g. 5SM3646-4 or 5SM3646-4+5SW3300 with an auxiliary disconnector (1 NC contact / 1 NO contact) for a rated current of 63 A and rated fault current of 0.3 A (see catalog "BETA Modular Installation Devices - ET B1")).
-
Page 109: Active Line Modules With Cold Plate
Active line modules with cold plate Description Active Line Modules generate a constant, regulated DC voltage in the DC link from the three- phase line supply voltage that supplies the connected Motor Modules with power. This ensures that they are not influenced by network fluctuations. When the motors are in feedback mode, Active Line Modules supply power back to the network. - Page 110 DANGER It is only permissible to establish connections to the DC link using the adapters that SIEMENS has recommended (DC link adapter and DC link rectifier adapter). CAUTION The tightening torque of the DC link busbar screws (1.8 Nm, tolerance +30%) must be checked before commissioning.
- Page 111 1000 m in active mode in conjunction with the Active Interface Module and Basic Line Filter. CAUTION Only Siemens cables may be used for DRIVE-CLiQ connections. CAUTION The DC link peripheral covers are supplied as standard with the components; they can also be ordered separately, if required (order no.: 6SL3162-5AA00-0AA0).
-
Page 112: Interface Description
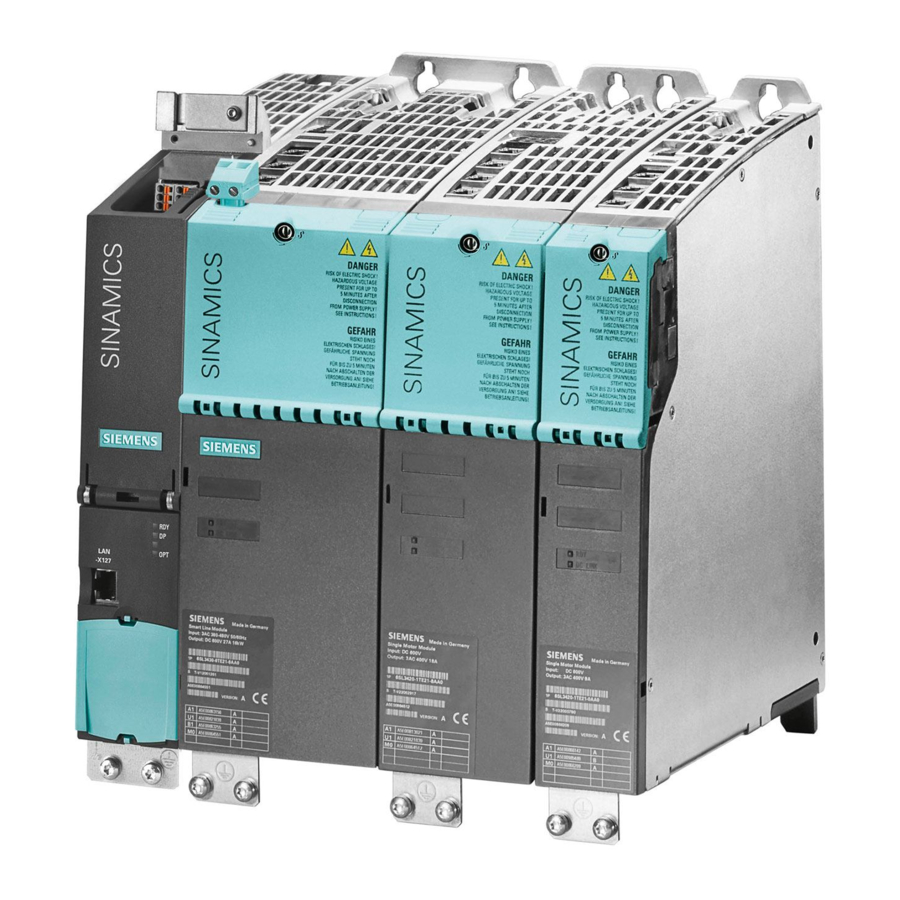
Active line modules with cold plate 5.3 Interface description Interface description 5.3.1 Overview Figure 5-1 Active line module With cold plate (example: 55 kW) Booksize cold-plate power units Manual, (GH4), 03.2007, 6SL3097-2AJ00-0BP4... -
Page 113: Connection Example
Active line modules with cold plate 5.3 Interface description 5.3.2 Connection example Figure 5-2 Connection example: active line module with cold plate Booksize cold-plate power units Manual, (GH4), 03.2007, 6SL3097-2AJ00-0BP4... -
Page 114: X1 Line Connection
Active line modules with cold plate 5.3 Interface description 5.3.3 X1 line connection Table 5-1 Terminal block X1 Active Line Module 16 kW Terminal Technical specifications Max. connectable cross-section: 10 mm Type: Screw terminal 6 (see Connection Methods) Tightening torque: 1.5 - 1.8 Nm PE connection Threaded hole M5/3 Nm 1 for ring cable lugs to DIN 46234... -
Page 115: X200-X202 Drive-Cliq Interfaces
Active line modules with cold plate 5.3 Interface description 5.3.4 X200-X202 DRIVE-CLiQ interfaces Table 5-3 DRIVE-CLiQ interface X200-X202 Signal name Technical specifications Transmit data + Transmit data - Receive data + Reserved, do not use Reserved, do not use Receive data - Reserved, do not use Reserved, do not use + (24 V) -
Page 116: X24 24 V Terminal Adapter
Active line modules with cold plate 5.3 Interface description 5.3.6 X24 24 V terminal adapter Table 5-5 Terminal block X24 Terminal Designation Technical specifications 24 V power supply 24 V DC supply voltage Ground Electronics ground The 24 V terminal adapter is supplied as standard Max. -
Page 117: Dimension Drawing
5.4 Dimension Drawing Cause and rectification of faults The following reference contains information about the cause and rectification of faults: Reference: /IH1/ SINAMICS S120, Commissioning Manual. Dimension Drawing Figure 5-3 Dimension drawing, Active Line Module with cold plate (16 kW) - Page 118 Active line modules with cold plate 5.4 Dimension Drawing Figure 5-4 Dimension drawing, Active Line Module with cold plate (36 kW, 55 kW, 80 kW, and 120 Table 5-8 Dimensions, Active Line Modules with cold plate (36 kW, 55 kW, 80 kW, and 120 kW) Line module type Order number W [mm] (inches)
-
Page 119: Installing The Cold-Plate Modules On Customer-Specific Heat Sinks
Note the installation position of the heat-conducting film (see diagram below). Note When a component is replaced, the heat-conducting film must also be replaced. Only heat-conducting film approved or supplied by Siemens can be used. Order No. Heat-conducting foil, 50 mm 6SL3162-6FB00-0AA0... - Page 120 To begin, tighten the screws by hand (approx. 0.5 Nm) in the sequence shown (steps 1 to 4) and then secure them (10 Nm). Help with the mechanical cabinet design is available from: Siemens AG A&D SE WKC CoC CabinetCooling P.O.
- Page 121 Active line modules with cold plate 5.5 Installing the Cold-Plate Modules on Customer-Specific Heat Sinks Properties of the heat sink AlMgSi 0.5 is recommended as the heat sink material. The roughness of the external heat sink surface should be at least Rz 16 and the contact surface between the heat sink and cold plate should have an evenness of 0.2 mm (applicable to a height of 450 mm and width of 300 mm).
-
Page 122: Technical Specifications
Active line modules with cold plate 5.6 Technical Specifications Technical Specifications Table 5-9 Technical data for Active Line Modules with cold-plate cooling 6SL3136-7TE 21-6AAx 23-6AAx 25-5AAx 28-0AAx 31-2AAx Rated power Connection voltages: Line voltage 3-ph. 380 V AC – 10% (-15% < 1 min) up to 3-ph. 480 V AC + 10% ACrms Line frequency 47 to 63... - Page 123 Active line modules with cold plate 5.6 Technical Specifications 6SL3136-7TE 21-6AAx 23-6AAx 25-5AAx 28-0AAx 31-2AAx Maximum permissible DC μF 20 000 20 000 20 000 20 000 20 000 link capacitance Power factor cosϕ Weight 10,2 13,8 20,3 20,4 Power loss See Chapter Cabinet design and EMC 1) The specified values apply for 380 V 2) The specified rated power values/currents can only be achieved if direct liquid cooling is used.
- Page 124 Active line modules with cold plate 5.6 Technical Specifications Derating as a function of the ambient temperature Figure 5-7 Derating as a function of the ambient temperature Derating as a function of the site altitude Figure 5-8 Derating as a function of the site altitude Booksize cold-plate power units Manual, (GH4), 03.2007, 6SL3097-2AJ00-0BP4...
- Page 125 Active line modules with cold plate 5.6 Technical Specifications Voltage derating as a function of the installation altitude Figure 5-9 Voltage derating as a function of the installation altitude Output power as a function of total cable length Figure 5-10 Output power as a function of total cable length Booksize cold-plate power units Manual, (GH4), 03.2007, 6SL3097-2AJ00-0BP4...
-
Page 127: Basic Line Modules With Cold Plate
Basic Line Modules with cold plate Description The Basic Line Modules provide an unregulated DC link voltage that matches the rectified line input voltage. One or more Motor Modules can be connected to the power supply network via the Basic Line Module. -
Page 128: Safety Information
DANGER It is only permissible to establish connections to the DC link using the adapters that SIEMENS has recommended (DC link adapter and DC link rectifier adapter). Booksize cold-plate power units Manual, (GH4), 03.2007, 6SL3097-2AJ00-0BP4... - Page 129 The DC link side covers are supplied as standard with the components; they can also be ordered separately, if required (order no.: 6SL3162-5AA00-0AA0). Note Only Siemens cables should be used for DRIVE-CLiQ connections. NOTICE If a drive line-up is switched off by means of the line disconnecting device, the voltage at terminals 3 (EP +24 V) and 4 (EP M) must be interrupted beforehand.
-
Page 130: Interface Description
Basic Line Modules with cold plate 6.3 Interface description Interface description 6.3.1 Overview Figure 6-1 Interface description: Basic Line Module with cold-plate cooling (20 kW) Booksize cold-plate power units Manual, (GH4), 03.2007, 6SL3097-2AJ00-0BP4... - Page 131 Basic Line Modules with cold plate 6.3 Interface description Figure 6-2 Interface description: Basic Line Module with cold-plate cooling (40 kW) Booksize cold-plate power units Manual, (GH4), 03.2007, 6SL3097-2AJ00-0BP4...
- Page 132 Basic Line Modules with cold plate 6.3 Interface description Figure 6-3 Interface description: Basic Line Module with cold-plate cooling (100 kW) Booksize cold-plate power units Manual, (GH4), 03.2007, 6SL3097-2AJ00-0BP4...
-
Page 133: Connection Example
Basic Line Modules with cold plate 6.3 Interface description 6.3.2 Connection example Figure 6-4 Connection example: Basic Line Module (20 kW and 40 kW) Booksize cold-plate power units Manual, (GH4), 03.2007, 6SL3097-2AJ00-0BP4... - Page 134 Basic Line Modules with cold plate 6.3 Interface description Figure 6-5 Connection example: Basic Line Module (100 kW) Booksize cold-plate power units Manual, (GH4), 03.2007, 6SL3097-2AJ00-0BP4...
-
Page 135: X1 Line Connection
Basic Line Modules with cold plate 6.3 Interface description 6.3.3 X1 line connection Table 6-1 Terminal block X1 Basic Line Module 20 kW Terminal Technical specifications Max. connection voltage: 480 V 3 AC +10 % at 47 Hz to 63 Hz Max. -
Page 136: X24 24 V Terminal Adapter
Basic Line Modules with cold plate 6.3 Interface description Table 6-3 Terminal block X1 Basic Line Module 100 kW Terminal Technical specifications Max. connection voltage: 480 V 3 AC +10 % at 47 Hz to 63 Hz Max. connectable cross-section: 120 mm Type: Threaded bolt M8 (see Connection Methods) Tightening torque: 13 Nm... -
Page 137: X200-X202 Drive-Cliq Interfaces
Basic Line Modules with cold plate 6.3 Interface description 6.3.5 X200-X202 DRIVE-CLiQ interfaces Table 6-5 DRIVE-CLiQ interface X200-X202 Signal name Technical specifications Transmit data + Transmit data - Receive data + Reserved, do not use Reserved, do not use Receive data - Reserved, do not use Reserved, do not use + (24 V) -
Page 138: X21 Ep Terminals
Basic Line Modules with cold plate 6.3 Interface description 6.3.7 X21 EP terminals Table 6-8 Terminal block X21 Terminal Designation Technical specifications + Temp Temperature switch type: Bimetallic-element switch with NC contact - Temp Response threshold of the temperature input: Temperature at the braking resistor in the operating range →... -
Page 139: Meaning Of The Leds On The Basic Line Module
Basic Line Modules with cold plate 6.3 Interface description 6.3.8 Meaning of the LEDs on the Basic Line Module Table 6-9 Meaning of the LEDs on the Basic Line Module Color State Description Electronics power supply outside the permissible tolerance range. Green Continuously lit The component is ready for operation and cyclic DRIVE-CLiQ... -
Page 140: Dimension Drawings
Basic Line Modules with cold plate 6.4 Dimension drawings Dimension drawings Figure 6-6 Dimension drawing: Basic Line Module with cold plate 20 kW Booksize cold-plate power units Manual, (GH4), 03.2007, 6SL3097-2AJ00-0BP4... - Page 141 Basic Line Modules with cold plate 6.4 Dimension drawings Figure 6-7 Dimension drawing: Basic Line Module with cold plate 40 kW Booksize cold-plate power units Manual, (GH4), 03.2007, 6SL3097-2AJ00-0BP4...
- Page 142 Basic Line Modules with cold plate 6.4 Dimension drawings Figure 6-8 Dimension drawing: Basic Line Module with cold plate 100 kW Booksize cold-plate power units Manual, (GH4), 03.2007, 6SL3097-2AJ00-0BP4...
-
Page 143: Installation
Note the installation position of the heat-conducting film (see diagrams below). Note When a component is replaced, the heat-conducting film must also be replaced! Only heat-conducting film approved or supplied by Siemens may be used. Order No. Heat-conducting foil, 50 mm 6SL3162-6FB00-0AA0... - Page 144 Basic Line Modules with cold plate 6.5 Installation Figure 6-9 Installation of Basic Line Module 40 kW with external heat sink and heat-conducting film To begin, tighten the screws by hand (approx. 0.5 Nm) in the sequence shown (steps 1 to 4) and then secure them (10 Nm).
- Page 145 6.5 Installation Figure 6-10 Installation of Basic Line Module 100 kW with external heat sink and heat-conducting film Help with the mechanical cabinet design is available from: Siemens AG A&D SE WKC CoC CabinetCooling P.O. Box 1124 09070 Chemnitz, Germany E-mail: cc.cabinetcooling@siemens.com...
- Page 146 Basic Line Modules with cold plate 6.5 Installation Properties of the heat sink AlMgSi 0.5 is recommended as the heat sink material. The roughness of the external heat sink surface should be at least Rz 16 and the contact surface between the heat sink and cold plate should have an evenness of 0.2 mm (applicable to a height of 450 mm and width of 300 mm).
-
Page 147: Replacing The Fan For Capacitor Cooling
Basic Line Modules with cold plate 6.6 Replacing the fan for capacitor cooling Replacing the fan for capacitor cooling Replacing the fan for capacitor cooling of a 100 kW Basic Line Module DANGER Before replacing the fan, you must switch off the power supplies (24 V DC and 400 V AC). Risk of electric shock. - Page 148 Basic Line Modules with cold plate 6.6 Replacing the fan for capacitor cooling Completely pull out the fan module Slightly push the fan holder apart and pull out the fan Observe the air flow direction markings when inserting the Observe the cable guide new fan Push in the fan in guide rails 1 and 2.
- Page 149 Basic Line Modules with cold plate 6.6 Replacing the fan for capacitor cooling Operating a 100 kW Basic Line Module from an insulated network (IT system) When a 100 kW Basic Line Module is operated from an insulated network (IT system), the connecting bracket to the interference-suppression capacitor must be removed.
-
Page 150: Electrical Connection
Basic Line Modules with cold plate 6.7 Electrical connection Electrical connection Figure 6-11 Busbar connections for booksize components DANGER The 24 V terminal adapter must not be removed or plugged in with 24 V applied. NOTICE The 24 V terminal adapter may only be withdrawn vertically to the front panel (i.e. not at an angle)! Booksize cold-plate power units Manual, (GH4), 03.2007, 6SL3097-2AJ00-0BP4... -
Page 151: Technical Data
Basic Line Modules with cold plate 6.8 Technical data Technical data Table 6-10 Technical data for Basic Line Modules with cold-plate cooling 6SL3136- 1TE22-0AA0 1TE24-0AA0 1TE31-0AA0 Rated power Connection voltages: Line voltage 3-ph. 380 V AC – 10% (-15% < 1 min) up to 3-ph. 480 V AC + 10% ACrms Line frequency 47 to 63... - Page 152 Basic Line Modules with cold plate 6.8 Technical data Infeed duty cycles for Basic Line Modules Figure 6-12 Infeed duty cycles for 20 kW and 40 kW Basic Line Modules Booksize cold-plate power units Manual, (GH4), 03.2007, 6SL3097-2AJ00-0BP4...
- Page 153 Basic Line Modules with cold plate 6.8 Technical data Figure 6-13 Infeed duty cycles for 100 kW Basic Line Module Booksize cold-plate power units Manual, (GH4), 03.2007, 6SL3097-2AJ00-0BP4...
- Page 154 Basic Line Modules with cold plate 6.8 Technical data Braking duty cycle for Basic Line Modules Figure 6-14 Braking duty cycle for 20 kW and 40 kW Basic Line Modules Derating as a function of the ambient temperature Figure 6-15 Derating as a function of the ambient temperature Booksize cold-plate power units Manual, (GH4), 03.2007, 6SL3097-2AJ00-0BP4...
- Page 155 Basic Line Modules with cold plate 6.8 Technical data Derating as a function of the site altitude Figure 6-16 Derating as a function of the site altitude Voltage derating as a function of the installation altitude Figure 6-17 Voltage derating as a function of the installation altitude Booksize cold-plate power units Manual, (GH4), 03.2007, 6SL3097-2AJ00-0BP4...
-
Page 156: Braking Resistors For Basic Line Modules
Basic Line Modules with cold plate 6.9 Braking resistors for Basic Line Modules Output power as a function of total cable length Figure 6-18 Output power as a function of total cable length Braking resistors for Basic Line Modules Figure 6-19 Dimension drawing: Braking resistor 7.5 kW and 15 kW Table 6-11 Dimensions of braking resistor 7.5 kW and 15 kW... - Page 157 Basic Line Modules with cold plate 6.9 Braking resistors for Basic Line Modules Figure 6-20 Dimension drawing: Braking resistor 30 kW and 75 kW ① T1 / T2 tunnel terminals ② Stud terminals Table 6-12 Dimensions of braking resistor 30 kW and 75 kW Order No.
- Page 158 Basic Line Modules with cold plate 6.9 Braking resistors for Basic Line Modules Table 6-13 Technical data of braking resistors for the Basic Line Modules Brake resistor Unit 6SE7018-0ES87-2DC0 6SE7021-6ES87-2DC0 6SE7023-2ES87-2DC0 6SE7028-0ES87-2DC0 Ω Peak power (Pmax) Rated power (Pn) 1,25 12,5 Can be used for Basic Line Modules...
- Page 159 Basic Line Modules with cold plate 6.9 Braking resistors for Basic Line Modules Braking duty cycles for braking resistors Figure 6-21 Braking duty cycles for braking resistors Booksize cold-plate power units Manual, (GH4), 03.2007, 6SL3097-2AJ00-0BP4...
-
Page 161: Smart Line Modules (5 Kw And 10 Kw) With Cold Plate
Smart Line Modules (5 kW and 10 kW) with cold plate Description The Smart Line Module is an unregulated infeed/regenerative feedback unit. The Smart Line Module supplies the Motor Module(s) with an unregulated DC voltage at the DC output. In the infeed mode the Smart Line Module exhibits the typical current and voltage waveforms of a 6-pulse diode rectifier bridge. - Page 162 DANGER It is only permissible to establish connections to the DC link using the adapters that SIEMENS has recommended (DC link adapter and DC link rectifier adapter). CAUTION The tightening torque of the DC link busbar screws (1.8 Nm, tolerance +30 %) must be checked before commissioning and with the complete system in a no-voltage condition (powered-down) and with the DC link discharged.
- Page 163 Smart Line Modules (5 kW and 10 kW) with cold plate 7.2 Safety Information CAUTION The total length of the power cables (motor supply cables and DC link cables) must not exceed 350 m. NOTICE Operation without the line reactor is not permissible. CAUTION The DC link side covers are supplied as standard with the components;...
-
Page 164: Interface Description
Smart Line Modules (5 kW and 10 kW) with cold plate 7.3 Interface description Interface description 7.3.1 Overview Figure 7-1 Smart line module with cold plate (10 kW) Booksize cold-plate power units Manual, (GH4), 03.2007, 6SL3097-2AJ00-0BP4... -
Page 165: Connection Example
Smart Line Modules (5 kW and 10 kW) with cold plate 7.3 Interface description 7.3.2 Connection example Figure 7-2 Connection example: smart line module with cold plate Booksize cold-plate power units Manual, (GH4), 03.2007, 6SL3097-2AJ00-0BP4... -
Page 166: X1 Line Connection
Smart Line Modules (5 kW and 10 kW) with cold plate 7.3 Interface description 7.3.3 X1 line connection Table 7-1 Terminal block X1 of Smart Line Module (5 kW and 10 kW) Terminal Technical data Max. connection voltage: 3 AC 480 V +10% at 47 Hz to 63 Hz Max. -
Page 167: X21 Terminals: Smart Line Module
Smart Line Modules (5 kW and 10 kW) with cold plate 7.3 Interface description 7.3.4 X21 terminals: smart line module Table 7-2 Terminal block X21 Terminal Designation Technical specifications DO: Ready Checkback: Smart Line Module ready The signal switches to high level when the following conditions have been met: Electronics power supply (X24) OK •... -
Page 168: X22 Terminals: Smart Line Module
Smart Line Modules (5 kW and 10 kW) with cold plate 7.3 Interface description 7.3.5 X22 terminals: smart line module Table 7-3 Terminal block X22 Terminal Designation Technical specifications 24 V power supply Electronics power supply for controlling digital inputs X22.2 and 3. -
Page 169: Meaning Of The Leds On The Smart Line Module With Cold Plate
The warning information on the components must be carefully observed! Cause and rectification of faults The following reference contains information about the cause and rectification of faults: Reference: /IH1/ SINAMICS S120, Commissioning Manual. Booksize cold-plate power units Manual, (GH4), 03.2007, 6SL3097-2AJ00-0BP4... -
Page 170: Dimension Drawing
Smart Line Modules (5 kW and 10 kW) with cold plate 7.4 Dimension drawing Dimension drawing Figure 7-3 Dimension drawing, Smart Line Module with cold plate (5 kW and 10 kW) Table 7-6 Dimension, Smart Line Module with cold plate (5 kW and 10 kW) Line module type Order number W [mm] (inches) -
Page 171: Installing The Cold-Plate Modules On Customer-Specific Heat Sinks
Mounting the cold plate module on customer-specific heat sinks Figure 7-4 Installing a cold-plate power section with an external heat sink Help with the mechanical cabinet design is available from: Siemens AG A&D SE WKC CoC CabinetCooling P.O. Box 1124 09070 Chemnitz, Germany E-mail: cc.cabinetcooling@siemens.com... - Page 172 5. The tightening torque for the screw connection is 10 Nm. Note When a component is replaced, the heat-conducting film must also be replaced. Only heat-conducting film approved or supplied by Siemens can be used. Order No. Heat-conducting foil, 50 mm...
- Page 173 Smart Line Modules (5 kW and 10 kW) with cold plate 7.5 Installing the Cold-Plate Modules on Customer-Specific Heat Sinks Remove the holder for securing the Control Unit. If an additional component is to be flush-mounted to the left of the component, the holders for securing the Control Unit must be removed.
-
Page 174: Technical Specifications
Smart Line Modules (5 kW and 10 kW) with cold plate 7.6 Technical Specifications Technical Specifications Table 7-7 Technical data for Smart Line Modules with cold-plate cooling 6SL3135-6AE 15-0AAx 21-0AAx Connection voltages: Line voltage 3-ph. 380 V AC – 10% (-15% < 1 min) up to 3-ph. 480 V AC Line frequency + 10% Electronics power supply... - Page 175 Smart Line Modules (5 kW and 10 kW) with cold plate 7.6 Technical Specifications Rated duty cycles of Smart Line Modules Figure 7-5 Rated duty cycles of Smart Line Modules Derating as a function of the ambient temperature Figure 7-6 Derating as a function of the ambient temperature Booksize cold-plate power units Manual, (GH4), 03.2007, 6SL3097-2AJ00-0BP4...
- Page 176 Smart Line Modules (5 kW and 10 kW) with cold plate 7.6 Technical Specifications Derating as a function of the site altitude Figure 7-7 Derating as a function of the site altitude Voltage derating as a function of the installation altitude Figure 7-8 Voltage derating as a function of the installation altitude Booksize cold-plate power units...
- Page 177 Smart Line Modules (5 kW and 10 kW) with cold plate 7.6 Technical Specifications Output power as a function of total cable length Figure 7-9 Output power as a function of total cable length Booksize cold-plate power units Manual, (GH4), 03.2007, 6SL3097-2AJ00-0BP4...
- Page 178 Smart Line Modules (5 kW and 10 kW) with cold plate 7.6 Technical Specifications Figure 7-10 Measuring range for max. permissible heat sink temperature for a Smart Line Module Booksize cold-plate power units Manual, (GH4), 03.2007, 6SL3097-2AJ00-0BP4...
-
Page 179: Motor Modules With Cold Plate
Motor Modules with Cold Plate Description A motor module is a power unit (inverter) that provides the power supply for the connected motor(s). Energy is supplied from the Infeed Module. A Motor Module must be connected to a Control Unit via DRIVE-CLiQ. The open-loop and closed-loop control functions for the Motor Module are stored in the Control Unit. - Page 180 DANGER It is only permissible to establish connections to the DC link using the adapters that SIEMENS has recommended (DC link adapter and DC link rectifier adapter). CAUTION The tightening torque of the DC link busbar screws (1.8 Nm, tolerance +30%) must be checked before commissioning.
- Page 181 Connect cables must be used for units with an integrated motor holding brake to ensure that the core insulation is effective. Risk of electric shock. CAUTION Only Siemens cables may be used for DRIVE-CLiQ connections. CAUTION Connecting cables to temperature sensors must always be installed with shielding. The cable shield must be connected to the chassis potential at both ends over a large surface area.
-
Page 182: Interface Description
Motor Modules with Cold Plate 8.3 Interface description Interface description 8.3.1 Overview Figure 8-1 Single motor module with cold plate (example 30 A) Booksize cold-plate power units Manual, (GH4), 03.2007, 6SL3097-2AJ00-0BP4... -
Page 183: Connection Examples
Motor Modules with Cold Plate 8.3 Interface description 8.3.2 Connection Examples Figure 8-2 Connection example of Motor Modules 3 A to 30 A and Double Motor Modules 3 A to 18 A Booksize cold-plate power units Manual, (GH4), 03.2007, 6SL3097-2AJ00-0BP4... -
Page 184: Motor/Brake Connection
Motor Modules with Cold Plate 8.3 Interface description Figure 8-3 Example connection of Single Motor Modules 45 A to 200 A 8.3.3 Motor/brake connection Table 8-1 Terminal block X1/X2 Motor Modules 3 A to 30 A and Double Motor Modules 3 A to 18 A Terminal Technical specifications U (U2) - Page 185 Motor Modules with Cold Plate 8.3 Interface description Table 8-2 Terminal block Single Motor Module 45 A to 200 A Terminals Technical specifications 45 A to 60 A: Threaded bolt M6/6 Nm 85 A: Threaded bolt M8/13 Nm 132 A to 200 A: Threaded bolt M8/13 Nm + (BR+) X11 brake connector...
-
Page 186: X21/X22 Ep Terminals / Temperature Sensor Connection For Motor Module With Cold Plate
Motor Modules with Cold Plate 8.3 Interface description 8.3.4 X21/X22 EP terminals / temperature sensor connection for motor module with cold plate Table 8-3 Terminal block X21/X22 Terminal Function Technical specifications +Temp Temperature sensor connection KTY84–1C130 -Temp EP +24 V (Enable Pulses) Supply voltage: 24 V DC (20.4 V - 28.8 V) Current consumption: 10 mA EP M1 (Enable Pulses) -
Page 187: Meaning Of The Leds On The Motor Module
The warning information on the components must be carefully observed! Cause and rectification of faults The following reference contains information about the cause and rectification of faults: Reference: /IH1/ SINAMICS S120, Commissioning Manual. Booksize cold-plate power units Manual, (GH4), 03.2007, 6SL3097-2AJ00-0BP4... -
Page 188: Dimension Drawings
Motor Modules with Cold Plate 8.4 Dimension drawings Dimension drawings Figure 8-4 Dimension drawing of Motor Module with cold plate 3 A to 18 A and 2 x 3 A to 2 x 9 A Table 8-6 Dimensions of Motor Module with cold plate 3 A to 18 A and 2 x 3 A to 2 x 9 A Motor Module type Order number W [mm] (inches) - Page 189 Motor Modules with Cold Plate 8.4 Dimension drawings Figure 8-5 Dimension drawing of Motor Module with cold plate 30 A and 2 x 18 A Table 8-7 Dimensions of Motor Module with cold plate 30 A and 2 x 18 A Motor Module type Order number W [mm]...
- Page 190 Motor Modules with Cold Plate 8.4 Dimension drawings Figure 8-6 Dimension drawing, Motor Module with cold plate 45 A, 60 A and 85 A Table 8-8 Dimensions, Motor Module with cold plate 45 A, 60 A and 85 A Motor Module type Order number W [mm] b [mm]...
- Page 191 Motor Modules with Cold Plate 8.4 Dimension drawings Figure 8-7 Dimension drawing of Motor Module with cold plate (132 A and 200 A) Table 8-9 Dimensions of Motor Module with cold plate (132 A and 200 A) Motor Module type Order number W [mm] b [mm]...
-
Page 192: Installing The Cold-Plate Modules On Customer-Specific Heat Sinks
Note the installation position of the heat-conducting film (see diagram below). Note When a component is replaced, the heat-conducting film must also be replaced. Only heat-conducting film approved or supplied by Siemens can be used. Order No. Heat-conducting foil, 50 mm 6SL3162-6FB00-0AA0... - Page 193 To begin, tighten the screws by hand (approx. 0.5 Nm) in the sequence shown (steps 1 to 4) and then secure them (10 Nm). Help with the mechanical cabinet design is available from: Siemens AG A&D SE WKC CoC CabinetCooling P.O.
- Page 194 Motor Modules with Cold Plate 8.5 Installing the Cold-Plate Modules on Customer-Specific Heat Sinks Properties of the heat sink AlMgSi 0.5 is recommended as the heat sink material. The roughness of the external heat sink surface should be at least Rz 16 and the contact surface between the heat sink and cold plate should have an evenness of 0.2 mm (applicable to a height of 450 mm and width of 300 mm).
-
Page 195: Technical Specifications
Motor Modules with Cold Plate 8.6 Technical Specifications Technical Specifications Table 8-10 Technical data of Motor Modules with cold plate cooling (3 A - 30 A) 6SL3126-1TE 13-0AA0 15-0AA0 21-0AA0 21-8AA0 23-0AA0 Voltage Infeed: DC link voltage 510 –720 Electronics power supply 24 (20.4 –... - Page 196 Motor Modules with Cold Plate 8.6 Technical Specifications Table 8-11 Technical data of Motor Modules with cold plate cooling (45 A - 200 A) 6SL3126-1TE 24-5AA0 26-0AA0 28-5AA0 31-3AA0 32-0AA0 Voltage Infeed: DC link voltage 510 –720 Electronics power supply 24 (20,4 –...
- Page 197 Motor Modules with Cold Plate 8.6 Technical Specifications Table 8-12 Technical data of Double Motor Modules with cold plate cooling (2 x 3 to 2 x18 A) 6SL3126-2TE 13-0AA0 15-0AA0 21-0AA0 21-8AA0 Voltage Infeed: DC link voltage 510 –720 Electronics power supply 24 (20,4 –...
- Page 198 Motor Modules with Cold Plate 8.6 Technical Specifications Figure 8-10 Peak current duty cycle without prior loading Figure 8-11 S6 current duty cycle with prior loading Figure 8-12 S6 peak current duty cycle with prior loading Booksize cold-plate power units Manual, (GH4), 03.2007, 6SL3097-2AJ00-0BP4...
- Page 199 Motor Modules with Cold Plate 8.6 Technical Specifications Figure 8-13 Current duty cycle with pre-loading Figure 8-14 Current duty cycle with pre-loading Booksize cold-plate power units Manual, (GH4), 03.2007, 6SL3097-2AJ00-0BP4...
- Page 200 Motor Modules with Cold Plate 8.6 Technical Specifications Derating as a function of the ambient temperature Figure 8-15 Derating as a function of the ambient temperature Derating as a function of the pulse frequency Figure 8-16 Derating as a function of the pulse frequency Booksize cold-plate power units Manual, (GH4), 03.2007, 6SL3097-2AJ00-0BP4...
- Page 201 Motor Modules with Cold Plate 8.6 Technical Specifications Derating as a function of the site altitude Figure 8-17 Derating as a function of the site altitude Voltage derating as a function of the installation altitude Figure 8-18 Voltage derating as a function of the installation altitude Booksize cold-plate power units Manual, (GH4), 03.2007, 6SL3097-2AJ00-0BP4...
-
Page 203: Connection Adapter
Connection adapter Description Connection adapter allow cooling water hoses to be attached to the cold plate. A connection adapter with a molded seal is attached to the top and bottom of the cold plate. The connection adapter is made of aluminum and has threads for attaching conventional hose connections. -
Page 204: Dimension Drawing
Connection adapter 9.3 Dimension drawing Dimension drawing Figure 9-1 Dimension drawing of connection adapter Table 9-1 Dimensions Width of the power section [mm] b [mm] (inches) of associated connection adapter (inches) 300 (11.81) 298 (11.73) Booksize cold-plate power units Manual, (GH4), 03.2007, 6SL3097-2AJ00-0BP4... - Page 205 Connection adapter 9.3 Dimension drawing Space requirements for connection adapter The connection adapter requires approx. 100 mm (3.94 inches) above and below the component. This does not, however, include the bending radius for the water hose, which means that extra space must be provided for the water supply lines. Figure 9-2 Space requirements for connection adapter Booksize cold-plate power units...
-
Page 206: Installation
Connection adapter 9.4 Installation Installation The connectors must be secured on site. The hose connections must be made of stainless steel. The water connection can be up to ½". Figure 9-3 Connection method Booksize cold-plate power units Manual, (GH4), 03.2007, 6SL3097-2AJ00-0BP4... - Page 207 Connection adapter 9.4 Installation Figure 9-4 Example: connection adapter with seal Booksize cold-plate power units Manual, (GH4), 03.2007, 6SL3097-2AJ00-0BP4...
-
Page 209: Internal Liquid Cooling
Internal Liquid Cooling 10.1 Cooling system requirements Open cooling systems must never be used. Only closed cooling systems - preferably with a mechanism for monitoring the quality of the cooling water - must be installed. The electrochemical processes that take place in a cooling system must be minimized by choosing the right materials. -
Page 210: Cooling Water Requirements
NOTICE Condensation must not be allowed to form on the SINAMICS S120 equipment as a result of supercooling. The temperature of the cooling water may have to be regulated. A particle filter (particle size < 100 µm) must be installed in the cooling water circuit. -
Page 211: Anti-Freeze Additive
Internal Liquid Cooling 10.3 Anti-Freeze Additive 10.3 Anti-Freeze Additive Antifrogen N (Clariant; http://www.clariant.com) is recommended as an antifreeze. The proportion of anti-freeze must be between 20 % and 30 %. This ensures frost protection in temperatures of at least –10°C. NOTICE If the proportion of anti-freeze is greater than 30 %, this can inhibit the transfer of heat and prevent the equipment from functioning correctly. -
Page 212: Biocide Additive (If Required)
Internal Liquid Cooling 10.5 Biocide Additive (If Required) 10.5 Biocide Additive (If Required) ● Adding Nalco N 77352 (ONDEO Nalco; http://www.ondeonalco.com) intermittently is recommended twice a month. Required amount: 5 – 15 mg / 100 liter of cooling water. This product does not impair the effectiveness of the corrosion inhibitor with Nalco 00GE056. - Page 213 Internal Liquid Cooling 10.7 Water-to-water heat exchanger 10.7 Water-to-water heat exchanger If a cooling circuit that does not exceed 35°C but does not fulfill the cooling water requirements is already installed in the system, the two cooling circuits can be linked via a water-to-water heat exchanger.
-
Page 214: Air-To-Water Heat Exchanger
Internal Liquid Cooling 10.8 Air-to-water heat exchanger 10.8 Air-to-water heat exchanger If a process water network is not installed but it is nonetheless best to use water-cooled frequency converters, an air-to-water cooling system can be used. The temperature of the ambient air must not be excessively high (e.g. -
Page 215: Active Cooling Unit
Internal Liquid Cooling 10.9 Active Cooling Unit 10.9 Active Cooling Unit If a process water network has not been installed and the ambient air is > 35°C (35°C < τ < 40°C), an active cooling unit can be used. This works in the same way as a refrigerator, whereby higher discharge air temperatures can be generated. -
Page 217: Dc Link Components
DC link components 11.1 Braking Module 11.1.1 Description A Braking Module (and an external braking resistor) are required for a controlled shutdown of drives during power failure (e.g. emergency retraction or EMERGENCY STOP Category 1) or to limit the DC link voltage during temporary regenerative operation when, for example, the regenerative capability of the Line Module is deactivated or not appropriately dimensioned. -
Page 218: Safety Information
DANGER It is only permissible to establish connections to the DC link using the adapters that SIEMENS has recommended (DC link adapter and DC link rectifier adapter). CAUTION The connection to the braking resistors must be made using a shielded cable. -
Page 219: Interface Description
DC link components 11.1 Braking Module 11.1.3 Interface description 11.1.3.1 Overview Figure 11-1 Interface description of braking module Booksize cold-plate power units Manual, (GH4), 03.2007, 6SL3097-2AJ00-0BP4... -
Page 220: Connection Example
DC link components 11.1 Braking Module 11.1.3.2 Connection example Figure 11-2 Example connection of Braking Module 11.1.3.3 Braking resistor connection X1 Table 11-1 Terminal block X1 Terminal Designation Technical specifications Braking resistor connection R1 Continued-short-circuit-proof Braking resistor connection R2 Max. connectable cross-section: 4 mm Type: Screw terminal 4 (see Connection Methods) Booksize cold-plate power units Manual, (GH4), 03.2007, 6SL3097-2AJ00-0BP4... -
Page 221: X21 Digital Inputs/Outputs
DC link components 11.1 Braking Module 11.1.3.4 X21 digital inputs/outputs Table 11-2 Terminal block X21 Terminal Designation Technical specifications DI low: enable Braking Module Voltage: -3 V to 30 V DI high: inhibit / acknowledge Typical current consumption: 10 mA at 24 V Edge change high ->... -
Page 222: Meaning Of The Leds On The Braking Module
The pre-warning for I*t monitoring is output as a high level on reaching 80% of the maximum braking resistor ON time. Only braking resistors approved by Siemens for this component are identified automatically. 11.1.3.5 Meaning of the LEDs on the braking module... -
Page 223: Dimension Drawing
DC link components 11.1 Braking Module 11.1.4 Dimension drawing Figure 11-3 Dimension drawing of the Braking Module Booksize cold-plate power units Manual, (GH4), 03.2007, 6SL3097-2AJ00-0BP4... -
Page 224: Installation
DC link components 11.1 Braking Module 11.1.5 Installation Figure 11-4 Methods of installing Braking Modules with/without spacer elements Booksize cold-plate power units Manual, (GH4), 03.2007, 6SL3097-2AJ00-0BP4... -
Page 225: Technical Specifications
DC link components 11.1 Braking Module 11.1.6 Technical specifications Table 11-4 Technical data Braking Module Booksize Voltages Supply: DC link voltage 510 - 720 ON threshold Electronics power supply 24 (20,4 - 28,8) Electronics current consumption (at 24 V DC) Strombelastbarkeit DC link busbar Current carrying capacity... -
Page 226: Braking Resistors For Braking Module
DC link components 11.1 Braking Module 11.1.7 Braking resistors for Braking Module Figure 11-5 Dimension drawing: Braking resistor 0.3 kW / 25 kW Booksize cold-plate power units Manual, (GH4), 03.2007, 6SL3097-2AJ00-0BP4... - Page 227 DC link components 11.1 Braking Module Figure 11-6 Dimension drawing: Braking resistor 1.5 kW / 100 kW CAUTION The surface temperature of the braking resistors may exceed 80 °C. Booksize cold-plate power units Manual, (GH4), 03.2007, 6SL3097-2AJ00-0BP4...
- Page 228 DC link components 11.1 Braking Module Figure 11-7 Duty cycle for braking resistors T [s] period duration of braking duty cycle A [s] load duration [W] continuous braking power of braking resistor [W] peak braking power of braking resistor Table 11-5 Example of duty cycles Unit R 25 kW...
-
Page 229: Capacitor Module
DC link components 11.2 Capacitor Module 11.2 Capacitor Module 11.2.1 Description Capacitor modules are used to increase the DC link capacitance to bridge momentary power losses. Capacitor modules are connected to the DC link voltage via the integrated DC link busbars. Capacitor modules function autonomously. - Page 230 DANGER It is only permissible to establish connections to the DC link using the adapters that SIEMENS has recommended (DC link adapter and DC link rectifier adapter). CAUTION The DC link side covers are supplied as standard with the components; they can also be ordered separately, if required (order no.: 6SL3162-5AA00-0AA0).
-
Page 231: Interface Description
DC link components 11.2 Capacitor Module 11.2.3 Interface description 11.2.3.1 Overview Figure 11-8 Interface description of the capacitor module Booksize cold-plate power units Manual, (GH4), 03.2007, 6SL3097-2AJ00-0BP4... -
Page 232: Dimension Drawing
DC link components 11.2 Capacitor Module 11.2.4 Dimension drawing Figure 11-9 Dimension drawing of the capacitor module Booksize cold-plate power units Manual, (GH4), 03.2007, 6SL3097-2AJ00-0BP4... -
Page 233: Installation
DC link components 11.2 Capacitor Module 11.2.5 Installation Figure 11-10 Installing a Capacitor Module with/without spacer elements The Capacitor Module can be attached to the cabinet panel with or without spacer elements. Booksize cold-plate power units Manual, (GH4), 03.2007, 6SL3097-2AJ00-0BP4... -
Page 234: Technical Specifications
DC link components 11.2 Capacitor Module 11.2.6 Technical Specifications Table 11-7 Technical data Capacitor Module Electronics power supply 24 (20,4 - 28,8) DC link voltage 510 - 720 Capacitance μF 4000 24 V DC busbar current carrying capacity DC link busbar current carrying capacity Power loss Weight... -
Page 235: Control Supply Module
DC link components 11.3 Control Supply Module 11.3 Control Supply Module 11.3.1 Description The Control Supply Module is a 24 V power supply with 20 A output current. The output voltage corresponds to protective extra low voltage (DVC A) with grounded frame. - Page 236 DANGER It is only permissible to establish connections to the DC link using the adapters that SIEMENS has recommended (DC link adapter and DC link rectifier adapter). CAUTION The tightening torque of the DC link busbar screws (1.8 Nm, tolerance +30 %) must be checked before commissioning.
-
Page 237: Interface Description
DC link components 11.3 Control Supply Module 11.3.3 Interface description 11.3.3.1 Overview Figure 11-11 Interface description: control supply module Booksize cold-plate power units Manual, (GH4), 03.2007, 6SL3097-2AJ00-0BP4... -
Page 238: Connection Example
DC link components 11.3 Control Supply Module 11.3.3.2 Connection example Figure 11-12 Example connection of Control Supply Module Booksize cold-plate power units Manual, (GH4), 03.2007, 6SL3097-2AJ00-0BP4... -
Page 239: Meaning Of The Leds On The Control Supply Module
DC link components 11.3 Control Supply Module The Control Supply Module (CSM) is connected to the line supply (3-ph. 380 V AC –10 % up to 480 V +10 %) via the appropriate screw terminals (0.2 to 4 mm ). This connection should preferably be made without using an isolating device (e.g. -
Page 240: Dimension Drawing
DC link components 11.3 Control Supply Module 11.3.4 Dimension drawing Figure 11-13 Dimension drawing of the Control Supply Module Booksize cold-plate power units Manual, (GH4), 03.2007, 6SL3097-2AJ00-0BP4... -
Page 241: Technical Specifications
DC link components 11.3 Control Supply Module 11.3.5 Technical Specifications Table 11-9 Technical data Control Supply Module Unit Value Input data Line voltage 3-ph. 380 - 480 V ± 15 % Line frequency 47 to 63 Rated input current Rated value (at U approx. -
Page 242: Voltage Clamping Module (Vcm)
DC link components 11.4 Voltage Clamping Module (VCM) 11.4 Voltage Clamping Module (VCM) 11.4.1 Description Under certain unfavorable conditions, voltage rises can occur in extended drive line-ups due to the stimulation of the system resonance frequency. This can be particularly damaging for the insulation systems of the connected motors since partial discharges can occur. -
Page 243: Safety Information
A ventilation clearance of 80 mm above and below the components must be observed. DANGER It is only permissible to establish connections to the DC link using the adapters that SIEMENS has recommended (DC link adapter and DC link rectifier adapter). Booksize cold-plate power units Manual, (GH4), 03.2007, 6SL3097-2AJ00-0BP4... - Page 244 DC link components 11.4 Voltage Clamping Module (VCM) CAUTION After being transported the screws must be tightened. The tightening torque of the DC link busbar screws (1.8 Nm, tolerance +30 %) must be checked before commissioning. CAUTION The DC link side covers are supplied as standard with the components; they can also be ordered separately, if required (order no.: 6SL3162-5AA00-0AA0).
-
Page 245: Interface Description
DC link components 11.4 Voltage Clamping Module (VCM) 11.4.3 Interface description 11.4.3.1 Overview Figure 11-14 Interface description: Voltage Clamping Module Booksize cold-plate power units Manual, (GH4), 03.2007, 6SL3097-2AJ00-0BP4... -
Page 246: X1 Functional Ground
DC link components 11.4 Voltage Clamping Module (VCM) Figure 11-15 Circuit diagram: Voltage Clamping Module 11.4.3.2 X1 functional ground X1 functional ground To ensure that the Voltage Clamping Module functions properly, a functional ground must be connected to X1. Please note: ●... -
Page 247: Dimension Drawing
DC link components 11.4 Voltage Clamping Module (VCM) 11.4.4 Dimension drawing Figure 11-16 Dimension drawing of the Voltage Clamping Module Booksize cold-plate power units Manual, (GH4), 03.2007, 6SL3097-2AJ00-0BP4... -
Page 248: Installation
DC link components 11.4 Voltage Clamping Module (VCM) 11.4.5 Installation See the instructions for installing other DC link components (e.g. Braking Module, Capacitor Module). Arrangement of the Voltage Clamping Module: The Voltage Clamping Module should ideally be placed directly next to the Line Module. ●... -
Page 249: Power Components On The Motor Side
Power components on the motor side 12.1 Motor reactors 12.1.1 Description Motor reactors reduce the voltage stress on the motor windings by reducing the voltage gradients at the motor terminals that occur when motors are fed from drive converters. At the same time, the capacitive re-charging currents that additionally load the output of the Power Module when longer motor cables are used are simultaneously reduced. -
Page 250: Safety Information
Note The connecting cables to the Motor Module must be kept as short as possible (max. 5 m). CAUTION When using motor reactors that SIEMENS has not approved for SINAMICS, then these can thermally damage the reactor. CAUTION The surface temperature of the motor reactors can exceed 80 °C. -
Page 251: Dimension Drawings
Power components on the motor side 12.1 Motor reactors 12.1.3 Dimension drawings Figure 12-1 Dimension drawings: Motor reactors Booksize cold-plate power units Manual, (GH4), 03.2007, 6SL3097-2AJ00-0BP4... - Page 252 Power components on the motor side 12.1 Motor reactors Figure 12-2 Mounting hole Table 12-1 Dimensions of motor reactors, all data in mm and (inches) 6SE7021-0ES87-1FE0 6SE7022-6ES87-1FE0 6SE7024-7ES87-1FE0 6SE7027-2ES87-1FE0 Fig. III Fig. III Fig. II Fig. I 178 (7,00) 219 (8,62) 197 (7,75) 267 (10,51) 153 (6,02)
- Page 253 Power components on the motor side 12.1 Motor reactors Table 12-3 Dimensions of motor reactors, all data in mm and (inches) 6SL3000- 2BE21-0AA0 150 (5,90) 178 (7,00) 88 (3,46) 111 (4,37) 67 (2,63) 159 (6,25) 64 (2,51) 113 (4,44) 68 (2,67) 166 (6,53) 5,8 (0,22) 11 (0,43)
- Page 254 Power components on the motor side 12.1 Motor reactors Flat connector Table 12-4 Dimensions of motor reactors, all data in mm and (inches) 6SL3000- 2BE26-0AA0 max. 228 (8.97) 267 (10,51) 107 (4,21) 125,5 (4,94) 72 (2,83) 220 (8,66) 56 (2,20) 100 (3,93) 70 (2,75) 176 (6,92)
-
Page 255: Technical Data
Power components on the motor side 12.1 Motor reactors 6SL3000- 2BE26-0AA0 Lengths n and n corresponds to the distance between holes 12.1.4 Technical Data Table 12-5 Technical data, motor reactors, part 1 Order No. 6SE7021- 6SL3000- 6SE7022- 6SE7024- 6SE7027- 0ES87-1FE0 2BE21-0AA0 6ES87-1FE0 7ES87-1FE0... - Page 256 Power components on the motor side 12.1 Motor reactors Table 12-7 Cable lengths, Part 1 Order No. 6SE7021- 6SL3000-2BE21- 6SE7022- 6SE7024- 6SE7027- 0ES87-1FE0 0AA0 6ES87-1FE0 7ES87-1FE0 2ES87-1FE0 Rated current [A] Shielded cables Maximum motor cable length, 1 reactor Maximum motor cable length, 2 reactors Maximum motor cable length, 3 reactors...
-
Page 257: Accessories
Accessories 13.1 Shield connecting plates 13.1.1 Description The line and motor cable shields are connected to the shield connecting plates. This ensures EMC compliance. Booksize cold-plate power units Manual, (GH4), 03.2007, 6SL3097-2AJ00-0BP4... -
Page 258: Overview
Accessories 13.1 Shield connecting plates 13.1.2 Overview Figure 13-1 Shield connecting plate for a 200 mm module with with a cold plate Booksize cold-plate power units Manual, (GH4), 03.2007, 6SL3097-2AJ00-0BP4... -
Page 259: Dimension Drawings
Accessories 13.1 Shield connecting plates 13.1.3 Dimension drawings Figure 13-2 Dimension drawing, shield connecting plate on a 100 mm component with cold plate Note The shield connecting plate is part of the scope of supply for a 100 mm Line Module. Recommended shield connections: from Weidmüller, order no. - Page 260 Accessories 13.1 Shield connecting plates Figure 13-3 Dimension drawing, shield connecting plate on a 150 mm component with cold plate Note Recommended shield connections: from Weidmüller, order no. KLBÜ CO1 and KLBÜ CO4 Weidmüller: http://www.weidmueller.com Booksize cold-plate power units Manual, (GH4), 03.2007, 6SL3097-2AJ00-0BP4...
- Page 261 Accessories 13.1 Shield connecting plates Figure 13-4 Dimension drawing, shield connecting plate on a 200 mm component with cold plate Note Recommended shield connections: Weidmüller, Order No. KLBÜ CO1 Weidmüller: http://www.weidmueller.com Booksize cold-plate power units Manual, (GH4), 03.2007, 6SL3097-2AJ00-0BP4...
- Page 262 Accessories 13.1 Shield connecting plates Dimension drawing, shield connecting plate on a 300 mm component with cold plate Note Recommended shield connections: Weidmüller, Order No. KLBÜ CO1 Weidmüller: http://www.weidmueller.com Booksize cold-plate power units Manual, (GH4), 03.2007, 6SL3097-2AJ00-0BP4...
-
Page 263: Mounting
Accessories 13.1 Shield connecting plates 13.1.4 Mounting Table 13-1 Mounting the shield connecting plate to a 100 mm component using as an example, internal air cooling Remove the screw with Hook in the shielded plate. Secure the shield connecting Mounted shield connecting screwdriver T25 plate with screwdriver T25/3 plate... - Page 264 Accessories 13.1 Shield connecting plates Table 13-2 Mounting the shield connecting plate to a 200 mm component using as an example, internal air cooling Loosen the lower mounting screws Hook the shield connecting plate into Secure the shield connecting plate by using a screwdriver the screws and on the line/motor shifting it to the left...
- Page 265 Accessories 13.1 Shield connecting plates Table 13-3 Mounting the shield connecting plate to a 300 mm component using as an example, internal air cooling Remove the screw with screwdriver T25 Hook the shield connecting plate into the line/motor connection Secure the shield connecting plate with screwdriver T25/3 Mounted shield connecting plate Booksize cold-plate power units Manual, (GH4), 03.2007, 6SL3097-2AJ00-0BP4...
-
Page 266: Electrical Connection
Accessories 13.1 Shield connecting plates 13.1.5 Electrical Connection Table 13-4 Electrical connection at the shield connecting plate for 100 mm component using as an example, internal air cooling Attach the protective Secure the power cable with Secure the shield clamp to The power cable is conductor (PE) using a flat-bladed screwdriver 4/1.8... - Page 267 Accessories 13.1 Shield connecting plates Table 13-5 Electrical connection at the shield connecting plate for 200 mm component using as an example, internal air cooling Unlock and remove the cover of the Remove nuts M8 using a suitable tool. Secure the earthing cable with terminal block.
- Page 268 Accessories 13.1 Shield connecting plates Close the cover of the terminal block. Booksize cold-plate power units Manual, (GH4), 03.2007, 6SL3097-2AJ00-0BP4...
-
Page 269: Dc Link Rectifier Adapter
Accessories 13.2 DC link rectifier adapter 13.2 DC link rectifier adapter 13.2.1 Description The DC link rectifier adapter supplies the DC link voltage directly. With a direct supply, each component is connected to the DC link separately. The internal DC link busbar is not used here. -
Page 270: Safety Information
DANGER It is only permissible to establish connections to the DC link using the adapters that SIEMENS has recommended (DC link adapter and DC link rectifier adapter). DANGER Components for which the recesses for the DC link rectifier adapter have been removed must no longer be operated without them. - Page 271 Accessories 13.2 DC link rectifier adapter DANGER If a 50 mm wide module or if a DC link component with the appropriate width (e.g. Braking Module, Control Supply Module, Voltage Clamping Module) is located at the lefthand end of the drive line-up, then the DC link bridge including all of the screws must be removed. It is not permissible to insert the screws without a DC link bridge.
-
Page 272: Interface Description
Accessories 13.2 DC link rectifier adapter 13.2.3 Interface description 13.2.3.1 Overview Figure 13-5 150 mm components with DC link rectifier adapter for 35 mm² to 95 mm² and 100 mm components with DC link rectifier adapter for 4 mm² to 10 mm² Booksize cold-plate power units Manual, (GH4), 03.2007, 6SL3097-2AJ00-0BP4... -
Page 273: Dc Link Connection
Accessories 13.2 DC link rectifier adapter 13.2.3.2 DC link connection Table 13-7 DC link rectifier adapter – description of the terminals Terminal Function Technical specifications DC link positive Supply voltage: 720 V-VDE/600 V-UL DC link negative Direct supply 4 – 10 mm² Current carrying capacity: 36 A connection cross-section: 4 –... -
Page 274: Dimension Drawings
Accessories 13.2 DC link rectifier adapter 13.2.4 Dimension drawings Figure 13-6 Dimension drawing, 100 mm components with DC link rectifier adapter for 0.5 mm² to 10 mm² Booksize cold-plate power units Manual, (GH4), 03.2007, 6SL3097-2AJ00-0BP4... - Page 275 Accessories 13.2 DC link rectifier adapter Figure 13-7 Dimension drawing, 150 mm components with DC link rectifier adapter for 35 mm² to 95 mm² Booksize cold-plate power units Manual, (GH4), 03.2007, 6SL3097-2AJ00-0BP4...
-
Page 276: Installation
Accessories 13.2 DC link rectifier adapter 13.2.5 Installation DANGER If a 50 mm wide component or if a DC link component with the appropriate width (e.g. Braking Module, CSM, VCM) is located on the left-hand side of the drive line-up, the DC link bridge including all of the screws must be removed. - Page 277 Accessories 13.2 DC link rectifier adapter Table 13-8 Installing the DC link rectifier adapter for 50 mm and 100 mm components Unlock and open the Opened cover with 24 V The DC link bridge and 24 V Removed DC link bridge and protective cover jumper and DC link bridge jumper have been removed.
- Page 278 Accessories 13.2 DC link rectifier adapter Table 13-9 Installing the DC link rectifier adapter for 150 mm, 200 mm, and 300 mm components Unlock and open the protective cover Opened cover with 24 V jumper Remove the 24 V jumper and unscrew the DC link screws.
- Page 279 Accessories 13.2 DC link rectifier adapter Table 13-10 Installing the 24 V adapter for 150 mm wide components Unlock and open the protective cover (example: Break out the recess using suitable pliers Active Line Module (36 kW)) Attach the 24 V adapter. Close the protective cover Booksize cold-plate power units Manual, (GH4), 03.2007, 6SL3097-2AJ00-0BP4...
-
Page 280: Electrical Connection
Accessories 13.2 DC link rectifier adapter 13.2.6 Electrical Connection Table 13-11 Connecting the DC link rectifier adapter for 50 mm and 100 mm components Connect the cable to the DC link rectifier adapter Electrical connection of the DC link rectifier adapter Table 13-12 Connecting the DC link rectifier adapter for 150 mm, 200 mm, and 300 mm components Connect the cable to the DC link rectifier adapter Electrical connection of the DC link rectifier adapter... -
Page 281: Dc Link Adapter
DANGER It is only permissible to establish connections to the DC link using the adapters that SIEMENS has recommended (DC link adapter and DC link rectifier adapter). DANGER The DC link discharge voltage hazard warning on the components on which the adapter is installed must be in the local language. - Page 282 Accessories 13.3 DC link adapter DANGER If a 50 mm wide module or if a DC link component with the appropriate width (e.g. Braking Module, Control Supply Module, Voltage Clamping Module) is located at the left-hand end of the drive line-up, then the DC link bridge including all of the screws must be removed. The screws must not be inserted without a DC link bridge.
-
Page 283: Interface Description
Accessories 13.3 DC link adapter 13.3.3 Interface description 13.3.3.1 Overview Figure 13-8 150 mm components with DC link adapter for two-row configuration 35 mm² to 95 mm² Booksize cold-plate power units Manual, (GH4), 03.2007, 6SL3097-2AJ00-0BP4... -
Page 284: Dc Link Connection
Accessories 13.3 DC link adapter 13.3.3.2 DC link connection Table 13-13 DC link adapter – description of the terminals Terminal Function Technical specifications DC link positive Two-row configuration of adapter 35 – 95 mm² Current carrying capacity: 200 A DC link negative Voltage: 720 V-VDE/600 V AC Connection cross-section: 35 –... -
Page 285: Dimension Drawing
Accessories 13.3 DC link adapter 13.3.4 Dimension drawing Figure 13-9 Dimension drawing, 150 mm components with DC link adapter for two-row configuration 35 mm² to 95 mm² Booksize cold-plate power units Manual, (GH4), 03.2007, 6SL3097-2AJ00-0BP4... -
Page 286: Installation
Accessories 13.3 DC link adapter 13.3.5 Installation DANGER If a 50 mm wide module or if a DC link component with the appropriate width (e.g. Braking Module, Control Supply Module, Voltage Clamping Module) is located at the left-hand end of the drive line-up, then the DC link bridge including all of the screws must be removed. The screws must not be inserted without a DC link bridge. - Page 287 Accessories 13.3 DC link adapter Table 13-14 Installing the DC link adapter for a 150 mm component Unlock and open the protective cover Unscrew the screws. Secure the adapter (1.8 Nm). The 24 V adapter is installed and the protective cover is closed. Note: By moving the adapter housing, the DC link adapter can be fitted on either the left-hand or right-hand side of the module.
-
Page 288: Electrical Connection
Accessories 13.3 DC link adapter 13.3.6 Electrical connection Required tools: ● Hexagon-socket spanner (size 6) ● Suitable tool for tube clips (e.g. flat-bladed screwdriver) Table 13-16 Electrical connection of the DC link adapter for a 150 mm component Route the cable through the tube clip and insert it into the Secure the cable. -
Page 289: Reinforced Dc-Link Busbars
Accessories 13.4 Reinforced DC-link busbars 13.4 Reinforced DC-link busbars 13.4.1 Description Reinforced DC link busbars (optional) are available for 50 mm and 100 mm wide components. Order number Reinforced DC link busbars for 50 mm components 6SL3162-2DB00-0AA Reinforced DC link busbars for 100 mm components 6SL3162-2DD00-0AA Booksize cold-plate power units Manual, (GH4), 03.2007, 6SL3097-2AJ00-0BP4... -
Page 290: Safety Information
Accessories 13.4 Reinforced DC-link busbars 13.4.2 Safety information DANGER Risk of electric shock. Dangerous voltages are still present for up to 5 minutes after the power supply has been switched off. The protective cover for the DC link must not be opened until this time has elapsed. The components must only be operated when the protective cover of the DC link is closed. -
Page 291: Removing The Dc Link Busbars
Accessories 13.4 Reinforced DC-link busbars 13.4.3 Removing the DC link busbars Unscrew the screws for the DC link busbar Remove the DC link busbars Remove the DC link busbars on the adjacent components View once the DC link busbars have been removed too. -
Page 292: Drive-Cliq Cabinet Gland
IP54 acc. to EN 60529. In addition to the data lines, the power supply contacts of DRIVE-CLiQ are also routed via the coupling. 13.5.2 Safety Information Note Only Siemens cables should be used for DRIVE-CLiQ connections. Booksize cold-plate power units Manual, (GH4), 03.2007, 6SL3097-2AJ00-0BP4... -
Page 293: Interface Description
Accessories 13.5 DRIVE-CLiQ cabinet gland 13.5.3 Interface description 13.5.3.1 Overview Figure 13-10 DRIVE-CLiQ cabinet gland DRIVE-CLiQ cabinet gland Covering cap, Yamaichi, order no.: Y-ConAS-24-S IP67 acc. to EN 60529 interface Mounting holes Rating plate IP20 or IPXXB acc. to EN 60529 interface Booksize cold-plate power units Manual, (GH4), 03.2007, 6SL3097-2AJ00-0BP4... -
Page 294: Dimension Drawing
Accessories 13.5 DRIVE-CLiQ cabinet gland 13.5.4 Dimension drawing Figure 13-11 Dimension drawing, DRIVE-CLiQ cabinet gland Accessories W [mm] D [mm] H [mm] DRIVE-CLiQ cabinet gland (with 69,3 (2.72) 62,2 (2.44) 48 (1.88) seal) Booksize cold-plate power units Manual, (GH4), 03.2007, 6SL3097-2AJ00-0BP4... - Page 295 Accessories 13.5 DRIVE-CLiQ cabinet gland Figure 13-12 Cut-out for the cabinet Booksize cold-plate power units Manual, (GH4), 03.2007, 6SL3097-2AJ00-0BP4...
-
Page 296: Installation
Accessories 13.5 DRIVE-CLiQ cabinet gland 13.5.5 Installation Figure 13-13 DRIVE-CLiQ cabinet gland Installation 1. Make an opening in the cabinet panel according to the Chapter "Dimension drawing" for the DRIVE-CLiQ cabinet gland. 2. Insert the components from the outer side of the cabinet through the opening in the cabinet. -
Page 297: Technical Data
Accessories 13.5 DRIVE-CLiQ cabinet gland 13.5.6 Technical data Table 13-17 Technical data DRIVE-CLiQ cabinet gland Unit 6SL3066-2DA00-0AAx Weight 0,135 Degree of protection IP20 or IPXXB acc. to EN 60529 in the electrical cabinet IP54 to EN 60529 outside the electrical cabinet Booksize cold-plate power units Manual, (GH4), 03.2007, 6SL3097-2AJ00-0BP4... -
Page 298: Drive-Cliq Coupling
In addition to the data lines, the power supply contacts of DRIVE-CLiQ are also routed via the coupling. 13.6.2 Safety Information Note Only Siemens cables should be used for DRIVE-CLiQ connections. 13.6.3 Interface description 13.6.3.1 Overview Figure 13-14 DRIVE-CLiQ coupling... -
Page 299: Dimension Drawing
Accessories 13.6 DRIVE-CLiQ coupling 13.6.4 Dimension drawing Figure 13-15 Dimension drawing, DRIVE-CLiQ coupling Table 13-18 Dimensions of the DRIVE-CLiQ coupling, all data in mm and (inches) Accessories W [mm] b [mm] H [mm] D [mm] DRIVE-CLiQ 111,5 (4.38) 57,1 (2.24) 61 (2.40) 38 (1.49) coupling... -
Page 300: Installation
Accessories 13.6 DRIVE-CLiQ coupling 13.6.5 Installation Figure 13-16 Hole drilling template for installation 1. Fit the DRIVE-CLiQ coupling to the mounting surface in accordance with the drilling template. 2. Remove the protective caps on the DRIVE-CLiQ coupling. 3. Insert the DRIVE-CLiQ connector at both ends of the DRIVE-CLiQ coupling. 13.6.6 Technical data Table 13-19 Technical data... -
Page 301: Cabinet Design And Emc
Cabinet Design and EMC 14.1 Information 14.1.1 General SINAMICS S components fulfill the requirements according to degree of protection IP20 in compliance with EN 60529. This provides protection against electric shock for chassis units. As far as UL 50 is concerned, the components are classified and certified as open type. Protection against mechanical and climatic stressing must be ensured by mounting the components in housings, cabinets or electrical rooms that can be closed and locked. -
Page 302: Safety Information
The tightening torque of the DC link busbar screws (1.8 Nm) must be checked before startup. To ensure that the encoder system works properly, you are advised to use the original Siemens accessories from catalog D21.1. Booksize cold-plate power units Manual, (GH4), 03.2007, 6SL3097-2AJ00-0BP4... -
Page 303: Directives And Standards
Cabinet Design and EMC 14.1 Information 14.1.3 Directives and Standards The following directives and standards apply within the European Union: Table 14-1 EC Directives Directive Description 73/23/EEC Directive of the Council of February 19, 1973, on the approximation of the laws of the member states relating to electrical equipment designed for use within certain voltage limits Low-Voltage Directive 98/37/EC... - Page 304 Cabinet Design and EMC 14.1 Information Standard Description EN 1037 Safety of machinery Prevention of unexpected startup EN 1050 Safety of machinery Principles for risk assessment EN 1921 Safety of integrated manufacturing systems EN 12417 Safety of machine tools Machining centres EN 50178 Electronic equipment for use in power installations EN 60073...
-
Page 305: Selection Of Devices Required For Operating Sinamics
Cabinet Design and EMC 14.2 Selection of Devices Required for Operating SINAMICS 14.2 Selection of Devices Required for Operating SINAMICS 14.2.1 General The following components are required for connection to the power supply network: ● Line disconnecting device ● Line fuse ●... -
Page 306: Overcurrent Protection By Means Of Line Fuses Or Circuit-Breakers
Cabinet Design and EMC 14.2 Selection of Devices Required for Operating SINAMICS 14.2.3 Overcurrent Protection by Means of Line Fuses or Circuit-Breakers The cables for the drive line-up power supply must be protected against overcurrent. LV HBC, D-type, and DO-type fuses with a gL characteristic or suitable circuit-breakers can be used. - Page 307 Cabinet Design and EMC 14.2 Selection of Devices Required for Operating SINAMICS The following tables list the requirements regarding line fuses and circuit-breakers for the Active Line Modules and Smart Line Modules. Table 14-3 Requirements regarding line fuses and circuit-breakers for the Active Line Modules 16 kW 36 kW 55 kW...
-
Page 308: Line Filter
14.2.4 Line filter A separate line filter (see catalog) must be used for the SINAMICS S120 drive line-up. An additional line filter must be used to suppress interference in other loads. To prevent mutual interference, this line filter must not be equipped with line-side capacitors with respect to ground. -
Page 309: Line Contactors
Cabinet Design and EMC 14.2 Selection of Devices Required for Operating SINAMICS 14.2.5 Line Contactors Line contactors are required for electrical isolation of the drive line-up from the power supply network. For selection of the line contactor, the characteristic values in the technical data apply. The cable routing, the bundling factor, and the factor for the ambient temperature according to EN 60204-1 must be taken into account in rating the conductors to be connected. -
Page 310: Dc Supply Voltage
Cabinet Design and EMC 14.3 24 V DC Supply Voltage 14.3 24 V DC Supply Voltage 14.3.1 General The 24 V DC voltage is required for the power supply of: 1. the electronics of the SINAMICS components via the integrated 24 V busbar 2. -
Page 311: Selecting Power Supply Units
The DC power supply should be set to 26 V. The CSM supplies 26 V. This ensures that the supply voltage for the brake remains within the permissible range when the following conditions are fulfilled: • Using Siemens three-phase motors • Using Siemens MOTION-CONNECT power cables • Motor cable lengths: max. 100 m 14.3.2 Selecting Power Supply Units You are advised to use the devices in the following table. -
Page 312: Typical 24 V Component Current Consumption
Cabinet Design and EMC 14.3 24 V DC Supply Voltage 14.3.3 Typical 24 V Component Current Consumption The following table can be used to calculate the 24 V DC power supply. Table 14-7 Overview: 24 V DC current consumption with cold-plate cooling Component Current consumption [A CU320 without load... - Page 313 Cabinet Design and EMC 14.3 24 V DC Supply Voltage Component Current consumption [A Braking Modules Sensor Modules Cabinet SMC10 0,25 SMC20 0,25 SMC30 0,33 Sensor Modules External SME20 0,19 SME 25 0,19 SME120 0,24 SME125 0,24 Additional system components TM15 (without digital outputs) 0,15 for each digital output...
-
Page 314: Overcurrent Protection
EN 60204-1, Section 14, can be used to determine the overcurrent protection devices. The recommended overcurrent protection devices on the primary side are circuit-breakers as specified in Siemens catalog NSK. Miniature circuit-breakers are recommended as overcurrent protection devices on the secondary side. The MCBs can be selected according to Siemens catalog "BETA Modular Installation Devices - ET B1". - Page 315 Cabinet Design and EMC 14.3 24 V DC Supply Voltage Figure 14-1 Example of 24 V DC fuse protection The following conditions apply to the cables when the MCBs are selected from the following table: ● Ambient temperature 40°C or 55°C ●...
- Page 316 Cabinet Design and EMC 14.3 24 V DC Supply Voltage Table 14-8 MCBs by conductor cross-section and temperature Conductor cross-section Max. value up to 40 °C Max. value up to 55°C 1.5 mm 10 A 10 A 2.5 mm 20 A 10 A 4 mm 25 A...
-
Page 317: Arrangement Of Components And Equipment
Cabinet Design and EMC 14.4 Arrangement of Components and Equipment 14.4 Arrangement of Components and Equipment 14.4.1 General The arrangement of the components and equipment takes account of ● Space requirements ● Cable routing ● Cooling ● EMC Components are usually located centrally in a cabinet. 14.4.2 Drive Line-Up Figure 14-2... - Page 318 Cabinet Design and EMC 14.4 Arrangement of Components and Equipment The components in the drive line-up must be properly connected to the external heat sink. In the case of Active Line Modules above 55 kW, the Motor Modules can be mounted at the right or left.
- Page 319 Cabinet Design and EMC 14.4 Arrangement of Components and Equipment Two-tier configuration Figure 14-4 Example of a multi-tier configuration with components between 200 and 300 mm wide The distance between the two module rows depends on the wiring and cable cross-section. For modules with a width of between 50 and 100 mm, the distance between the upper and lower module row must be at least 300 mm.
- Page 320 Cabinet Design and EMC 14.4 Arrangement of Components and Equipment CAUTION Signal cables must not be routed parallel to power cables. Overview of the DC link rectifier adapter and DC link adapter Suitable for module width: Max. connectable cross-section Max. current carrying capacity DC link rectifier adapter (cable outlet on top) 6SL3162-2BD00-0AAx 50 mm, 100 mm...
-
Page 321: Three-Tier Configuration
Cabinet Design and EMC 14.4 Arrangement of Components and Equipment 14.4.3 Three-tier configuration Multiple-tier configuration Figure 14-5 Example of a three-tier configuration with components between 50 and 200 mm wide Booksize cold-plate power units Manual, (GH4), 03.2007, 6SL3097-2AJ00-0BP4... -
Page 322: Information On Connecting The Cooling Water
Cabinet Design and EMC 14.4 Arrangement of Components and Equipment Note When the power supply input is on the right-hand side of the drive line-up (e.g. in a multiple- tier configuration), the above rules apply in reverse. This means that: The Motor Modules are arranged in order of power from the highest power to the lowest power followed by the DC link components, such as the Braking Module. - Page 323 Cabinet Design and EMC 14.4 Arrangement of Components and Equipment Commissioning CAUTION The system must only be vented once it has been disconnected from the power supply. ● When the equipment is filled for the first time, the heat sinks must be vented. ●...
-
Page 324: Electromagnetic Compatibility
● Operation in TN systems with SINAMICS line filters ● Observance of information about cable shielding and equipotential bonding ● Use of recommended Siemens power and signal cables. ● Only Siemens cables may be used for DRIVE-CLiQ connections. For MOTION-CONNECT cables see catalog D21.1. CAUTION For DRIVE-CLiQ connections it is not permissible to use cables and couplings (connectors) that you have configured yourself. - Page 325 The cable shields must be connected as close to the conductor terminal connections as possible to ensure a low-impedance connection with cabinet ground. For Siemens power cables in which the shield is connected to the connector shell (see relevant catalog), this is a sufficiently good shield contact.
- Page 326 Cabinet Design and EMC 14.5 Electromagnetic Compatibility Signal and DC power supply cables Operating unshielded signal and direct current supply cables (e.g. 24 V infeed with external supply): ● Direct current supply cables: Max. permissible length: 10 m ● Unshielded signal cables: Max. permissible length: 30 m (without additional wiring) For greater lengths, suitable wiring must be connected by the user to provide overvoltage protection.
- Page 327 Cabinet Design and EMC 14.5 Electromagnetic Compatibility Table 14-11 Maximum cable lengths Type Maximum length [m] 24 V DC power cables 24 V signal cables DC link, including extensions Total length of power cables in the drive line-up 350 (shielded) comprising the following: Motor power cables, DC 560 (unshielded) link cable(s) and line feeder cable from the line...
-
Page 328: Equipotential Bonding
Cabinet Design and EMC 14.5 Electromagnetic Compatibility 14.5.3 Equipotential Bonding The SINAMICS S booksize drive system is designed for use in cabinets with a PE conductor connection. The machine manufacturer is responsible for ensuring that the technical user/manufacturer documentation clearly specifies all conditions relating to the connection and terminal assignments of ground cables, ground connection cables, protective conductors and equipotential bonding conductors (this is particularly important when the device features multiple protective conductor/equipotential bonding conductor connections/terminals). -
Page 329: Connection Methods
Cabinet Design and EMC 14.6 Connection Methods 14.6 Connection Methods 14.6.1 Spring-Loaded Terminals/Screw Terminals Connectable conductor cross-sections of spring-loaded terminals Table 14-12 Spring-loaded terminals Spring-loaded terminal type Connectable conductor cross- Flexible 0.14 mm to 1.5 mm sections With wire end ferrule, without plastic sleeve 0.25 mm to 1.5 mm With wire end ferrule, with plastic sleeve... -
Page 330: Connectable Cable Cross-Sections
Cabinet Design and EMC 14.6 Connection Methods Screw terminal type Connectable conductor cross- Flexible 0.5 mm to 6 mm sections With wire end ferrule, without plastic sleeve 0.5 mm to 6 mm With wire end ferrule, with plastic sleeve 0.5 mm to 6 mm Insulation stripping length 12 mm... - Page 331 Cabinet Design and EMC 14.6 Connection Methods Table 14-15 Connectable cable cross-sections: Power supply cable / motor cable, part 2 Connection cross-section [mm Component Terminal type Motor Module Motor connector 30 A 3+2 pin 3 A to 30 A 2 x 3 A to 2 x 18 A Motor Module Threaded bolt M6/6 Nm 45 A to 60 A...
- Page 332 Cabinet Design and EMC 14.6 Connection Methods Table 14-17 Connectable cable cross-sections: Power supply cable / connection for braking resistor, part 4 Connection cross-section [mm Component Terminal type Basic Line Module 20 kW Screw-type line connection terminal Basic Line Module 20 kW Screw-type Connection for braking terminal...
-
Page 333: Motor Connector
Cabinet Design and EMC 14.6 Connection Methods 14.6.3 Motor connector Figure 14-6 Motor connector The figure below shows how to remove the motor connector using a pair of engineer's pliers, for example, to pull the cable through narrow cable bushings. Figure 14-7 Removing the motor connector Booksize cold-plate power units... - Page 334 Cabinet Design and EMC 14.6 Connection Methods The following figure shows how the motor connector is coded to prevent incorrect connection (especially relevant for Double Motor Modules). Figure 14-8 Coding the motor connector The coding plugs are supplied with the motor cables. Booksize cold-plate power units Manual, (GH4), 03.2007, 6SL3097-2AJ00-0BP4...
-
Page 335: Power Connector (X1/X2)
Cabinet Design and EMC 14.6 Connection Methods 14.6.4 Power connector (X1/X2) with screw terminals Structure and assembly Figure 14-9 Setting up and installing the power supply connector (X1/X2) Screwdriver 1) SZS 0.6 x 3.5 2) SZS 1.0 x 4.0 3) Torx TX20 Booksize cold-plate power units Manual, (GH4), 03.2007, 6SL3097-2AJ00-0BP4... - Page 336 Cabinet Design and EMC 14.6 Connection Methods Figure 14-10 Dimensions: Power connector Booksize cold-plate power units Manual, (GH4), 03.2007, 6SL3097-2AJ00-0BP4...
- Page 337 Cabinet Design and EMC 14.6 Connection Methods Various options are available for the shield contact: 1. Shield contact with shield plate supplied. This type of shield contact should be preferred. Table 14-18 Installing the shield plate Shield plate supplied for power connectors Frontal alignment of the shield plate Lateral alignment of the shield plate Lateral alignment of the shield plate...
-
Page 338: Terminal Adapter
Cabinet Design and EMC 14.6 Connection Methods Note Measures must be taken on site to relieve strain on the cables. Max. permissible cable tension in the connection direction: 100 N With these variants, the shield for the brake connection wires must be laid with the cable shield. -
Page 339: Cooling
Cabinet Design and EMC 14.7 Cooling 14.7 Cooling 14.7.1 General The following devices are available as cooling equipment: ● Internal liquid cooling (in preparation) ● External air cooling ● External liquid cooling The decision in favor of one of these methods will depend on the prevailing ambient conditions and the cooling power required. - Page 340 Cabinet Design and EMC 14.7 Cooling Table 14-19 Ventilation clearances above and below the components Component Order No. Clearance [mm] Line filter for line module 5 kW - 120 kW 6SL3000-0BExx-xAAx Line reactor for active line module 16 kW – 120 kW 6SN1111-0AA00-xxAx Line reactor for Basic Line Module 20 kW –...
-
Page 341: Ventilation
Cabinet Design and EMC 14.7 Cooling 14.7.2 Ventilation With cold-plate cooling, the SINAMICS devices must always be ventilated separately by means of a fan in the cabinet or by some other means. When an external air heat sink is used, ventilation must also be provided outside the cabinet or by some other means. -
Page 342: Anti-Condensation Measures
Cabinet Design and EMC 14.7 Cooling 14.7.3 Anti-condensation measures Special measures must be taken to prevent condensation. Condensation occurs when the inlet temperature of the cooling medium is significantly lower than room temperature (ambient temperature). The table below shows the dew points (in °C) for an atmospheric pressure of 1 bar (≈ installation altitude: 0...500 m). -
Page 343: Power Loss Of Components In Rated Operation
Cabinet Design and EMC 14.7 Cooling 14.7.4 Power Loss of Components in Rated Operation With cold-plate cooling, only part of the power loss remains in the cabinet. The table below shows the internal and external power loss of the components. The characteristic values apply for the following conditions: ●... - Page 344 Cabinet Design and EMC 14.7 Cooling Electronic losses of Motor Modules/Line Modules Table 14-22 Electronic losses of Motor Modules/Line Modules Component Cold plate Current consumption Power loss Motor Modules 14,4 14,4 14,4 18 A 14,4 30 A 14,4 45 A 16,8 60 A 16,8...
-
Page 345: Service And Maintenance
Service and Maintenance 15.1 Replacing Components with Internal Liquid Cooling (in Preparation) Replacing components essentially depends on the design of the liquid installation. With a serial connection system, the entire circuit is interrupted when components are replaced. With a parallel connection system, appropriate valves in the cooling pipes (not included in the component) mean that individual components can be removed from the line-up without the need to interrupt the cooling circuit. - Page 346 Service and Maintenance 15.2 Reforming the DC link capacitors Procedure The DC link capacitors are re-formed by applying the rated voltage without load for at least 30 minutes at room temperature. Date of manufacture The date of manufacture can be determined from the following assignment to the serial number (e.g.
- Page 347 Service and Maintenance 15.2 Reforming the DC link capacitors Figure 15-1 Line Module interface Booksize cold-plate power units Manual, (GH4), 03.2007, 6SL3097-2AJ00-0BP4...
- Page 348 Service and Maintenance 15.2 Reforming the DC link capacitors Figure 15-2 Motor Module interface Procedure ● Before you form the DC link capacitors, the DC link bridge must be removed. ● It is not permissible that the drive unit receives a power-on command (e.g. from the keyboard, BOP20 or terminal strip).
-
Page 349: Spring-Loaded Terminals/Screw Terminals
Spring-Loaded Terminals/Screw Terminals Spring-Loaded Terminals/Screw Terminals Connectable conductor cross-sections of spring-loaded terminals Table A-1 Spring-loaded terminals Spring-loaded terminal type Connectable conductor cross- Flexible 0.14 mm to 1.5 mm sections With wire end ferrule, without plastic sleeve 0.25 mm to 1.5 mm With wire end ferrule, with plastic sleeve 0.25 mm to 0.5 mm... - Page 350 Spring-Loaded Terminals/Screw Terminals A.1 Spring-Loaded Terminals/Screw Terminals Screw terminal type Insulation stripping length 9 mm Tool Screwdriver 0.6 x 3.5 mm Tightening torque 0.5 to 0.6 Nm Connectable conductor cross- Flexible 0.2 mm to 4 mm sections With wire end ferrule, without plastic sleeve 0.25 mm to 4 mm With wire end ferrule, with plastic sleeve...
-
Page 351: List Of Abbreviations
List of abbreviations List of Abbreviations Table B-1 List of abbreviations Abbreviation German English A... Warnung Alarm Wechselstrom Alternating Current Analog-Digital-Konverter Analog Digital Converter Analogeingang Analog Input Active Interface Module Active Interface Module Active Line Module Active Line Module Analogausgang Analog Output Advanced Operator Panel Advanced Operator Panel... - Page 352 List of abbreviations B.1 List of Abbreviations Abbreviation German English Befehlsdatensatz Command Data Set CompactFlash CompactFlash Konnektoreingang Connector Input Computerunterstützte numerische Steuerung Computer Numerical Control Konnektorausgang Connector Output CO/BO Konnektor-/Binektorausgang Connector Output/Binector Output COB-ID CAN Object-Identification CAN Object-Identification Mittelkontakt eines Wechselkontaktes Common contact of a change-over relay Kommunikationsprozessor Communications Processor...
- Page 353 List of abbreviations B.1 List of Abbreviations Abbreviation German English F… Störung Fault Häufig gestellte Fragen Frequently Asked Questions Freie Funktionsblöcke Free Blocks Function Control Chart Function Control Chart Flussstromregelung Flux Current Control F-DI Fehlersicherer Digitaleingang Failsafe Digital Input F-DO Fehlersicherer Digitalausgang Failsafe Digital Output Fremderregter Synchronmotor...
- Page 354 List of abbreviations B.1 List of Abbreviations Abbreviation German English Drehstromversorgungsnetz ungeerdet Insulated three-phase supply network Interner Spannungsschutz Internal Voltage Protection Tippen Jogging Kreuzweiser Datenvergleich Data cross-checking Kinetische Pufferung Kinetic buffering Proportionalverstärkung Proportional gain Spezieller Temperatursensor Special temperature sensor Induktivität Inductance Leuchtdiode Light Emitting Diode...
- Page 355 List of abbreviations B.1 List of Abbreviations Abbreviation German English Open Architecture Open Architecture Original Equipment Manufacturer Original Equipment Manufacturer Busstecker für Lichtleiter Optical Link Plug Option Module Interface Option Module Interface p… Einstellparameter Adjustable parameter PROFIBUS PROFIBUS PcCtrl Steuerungshoheit Master Control PROFIdrive PROFIdrive...
- Page 356 List of abbreviations B.1 List of Abbreviations Abbreviation German English Echtzeituhr Real Time Clock Raumzeigerapproximation Space vector approximation (SVA) Dauerbetrieb Continuous operation Aussetzbetrieb Periodic duty Sichere Bremsenansteuerung Safe Brake Control Sicherer Betriebshalt Safe operating stop Sichere Bremsrampe Safe Brake Ramp Sicherer Bremsentest Safe Brake Test Sicherer Nocken...
- Page 357 List of abbreviations B.1 List of Abbreviations Abbreviation German English Drehstromversorgungsnetz geerdet Grounded three-phase supply network Nachstellzeit Integral time TPDO Transmit Process Data Object Transmit Process Data Object Drehstromversorgungsnetz geerdet Grounded three-phase supply network Transistor-Transistor-Logik Transistor-Transistor Logic Underwriters Laboratories Inc. Underwriters Laboratories Inc.
- Page 358 List of abbreviations B.1 List of Abbreviations Booksize cold-plate power units Manual, (GH4), 03.2007, 6SL3097-2AJ00-0BP4...
- Page 359 List of abbreviations B.1 List of Abbreviations If you come across any misprints in this document, please let us know using this form. Suggestions for improvement are also welcome. Booksize cold-plate power units Manual, (GH4), 03.2007, 6SL3097-2AJ00-0BP4...
-
Page 361: Index
Index Line reactors for Active Line Modules, 84 Line reactors for Basic Line Modules, 94 Line reactors for Smart Line Modules, 88 Motor Module with Internal Air Cooling, 179 Active Interface Module, 72 Motor reactors, 249 Active Line Modules with Internal Air Cooling, 109 Smart Line Modules with internal air cooling, 161 Air heat sink, 29 Wideband Line Filter for Active Line Modules, 51... - Page 362 Index Electrical Connections Motor connector, 333 Active Line Module, 150 Motor Module with Internal Air Cooling, 179 DC link adapter, 288 Motor reactors, 249 DC link rectifier adapter, 280 EMC Directive, 324 Environmental conditions, 23 Equipotential Bonding, 328 Overcurrent, 314 ESD information, 8 Overcurrent Protection, 307 Hotline, 6...
- Page 363 Index Active Line Modules, 122 Basic Line Filter for Active Line Modules, 44 Basic Line Filter for Basic Line Modules, 65 Basic Line Filter for Smart Line Modules, 71 Basic Line Modules, 151 Braking Module, 225 Capacitor Module, 234 Control Supply Module, 241 DRIVE-CLiQ cabinet gland, 297 DRIVE-CLiQ Coupling, 300 Line reactors, 87...
- Page 364 Siemens AG 6SL3097-2AJ00-0BP4 Automation and Drives Motion Control Systems Postfach 3180 91050 ERLANGEN GERMANY www.siemens.com/motioncontrol...
















